The in-app purchase market has the potential to generate billions of dollars in revenue with every passing year. A report by Statista estimates that in 2021, mobile apps can create more than 693 billion U.S. dollars in revenue using app monetization strategies like in-app purchases, in-app advertising, and paid downloads.
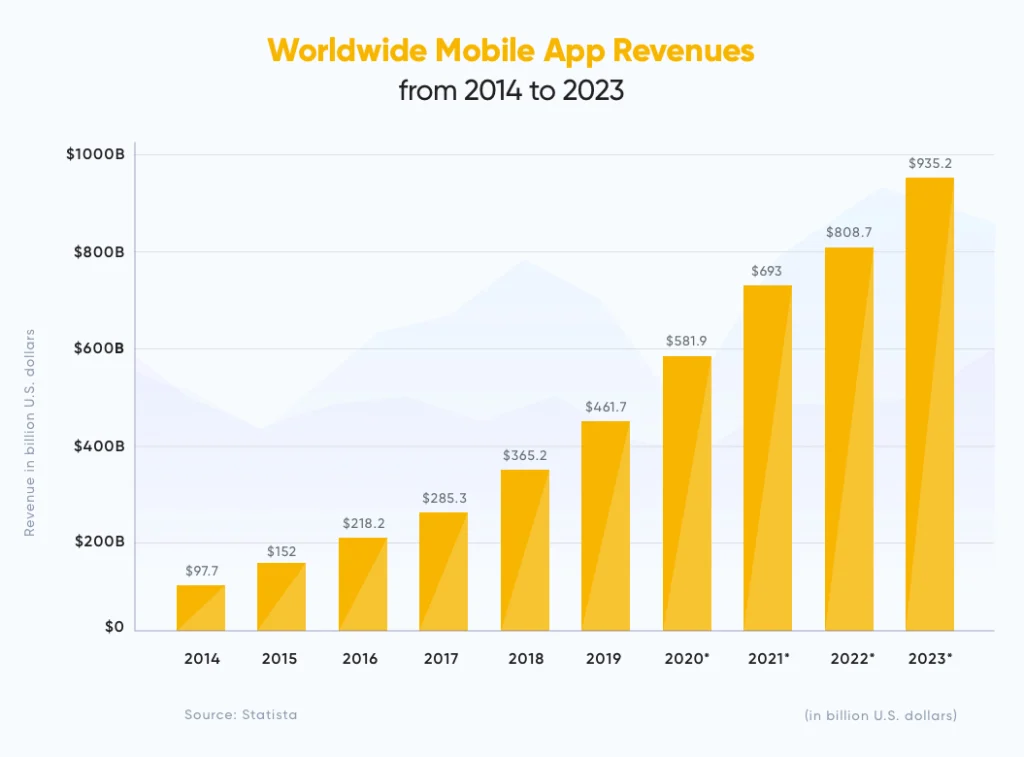
However, not every mobile app developer is fortunate enough to get these dollars transferred straight to their bank accounts. There are over 4 million mobile apps (and counting) that are available in Google and Apple app stores which imply competition in the market for making even a small piece of this revenue is sky-high.
In such a situation, one thing that can help businesses turn their money-making dream into reality is a robust app monetization model that delivers an UX experience and millions of app downloads. Let’s see what options are available to explore for creating such an app revenue model:
Mobile App Monetization Strategies: How to Monetize an App?
A suitable mobile app monetization model will match the organization’s goals with the expectations of its target audience. Organizations should choose an app’s revenue streams before developing an app to build it into the user experience seamlessly.
These app-monetization strategies can help businesses earn money from an app without explicitly charging their users:
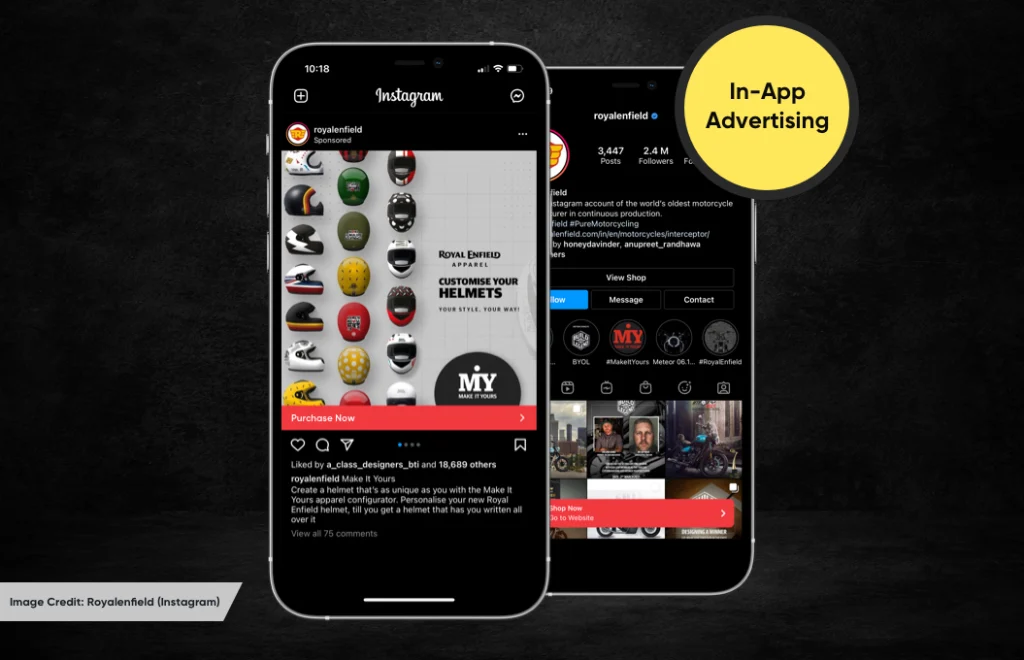
In-App Advertising
Customers are hesitant about making in-app purchases and the moment the app owner asks to pay, they tend to uninstall it. A better tactic for app monetization is through in-app advertisement – where the app owner needs to select an app pricing model to generate revenue.
The app needs an extensive user base and sufficient user behavioral data to place highly targeted ads. One of the best examples of apps using the In-App Advertising model is Instagram – it brought in an $18.6 billion in annual ad sales in 2021.
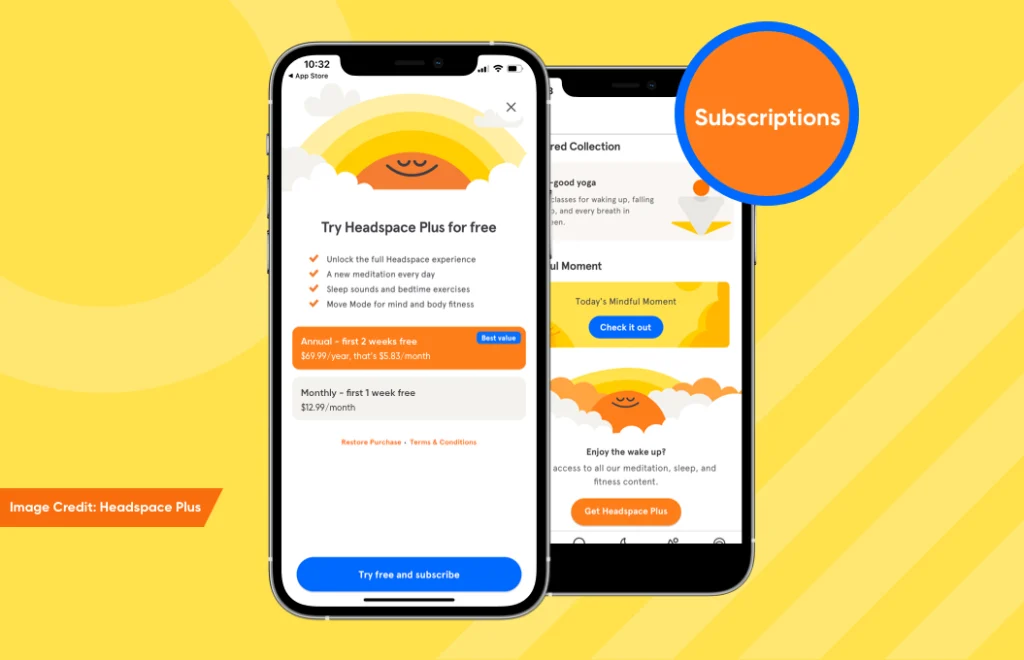
Subscriptions
Just like advertising, this is also an in-trend mobile app monetization model. Here, the app (and some of its content) is free to use, but users need to buy a subscription on a monthly or yearly basis to access premium content or advanced mobile app features. Though this model is not considered as a money-magnet, it can drive billions in the long run.
A great example of an app using this model is Headspace. It has more than 65 Million downloads and generated $100 million revenue per year from paid subscriptions. And the expected revenues for the coming years are anticipated between $100 and $150 million, as per NPR.
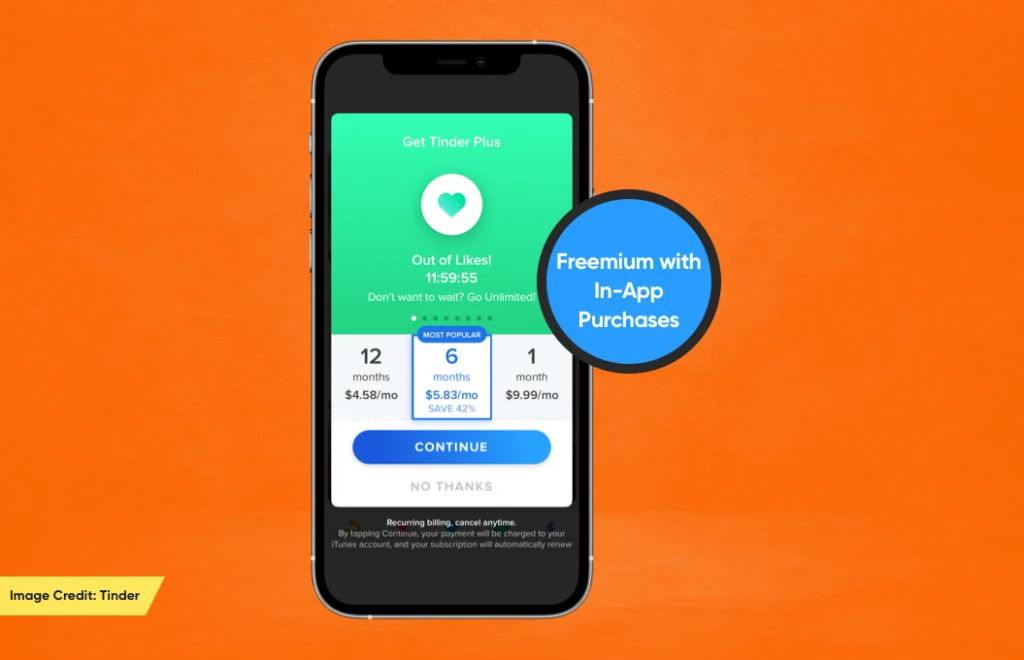
Freemium with In-App Purchases
This is one of the best app monetization strategies to make billions using the mobile app.
By offering the app for free and allowing users to purchase a wide range of digital add-ons within the app. These elements can be anything – game currency, extra lives, or premium app content.
Though this monetization model is used mainly by game applications (for example, PUBG, Clash of Clans, and many others), it is also prominent in non-game apps. One of the apps using this monetization model is Tinder – the highest-grossing non-game app of 2021 globally, reaching about 384.6 million.
The Global In-App Purchase Revenue: Statistics and Trends
App developers build an app to increase brand awareness, user loyalty, acquire new users, and add value to their businesses. But, more than anything, most app developers desire their apps to be a sustainable source of revenue, which requires a well-designed plan.
While a paid application may seem like a great way to make money, it is not the most popular business model. That’s why out of over four million mobile apps available in the app stores, just 10% are the paid ones as of January 2021.
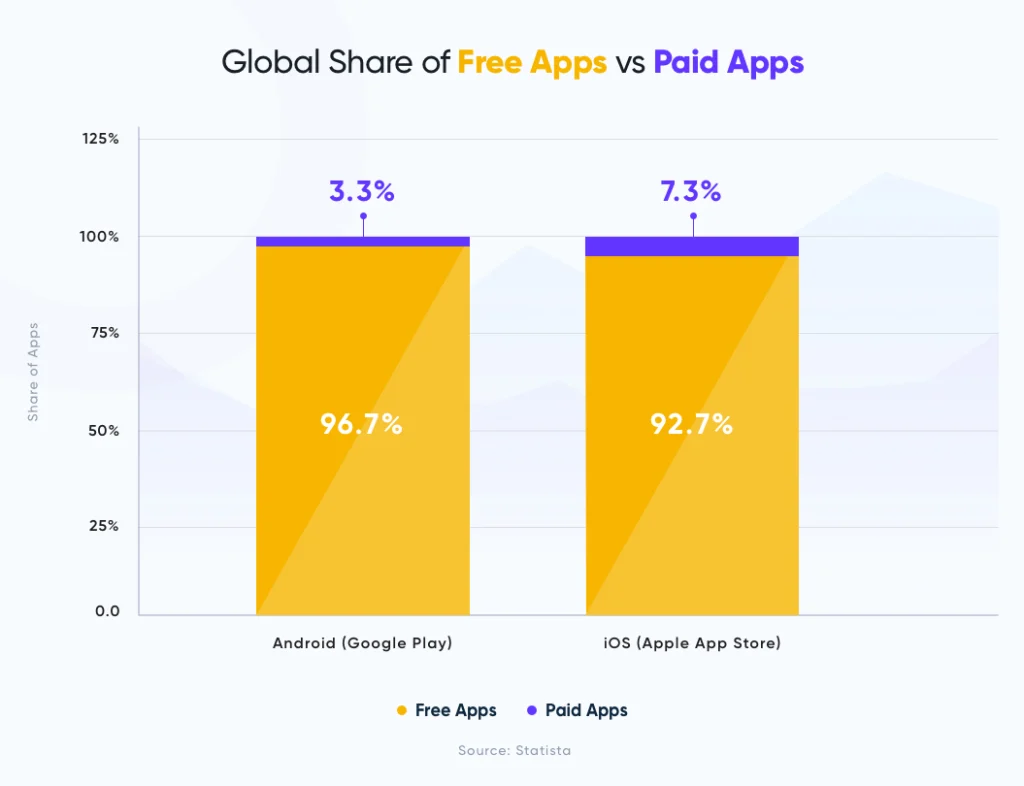
The Freemium or in-app purchase business model is presently dominating the mobile app market for obvious reasons – it offers many benefits to users and app developers such as:
- Access To The Freemium Model
- Greater Exposure
- Greater Brand-loyalty
- Ease of payments
- Ease of promotions
Also, to generate millions using a mobile app requires billions of users to download it, and the freemium model does that efficiently. It helps to build the user base and provides an audience to sell advanced features or content.
Global consumer spending on in-app purchases across iOS and Google Play amounted to $32 billion in 2021
Sensor Tower intelligence report shows that Apple’s App Store is projected to generate $41.5 billion in consumer spending globally from in-app purchases, subscriptions, and premium apps and games in the first half of 2021. This is about 1.8 times the revenue generated by Google Play, which saw an estimated $23.4 billion in the same period.

The report also says that after the surge in adoption last year driven by COVID-19’s impact on consumer behavior, app install growth was slight in the first half of 2021.
The pandemic also caused advertisers to spend less on in-app advertising due to users becoming fatigued with frequent ads. However, in-app purchases did not waver even amid the tough times, and revenues are now likely to shift more from in-app advertising to in-app purchases.
In 2020, App Developers See Revenues from In-App Purchases Outpace Advertising Revenues and increasing year after year
This trend of more revenue coming from in-app purchases began in 2019 but accelerated in 2020. It was the time when advertising revenue dropped by 11% and IAP revenue increased by 15%.
Now what the future holds for the mobile app industry’s upcoming revenue drivers is not very predictable. However, one thing is clear, in-app purchases are going to be a great way to boost the app’s revenue in the coming years. Thus, more attention should be devoted to finding what in-app purchases really mean and how to make an effective strategy to implement it in your mobile application.
What Does In-App Purchase Mean?
While in-app purchases may seem very easy to use at first glance, they take many forms in a mobile app and are sometimes hard to implement. Basically, IAP or in-app purchases let app users buy various types of virtual elements within the app. These elements can be extra lives to keep playing a game, advanced features, or access to premium app content.
The below-mentioned points describe various forms of IAPs:
-
Create a highly addictive gaming application employing psychological triggers that keep users glued to their game and boost in-apps profits and let users buy extra lives, game currency, cosmetic skins, or moves to monetize the game app. Several famous games like PUBG, Clash of Clans, and COD use this business model and earn millions. The key is to Personalize the Experience Through User Behavior where Mobile games take personalization much further by tailoring the game according to each user’s behavior and ability.
- Offer an application for free and charge a fee for advanced services or premium app content. For example, Tinder lets its customers buy extra swipes in-app to boost the app experience.
- Offer a free trial period for the application and let users unlock the full versions by paying a fee. For example, Netflix provides a one-month free subscription plan and then charges on a monthly and yearly basis.
- Businesses can also offer their app for free with ads and let users pay a fee for removing ads from the platform – another great way of using in-app purchases. For example, Spotify enables users to play music ad-free if they buy a premium version of the app.
A combination of all of them can also be used in the mobile app if the app features allow doing the same. Freemium app monetization provides the flexibility to earn using any of the app features, which provides multiple revenue streams using a single app. However, the only condition is, the app must be useful for users.
The widespread success of mobile games with in-app purchases like PUBG attracts budding entrepreneurs towards using in-app purchases in their apps. It is a simple, scalable, and versatile app monetization idea with the lucrative potentials of generating millions.
PUBG earned approximately $270 million in player spending in August 2021 which represented 4.7% growth from August 2020
The game is free to download but provides a wide variety of in-app purchases to generate revenue.
The Pros of In-App Purchase Business Model
Following are some of the benefits of monetizing mobile apps using freemium apps with in-app purchases:
Enhances the App User Experience
In-app purchases make mobile apps more enticing for users. For example, games like Pokemon Go where items like lucky eggs or poke balls speed up the game faster. Though it is possible to reach a new level without these items, purchasing makes it much easier.
Moreover, such games’ users are impatient. They want to unlock a new level as soon as possible. So, in such a scenario, mobile in-app purchases act as a double-edged sword. It keeps users hooked by improving their in-app experience and also drives revenue for the app.
Free Apps Attract More Users
It is crucial to keep a large user base hooked to the app for making money and the freemium model does that easily. The tag “Free” attracts users and keeps the trajectory of the app downloads high.
If a freemium app can find the right balance between paid and free offerings, it often results in an increased user base, more app downloads, and higher revenue.
Generates Hefty Revenues
With this business model, the profit margin is generally high. Buying virtual elements in-app leads to deeper app engagement, and users become addicted to the app’s premium features.
Also, making a purchase in-app does not require users to fill lengthy forms. It is a simple process that leads to increased user satisfaction and attracts more users to pay because of fewer hassles and more benefits.
The Cons of In-App Purchase Business Model
While the in-app-purchase business model offers many benefits, it has the following disadvantages as well:
Requires Extra Work on Development
Implementing in-app purchases makes a developer’s job challenging as it requires extra coding efforts on the backend during mobile app development. App developers must write code not just for the storefront, items, upgrades, and other instances when a user purchases something from the in-app store.
This extra code will also require strict testing to ensure that the system runs smoothly without affecting the app’s overall performance.
Needs a Large User Base to Deliver Profits
The major disadvantage of using the in-app purchase business model is that it requires a considerable number of users to deliver significant profits. Therefore, extensive user acquisition efforts are needed, which can be a bit expensive for startups.
A less expensive way to drive a large number of users to the app is App Store Optimization. If the app ranks well in the app stores, its downloads will experience a substantial increase, and the user base will expand. To supplement your reading, here is the ultimate guide to App Store Optimization for 2024.
Also, to make the in-app purchase business model work, app developers need to avoid complications and get a bit creative while strategizing the entire process. For example, start with just one in-app purchase option that provides value to the users and notice their responses. Or, try offering additional benefits in return for a referral or social media share.
How Does In-App Purchase Work?
The whole concept of IAP is pretty straightforward. It involves the transfer of monetary funds from one party to another in exchange for virtual goods. However, mobile app developers need to understand the technical details of implementing in-app purchases, which are different for Google and Apple app stores.
Google Play In-App Purchase
In-app purchases on Android apps are managed using Google Play’s in-app billing. Google play manages the checkout details so that Android apps don’t have to process financial transactions. The application will use the same checkout flow that is used for content purchases on Google Play to offer users a secure, reliable, and familiar experience.
Following Google Play’s willing can be used to sell the following in-app purchases types:
One-time products
Users can purchase such digital products or content with a single and non-repetitive charge. There are two types of one-time products – consumable and non-consumable.
- A consumable product is a product that a user consumes to buy in-app content, for example, game currency.
- A non-consumable product is the one that users purchase once to get the permanent benefit—for example, premium upgrades.
Subscriptions
When users purchase an app’s subscription, they get access to the app’s content repeatedly. Examples of subscriptions include access to online magazines and streaming services.
The content must fall into one of the categories mentioned above to sell through in-app purchases on Google Play. Also, a Google Wallet merchant account will be required to use the in-app billing service. Here is a full official guide by google on how to integrate Google Play’s billing system in the app.
Apple In-App Purchase
The process to implement in-app purchases in iOS apps is almost the same as in Android apps. Developers will have to design an in-app purchase store and integrate it with an app using the Store Kit framework provided by Apple.
The Store Kit acts as an interface to communicate with the App store for processing secure payments. It notifies the app when the user pays for the item, and the app needs to provide the purchased item to users.
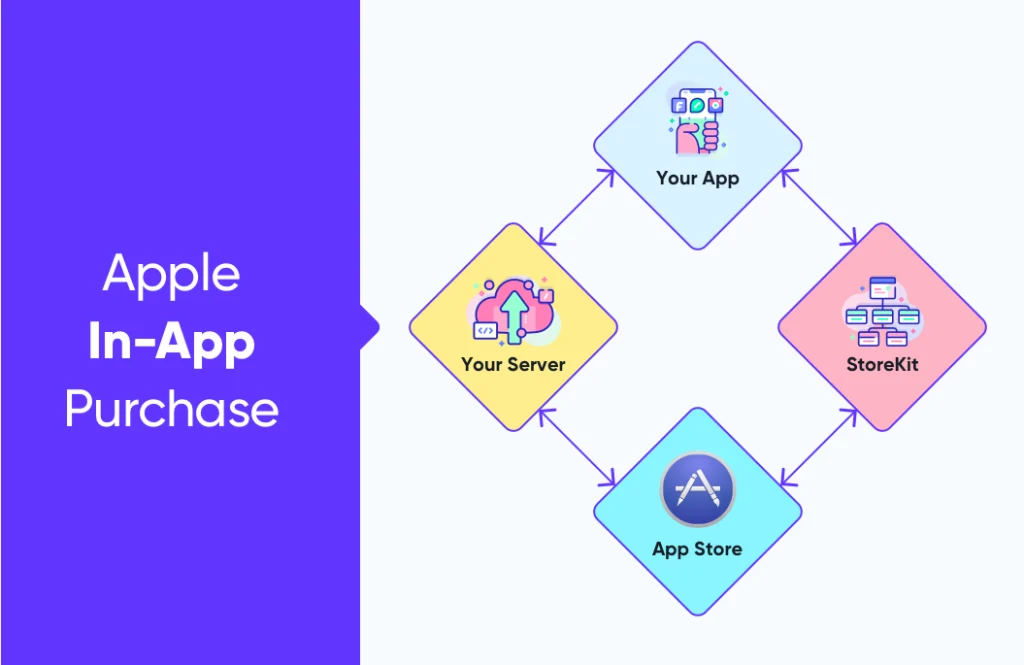
Apple in-app purchase rules help to sell the following types of digital items to users:
- Consumables: These are items that are depleted after one use, and users can purchase them multiple times.
- Non-Consumables: These are the items that users can purchase once, and they don’t expire.
- Auto-Renewable Subscriptions: These are types of subscriptions that app users purchase once and it gets renewed on a recurring basis automatically until the user cancels it.
- Non-Renewing Subscriptions: These types of subscriptions are for a limited period of time and don’t renew automatically.
Before launching in-app purchases in the app, Apple suggests testing them via iTunes Connect. To do the testing, developers will need to create products for purchase and test accounts.
Apple provides a special testing sandbox environment that helps in the testing without any incurring charges. For more information on implementing in-app purchases on the Apple app store, check out their official guide here.
The Fee Charged on Transactions
Google and Apple both charge a commission for managing in-app purchases on app developer’s behalf through their web servers. Both tech giants charge a 30% commission fee on in-app purchases. In contrast, subscription commission falls to 15% after a year.
Now that we know what in-app purchases mean and how to implement them in the application, let’s shed some light on some essential mobile app development tips to successfully boost in-app purchases.
5 Ways to Lift Your In-App Purchases
Below mentioned are a few essential tips that you can follow to set the stage for your app users to make in-app purchases:
1. Analyze User Behavior and Target the Right Ones
Customer data is the foundation of any marketing campaign, and in-app purchases are not different. Users’ behavioral data will help in targeting them based on demographics, interests, and personalization so that the users feel valuable.
Therefore, rather than targeting new users of the app with plenty of discount offers, it makes sense to wait until they look interested in buying those offers. Analyze how they use the app and then offer in-app purchases.
For example, suppose while building a free game app. Many users might find it exciting and would be happy to deal with some inconvenience initially. It won’t help the app if companies start targeting new users by promising them more lives, an ad-free version, weapons, or score multipliers.
Customers don’t know much about their app in the beginning and will never buy any of these items. New users want to try out the game and see whether it is exciting.
However, with time, their interest in such things will increase. For example, they might consider buying extra lives after losing some of them. However, at this stage also, they must have the urge to continue playing the game.
All in all, it is best to make the app addictive and offer in-app purchases at the right time. Precisely, when in-app purchase promises real value for users, they work wonders in increasing the app’s revenues.
2. Create Fear Of Missing Out
50% Off – Sale Ends Tomorrow!
Grab the Offer – 02 days 23 hours left!
Just 1 Left at $600 – Buy Now!
If an app user gets to read these messages in the app or via push notifications, this will create urgency. Chances are (if they are too addicted to the app), they may end up thinking, “I will miss out on something beneficial if I ignore this offer.” This fear will compel them to click the button.
That’s the power of FOMO driven by basic needs:
- Grabbing an offer/opportunity
- Winning a level or lives in games
An effective FOMO strategy can drive significant in-app purchases and eventually higher revenues. There are several ways to use FOMO to set the path for users:
a. Create a limited time offer
Bringing urgency into the picture shows the users that they might miss something if they ignore the deal now. For example, send them an email like this:

b. Show Scarcity
Suppose a user is planning to buy something and suddenly they get to know there’s limited stock of that item. What will they do? They will show a hurry in purchasing it. That’s how the human mind works.
c. Offer Special In-App Purchases
If the users know that the in-app purchase offers are available 365 days a year – they won’t care much. But, if businesses provide some special discounts on holiday seasons or any other festivals, it can increase their sales. Have a look at how Pokemon Go uses this strategy.

FOMO is one of the best strategies to drive in-app purchases responsibly. All that is required is to keep in mind, to have the users do something in their best interest. Try not to manipulate them into doing something which is just in the app’s best interest.
3. Use In-App Messages to Drive In-App Purchases
In-app messages are notifications that are sent to users when they are using the app. These messages let the target users at the right time to promote and sell in-app purchases.
For example, the photo editing application VSCO locks some of their advanced filters and sends users in-app messages to tell them about this paid feature. The message also has a button that takes users directly to the checkout page.
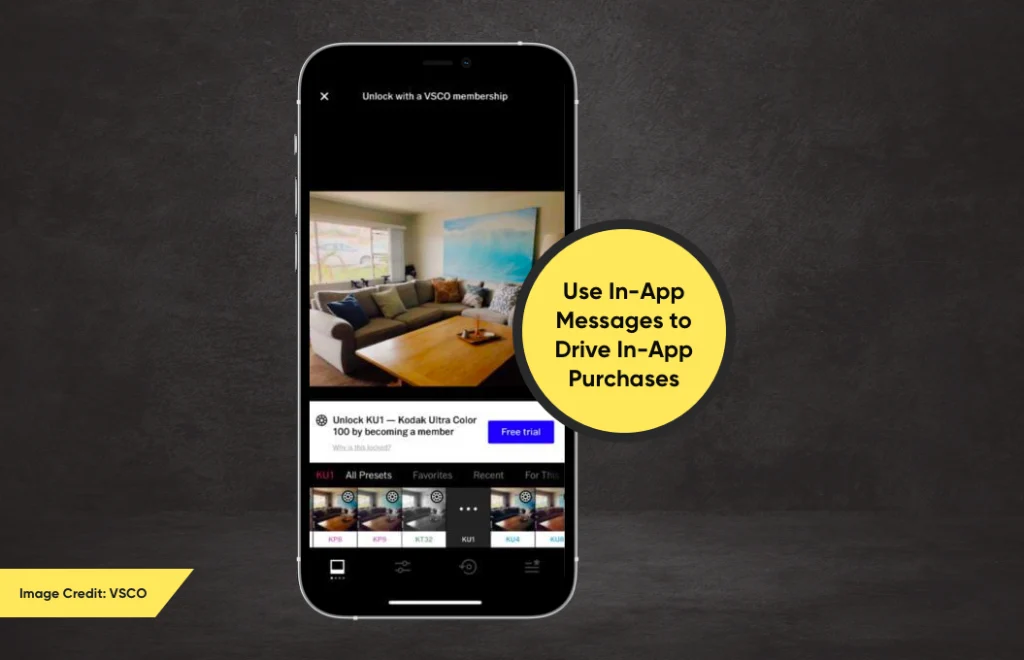
By using the users’ browsing and purchasing history, send them a personalized in-app message that triggers their emotions. There is no better advertising strategy than appealing to emotion one-on-one.
4. Use Email and Push Notifications to Increase Sales
Push notifications and emails are among the best ways to boost in-app purchases as they reach users outside the application. Thus, using them can help to target people who are not regularly active users.
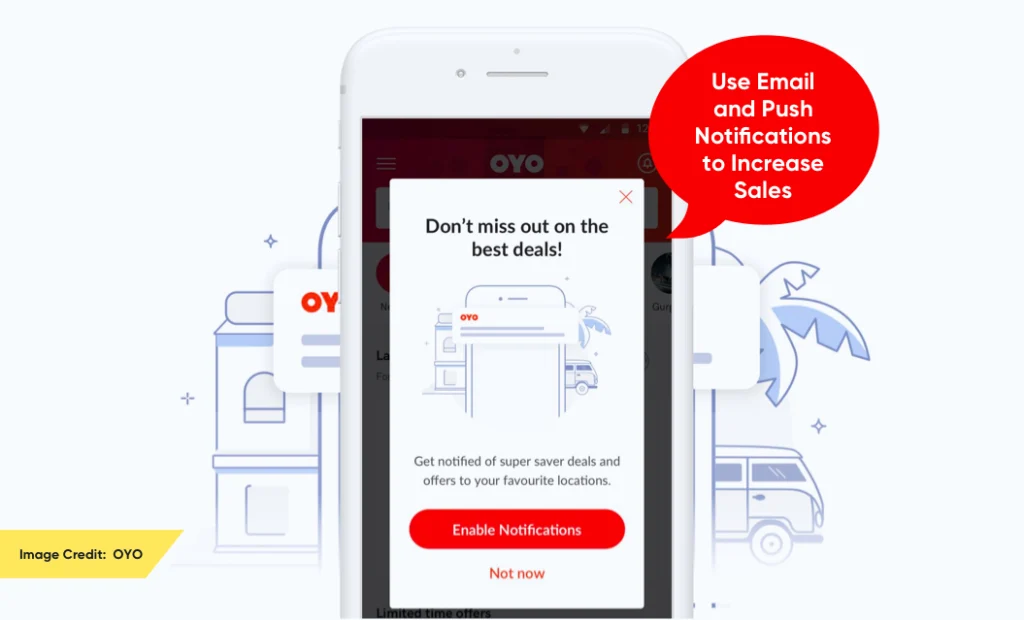
However, using push notifications or emails to drive purchases is an art. There are various ways to use these messages to get a higher success rate:
- Mention the name of users in the content to drive attention
- Choose the right time that triggers the users
- Create a sense of urgency and FOMO in the copy
On average, brands experience up to 9.6X increased in-app purchases when using push notifications, as per AppAnnie. Therefore, one must not ignore setting up an amazing push notification campaign to drive revenues. Just make sure not to overuse this strategy. Else it can irritate the app users, and they may end up uninstalling the app.
16% increase in purchases on the app, directly attributed to pushing amplification
– MoEngage
5. Set Your Pricing Right
It may seem obvious, but many businesses fail to understand the importance of the right pricing.
If the in-app purchase pricing is too high, enough conversions may not get supported. If pricing is too low, the revenue will suffer, and users may think it isn’t worthwhile.
Therefore, do some research on average industry rates and get the pricing just right – neither too high nor too low. Make sure it is competitive and matches the standard industry rates. A little bit of industry exposure and smart tactics will help in getting far in the mobile app market.
Conclusion
While there is no sure-shot way of convincing users to buy something or drive in-app purchases, the tips mentioned above can help in making an effective strategy. Make sure the plan supposed to follow is based on the customers’ behavioral data and business goals.
The brands aligning their marketing efforts with customers’ needs and experience set the foundation for making a loyal relationship with the app’s user base, which leads to effective monetization.
SHARE THIS POST
Table of Contents
Related Resources
- What is App Store Optimization (ASO)? The in-depth guide for 2024
- The Mobile App Architecture Guide for 2024
- 7-Step Mobile App Development Checklist (Free Download)
- How Much Does it Cost to Build an App [A Complete Breakdown]
- How To Protect Data In Mobile & Web Apps Using Encryption
- eCommerce Mobile App Development: A Step-by-Step Guide
- 7-Step Mobile App Development Checklist (Free Download)
- How Firebase is Emerging as an Innovation in App Development
- Low-Cost Mobile App Development: A Comprehensive Guide
- How to Make an App in 2024: 5 Stages of Mobile App Development
- What is Mobile-first Design (+9 Best Practices)
- The Ultimate Guide for New App Ideas
- Offshore Mobile App Development: An In-Depth Guide
- Most Popular Programming Languages for Mobile App Development
- 7 Mobile App Development Tips for Acquisition & Retention
- Top 15 Mobile App Development Trends to Watch for in 2024
- The Fundamentals of Android App Development: Basic Tutorial

