eCommerce customer journey mapping helps understand the different stages a customer goes through when making a purchase. This helps optimize journeys across channels and touchpoints. Read on to learn what is eCommerce customer journey mapping and how you can significantly boost your conversation rates with it.
To win more customers, you have to think like a customer—and that’s not quite as easy as it sounds. While it’s tempting to imagine that you know how customers interact with your brand in a simple, linear path (e.g., Google search → Website → Order Button), failing to understand their journey can lead to abandoned shopping carts, failure to achieve repeat business, bad reviews, and all kinds of missed opportunities.
When you struggle to convert visitors or receive repeat business, you need to identify the root cause. Do your product descriptions fall short? Is an inferior User Interface negatively impacting the customer experience? Is it something else? An eCommerce customer journey map helps answer all these questions.
An essential practice for online retailers, eCommerce customer journey mapping helps you track the steps your customers follow when finding your website or app, making a purchase, and returning later for additional purchases. Journey maps help identify the impediments across every touchpoint, on each device, and they enable you to understand your visitors’ psychology. Ultimately, this empowers businesses to mend and improve any broken parts of the customer experience that they might’ve skipped during the ecommerce development.
Here’s everything you need to know about how to track customers across various touchpoints, using eCommerce customer journey mapping to optimize their experience and boost conversions.
What is an eCommerce Customer Journey?
An eCommerce customer journey describes the paths customers follow when interacting with a brand across all its platforms, channels, and touchpoints. These touchpoints include all interactions with the brand, from the moment they discover it exists to their experience using the brand’s product… and beyond! That’s right, the customer’s journey doesn’t end when they receive their purchase. It ideally includes leaving reviews, talking to friends, and (if you play your cards right) repeat business for many years.
What is eCommerce Customer Journey Mapping?
Customer journey maps are visual representations of the steps a customer follows while interacting with your digital commerce platform. This holistic view can help you gather essential data about what delights customers, what disappoints them, and how to improve the user experience.
An eCommerce journey map helps answer:
- At what stage/touchpoint did you lose a visitor (i.e., fail to convert them)?
- What elements contribute to a bad customer experience?
- Which channels bring you the most traffic and sales?
Creating an eCommerce journey map is about surveying your ideal customers’ entire paths and removing all the roadblocks to conversion and repeat business.
What are the Stages of the Customer Journey?
Before moving ahead with eCommerce journey mapping, it’s a good idea to understand and conceptualize the different stages of the customer journey. These are the general customer journey steps when a customer purchases anything from plane tickets to hamster cages.
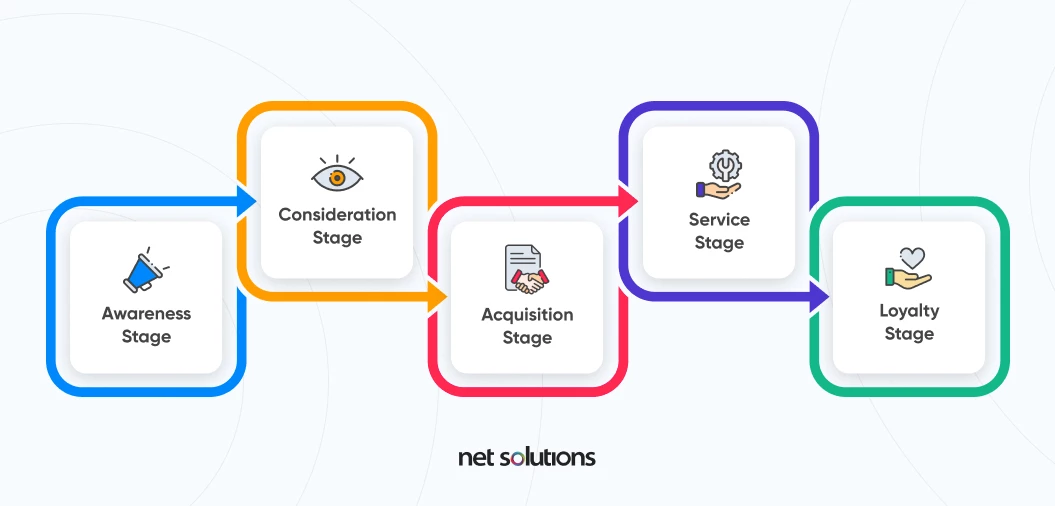
1. Awareness Stage
During the awareness stage, customers discover brands through online advertising, Google searches, word-of-mouth recommendations, reviews, and other channels.
Objective: Make your target audience aware of your brand by using the right channels to reach them.
2. Consideration Stage
When a visitor discovers your website or app and browses through your catalog, they’re at the consideration stage. There’s an excellent chance they’re comparing your products and brand to those of your competitors.
Objective: Create a seamless User Experience (UX) with a platform that’s easy to navigate. Include this seamless UX thorough product descriptions, engaging photos, and by highlighting your best reviews and testimonials if possible.
3. Acquisition Stage
This is the make-or-break moment. At this stage, the customer will decide whether to move ahead with the purchase by adding the product to their shopping cart, giving you their payment information, and clicking purchase. The process continues until they receive the product.
Objective: Make the purchasing experience as simple and straightforward as possible.
4. Service Stage
If a customer decides to exchange, return, or get help with the product, make the option obvious and the process easy. The after-sales service experience is just as important as the purchase experience when evaluating customer satisfaction.
Objective: To offer a simple, clear after-sales service experience.
5. Loyalty Stage
The ultimate goal is to create repeat business, since acquiring a new customer can cost up to 25 times more than retaining one, according to the Harvard Business Review.
An important part of earning repeat business is marketing to past customers. You can do this by sending them newsletters, discounts, push notifications, and other forms of marketing communication. Asking them to leave feedback is also a good way to stay top of mind.
Objective: Retain your customers and drive profits.
Why is eCommerce Customer Journey Mapping Important?
The goal of eCommerce customer journey mapping is to ensure your customers have a seamless and consistent customer experience at every touchpoint. It boils down to understanding their needs and building ongoing communication with them across marketing channels.
There’s a concept that marketers call the “Experience and Expectation Gap” or the “Perception Gap.” This is a measurement that compares what users expect from a brand with what they experience, and it identifies the percentage of customers who expect a certain experience and don’t receive it. PwC identifies this gap at 21% in the retail industry, which leaves quite a bit of room for improvement.
Customer journey mapping can help improve this gap by:
- Offering insights into the broken parts of the customer experience
- Demonstrating customer pain points and what creates a delightful experience
- Helping to prioritize rework based on customer journey stages
What are the Five Steps to Map a Customer Journey?
Customer journey maps can range from simple to highly detailed and intricate. Your level of complexity will typically be determined by the number of channels your customers use to reach you, the number of paths they might take to discover products and make purchases, and the range of customers you serve. The following is a general outline of the process.
Step 1: Set Goals/Targets
Identify what you’re trying to achieve, and which set of customers you want to study, by creating your customer journey map. It will also help you address various ecommerce business challenges in a more focused manner.
Step 2: Build Buyer Personas
Buyer personas are semi-fictional profiles of your ideal customers (rooted in data). In other words, when you look through your customer data, you’ll want to identify patterns and create user personas that sum up each major type of buyer.
For example, if you sell fine wines online, you might find that a large percentage of your buyers are retired baby boomers, while another key demographic is urban millennials. You could come up with personas with names like Retired Ralph and Hipster Hannah. Each persona would feature demographic and psychographic elements, which we’ll discuss further below.
Step 3: Identify Pain Points
Every purchase a customer makes is designed to address and solve a problem in their lives. It’s important to determine what drives them to search for a solution that your products solve. Consider both emotional drives and tangible life.
Step 4: Map out the Journey
This one probably seems obvious—every journey map needs the map itself. The form that the map takes, however, could vary considerably from one map to the next. You’ll read more below about the essential components of a customer journey map, but your level of detail will vary depending on the number of channels you use to drive business and the complexity of each customer journey.
Step 5: Identify Key Touchpoints
Map out all the relevant touchpoints and identify the ones where potential buyers get stuck or drop off. You will use this information to design a more optimal journey—one that reduces friction and guides customers toward better (higher converting) experiences.
Key Components of an eCommerce Customer Journey Template
Customer journey maps should include the following five elements. It will help you better understand the journey as a whole.
1. Buyer Personas
As discussed above, buyer personas are semi-fictional profiles of your ideal customers, based on the customer data you’ve gathered. A solid buyer persona should include both a demographic and a psychographic dimension.
The demographic dimension identifies factors like location, gender, age, income, marital status, etc. The psychographic dimension identifies the emotion of psychological drives, such as lifestyle patterns, interests, etc.
2. Expectations
What do visitors expect from your website? What are they hoping to achieve? It’s important to identify visitor and customer expectations so you can find ways to meet and exceed them.
3. Journey Stages
Before you map your eCommerce customer journey, it is essential to identify the stages a customer passes through when interacting with your brand, from awareness to loyalty (see above). At each stage, list all the different paths a customer might take to achieve their goals.
4. Mindset and Emotions
How the visitor feels as they’re interacting with your eCommerce interface is vital information, which you can capture through on-page surveys. Determine how they feel at each leg of their journey by asking them whether they’re finding what they need, whether they’re experiencing frustration, and how you could improve the experience. Be sure to include all this information in your online customer journey map.
5. Opportunities
The insights you gather from your research will point toward opportunities to improve the customer experience and increase conversions. In other words, opportunities list the ways that will aid in customer journey enhancement.
Here’s an eCommerce customer journey template that covers all five components discussed above.

Helpful Tools for Creating a Customer Journey Map
1. Analytics
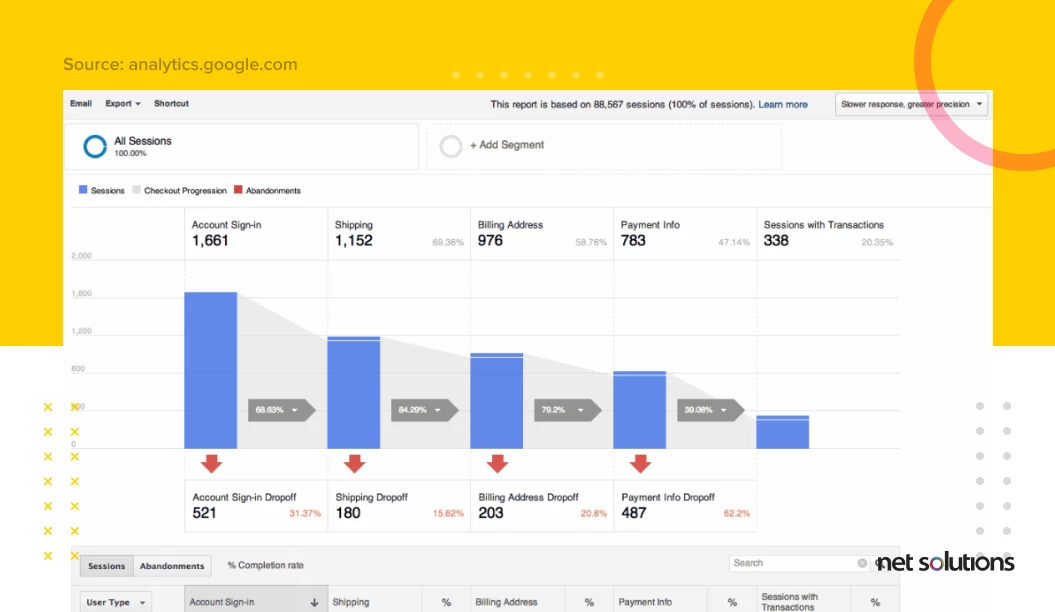
There are several digital customer journey mapping tools that will help you analyze and understand how your visitors behave. They’ll help you determine how visitors find you, where they drop off, and what inspires them to convert.
Google Analytics is great for identifying traffic sources, time spent on pages, etc. Another tool, BrandMentions, helps you track the number of times your eCommerce brand was mentioned on any of the top social media platforms. Learn from both the positive and negative mentions.
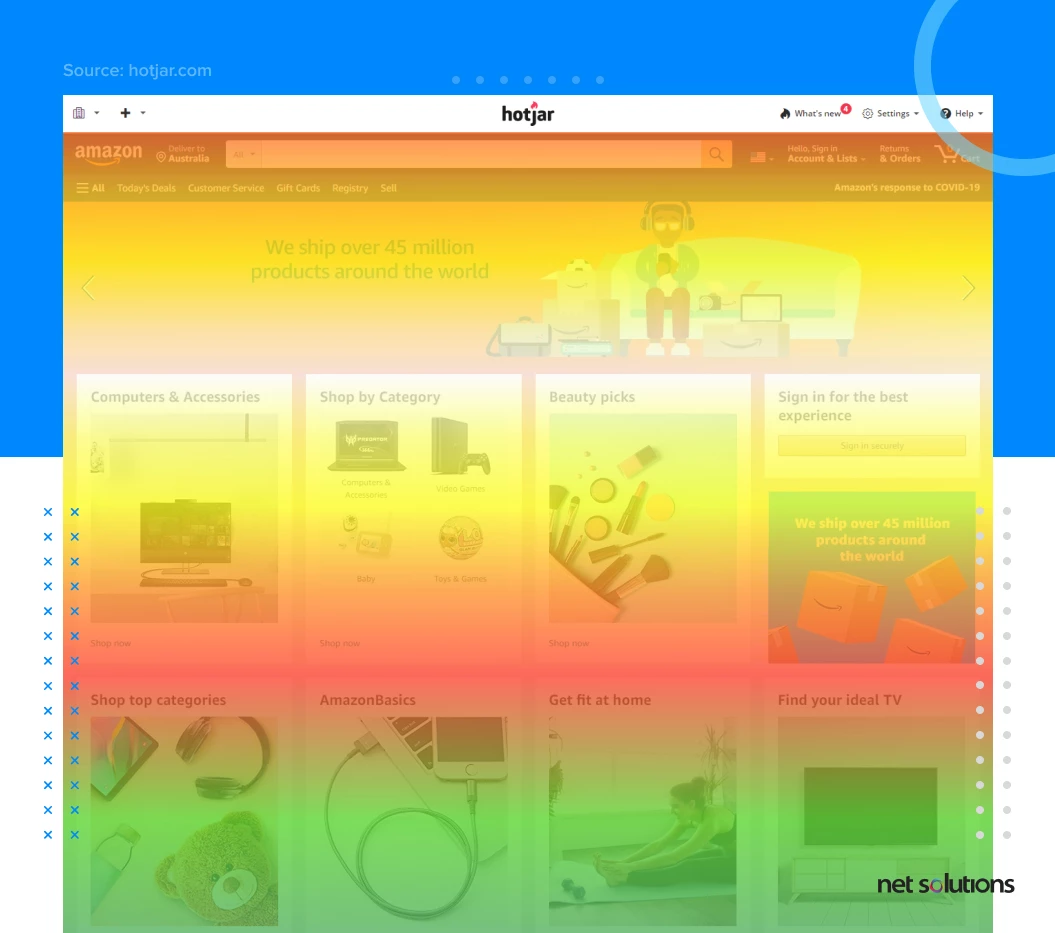
2. Heatmaps
A heatmap is a data visualization tool that helps you understand how users behave when interacting with your website. Heatmaps use color codes to show aggregate data about where the majority of your visitors click, how far they scroll, and where their mouse pointer hovers (which has been shown to correlate with eye movements). Heatmap tools like Hotjar will help you optimize your user experience.
3. Surveys
Surveys help you understand the customer experience, and you can ask open-ended questions to get them to elaborate on what they liked and what can be improved. You can email surveys to your customers using tools like Survey Monkey. You can also use Hotjar (mentioned above as a heatmap tool) to create on-page surveys—short surveys that rise up from the bottom of the screen and ask visitors to rate or discuss their experience.
What Are Some Best Practices for eCommerce Customer Journey Mapping?
There are many different ways to create eCommerce customer journey maps. The following best practices will help you stay focused and find the right level of detail for your business.
- Focus on the customers who deliver the highest profits, rather than trying to identify dozens of separate customer journeys for many different products
- Leverage the power of your Client Relationship Management (CRM) software, if you use one, gathering data from your CRM to identify your best customers and the paths they take to make a purchase. Of course, if you sell high-volume, less-profitable items, you probably won’t use a CRM. That’s fine! CRMs are typically designed to address more complex sales processes
- Use real customer data when building your buyer personas
- Consider using separate maps for different buyers’ personas if their journeys are distinct
A Bird’s Eye View that’s ever-evolving
In the end, eCommerce customer journey mapping provides a full picture and a reality check regarding your customer experience. By identifying your trouble spots, you can deliver a better customer experience and improve your conversion rates.
Of course, customer journey mapping isn’t a one-time, set-it-and-forget-it thing. Once you begin trying out changes, you’ll receive data about what improves the experience at each touchpoint. Keep the elements that work, ditch the ones that don’t, and keep revising and refining as you watch your market share grow.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the 5E’s Framework of Customer Journey Mapping?
The 5E’s framework helps in the explicit understanding of the customer journey stages. The 5E’s stand for:
- Entice: What led the users to land on the website/app?
- Enter: What are the first few actions that the customers initially took?
- Engage: What are the customer’s intended actions?
- Exit: Did the customer complete the action or abandoned the journey?
- Extend: Did the customers come back for further purchases?
2. What are Some of the Popular Customer Journey Mapping Tools?
Some of the popular customer journey mapping tools include MIRO, UXPressia, Smaply, and Gliffy.
3. What are the Benefits of eCommerce Customer Journey Mapping?
Some of the benefits of eCommerce customer journey mapping include:
- Optimize customer journeys to enhance customer experience.
- Understand the customer’s mindset and pain points.
- Identify the customer experience gaps.
- Help build predictive analysis model based on customer behavior.
- Help improve conversions and achieve revenue goals.
SHARE THIS POST
Table of Contents
Related Resources
- eCommerce App Development Cost: Budgeting In-Depth Guide
- 13 Differences Between B2B and B2C eCommerce Websites
- Top 10 eCommerce Challenges and Easy Ways to Overcome Them
- 3 Types of eCommerce Business Models That Work in 2024
- eCommerce for Business: Is eCommerce Applicable for All Business Types
- What is Headless Commerce? The Ultimate Guide
- Top 15 eCommerce KPIs to Track the Performance of Your Online Business
- What is Adobe Commerce (Magento)? Everything You Need to Know in 2024
- Why Your Business Needs a Mobile eCommerce App
- Omnichannel Retail Strategy: A Comprehensive Guide
- Omnichannel vs Multichannel Retailing: The Complete Guide
- What is eCommerce Order Fulfilment? (And 6 Steps to Improve the Process)
- PCI Compliance: Everything You Need To Know
- The BEST Guide to eCommerce Personalization
- 12 Essential Factors for Choosing the Best eCommerce Platform
- The Ultimate Guide to Product Information Management (PIM) Systems for Ecommerce
- What is a Product Recommendation Engine (And How it Helps Boost Sales)
- eCommerce Replatforming: Challenges, Benefits, and Best Practices
- The Ultimate Guide to eCommerce Security
- Top 13 eCommerce Trends in 2024
- How Voice Search will Transform the Future of eCommerce
- What is Web Accessibility (And Why it Matters for Your eCommerce Business)

