Building products that solve user problems is only the first step towards success. The second step is to ensure that its interface is easy and intuitive to use and is perceived well by the users (i.e., its user experience (UX) satisfies their needs).
For instance, a business builds a time management application for improving employee productivity. It is a great and well-researched idea that is likely to be a product-market fit (i.e., it will solve a real problem of the target audience). However, when the minimum viable product (MVP) is launched, the engagement is pretty low despite endless marketing campaigns.
One reason could be the bad user experience (UX) that the application offers. The users discovered the product but abandoned it midway because of its usage complexity. Therefore, nailing user experience is as important as matching the criteria for product-market fit.
In fact, every dollar spent on UX brings between $2 and $100 dollars in return.
There’s way more to UX to understand. Here is a guide that covers it all:
What is User Experience?
According to the International Organization for Standardization, user experience (UX) is a — “person’s perceptions and responses resulting from the use and or anticipated use of a product, system or service.”
In other words, UX is how a user interacts with technology and what perception that user builds of the product in terms of ease to perform intended actions.
What is User Experience Design?
User experience is most relevant when designing mobile apps, software, or website interfaces. A good UX design ensures that technology is intuitive and easy to use.
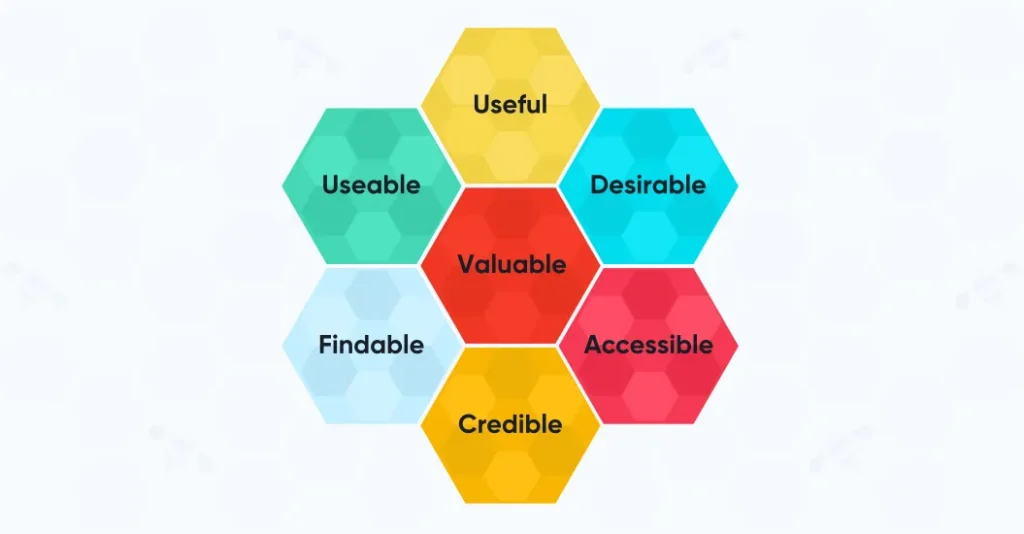
Peter Morville has introduced a UX honeycomb that describes the primary characteristics of user experience design, including:
- Usable: The product is easy to use and navigate through
- Useful: The product should be able to fulfill the needs of the user (i.e., the users should be able to perform an intended action)
- Desirable: The product’s interface should be neat and clean and interesting to look at
- Findable: The user should be able to locate features and pages they are looking for
- Accessible: The product should rank high on accessibility (i.e., the people with disabilities should be able to interact with the technology without much hassle)
- Credible: The users should believe in the business and everything it has to offer
Why is User Experience important in Software Development?
User Experience helps improve Usability-
Having a working application is excellent, but will it cater to and retain customers if it’s not user-friendly? UX and UI interfaces are designed to retain users for your application.
An intuitive user design will help users better engage with your content and make their navigation straightforward. Satisfied customers often advise others on your submission. This will help you keep your loyal customers longer in their customer lifecycle and hence fuel your brand’s ROI.
User Experience Can Help Eliminate Consumer pain points-
- User Experience issues when detected initially save future development expenses by eliminating any potential subjects of concern like-
- Clarifying Vision
- Engaging Users as Customers
- Validating Concepts
- Increasing Sales
- Improving Users’ Quality of Life
- Understanding the consumer’s pain points
A UX issue worked at the design stage is much lower cost-effective than during development or production.
Although rare, UX designers can also work alongside quality assurance (QA) to identify usability issues. Software that is user-centered is what is most important at the end of the day.
Established Brand Value-
Continually investing in interesting UI/UX design trends will engage your customers towards building loyalty and eventually happier customers. Customers tend to collaborate and associate with brands that prioritize their requirements and please them.
Moreover, when you care about your consumer’s experience and invest in functionality to update and upgrade your application, this works in favor to enhance your brand’s reputation as a customer creates good ties with your business and brand. Consequently, your brand values rise up.
Attractive yet simplistic applications have more users and Popular UI/UX designs have lured millions of users like Twitter, Facebook, Instagram, etc. Great User Experiences lead to happy customers and thus trustworthy customers.
Difference Between User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX)
UI and UX design are two different sides of the same coin. They both represent and help improve different things but, collectively, they help to enhance the overall customer experience.
What is User Interface (UI)?
A user interface (UI) design defines how the different elements of the interface are placed, organized, and designed across the different interfaces. These are the elements that the user can see on their screens and interact with.
What is User Experience (UX)?
User experience (UX) defines the user’s overall experience (e.g., delights and frustrations) when interacting with technology. UX encompasses all aspects of the user journey and their experience when performing the desired action.
Common Myths Around User Experience Design (and Facts)
The common myths and the corresponding facts related to UX design include:
- Myth: UX and usability are the same
Fact: UX defines how the user feels about the overall experience while interacting with the product. Are they happy, frustrated, or just merely satisfied?
On the other hand, usability is about creating products that have user-friendly interfaces and promote findability and discoverability. That is, a user should be able to efficiently find what they are looking for and discover new features without much hassle.
- Myth: UX Design is a one-time task
Fact: The business will have to strategize around UX design differently for different channels (website and app) and devices (mobile, desktop, tablet, etc). Though the design will be consistent across all these devices and channels, different UI elements that complement the respective channels will have to be identified.
Also, focus on creating unique user experiences for the target audience instead of following a competitors’ UX design strategy.
- Myth: If the design is great, small details do not matter much
Fact: No matter how interactive and aesthetically beautiful a design is, users will abandon the product if they feel a gap in UX at any stage. This is why a business must pay attention to details at every stage of development.
For example, on BestBuy.com, the small change of allowing people to skip sign-up during checkout resulted in $300 million extra revenue per year.
- Myth: The business members are the Users Fact: Many businesses convert their opinions into system requirements because they have a perception that they are the users. Do not commit this mistake! Invest time and efforts in UX research and involve the insights gained from the beginning.
Elements of User Experience
Several elements act as building blocks for creating a powerful UX. The most prominent ones include:
- Information Architecture (IA)
Information architecture (IA) defines how to organize, label, and structure information across different platforms. IA promotes findability and discoverability, which, in turn, helps users to locate what they are looking for and learn about new features they were not aware of initially.
An overview of the four elements of information architecture:
- Structure: This refers to how information is organized and categorized across the product’s interface
- Labeling: The labels of the pages and features should be written in human-readable language so that they are easy to understand
- Navigation: Users should be able to find and discover information across the interface without much hassle
- Search System: There should be a search option across touchpoints and channels so that the users can quickly search for what they are looking for
- Interaction-Oriented Design (IxD)
Interaction-oriented design (IxD) focuses on creating an interactive experience between the product’s interface and the users. IxD is created based on extensive user research that helps infer how users interact with technology and their corresponding delights and frustrations.
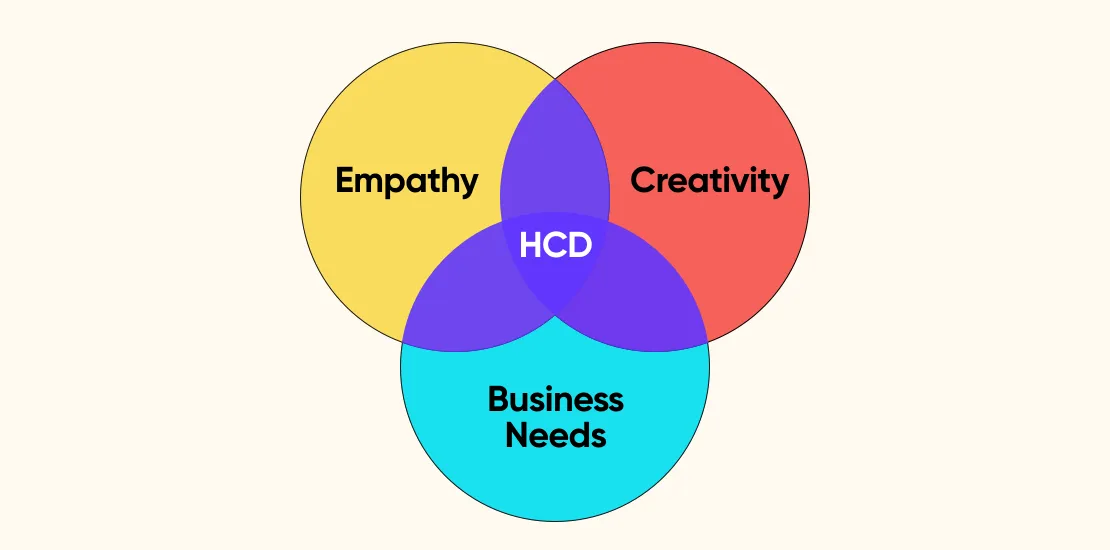
- Human-Centered Design (HCD)
Human-Centered Design (HCD) is an approach to designing products where the target audience takes center stage. In other words, in the HCD process, humans (target audience or real users) are present in the design stage for understanding the problem, brainstorming, and coming up with a solution.
- Skeuomorphism
Skeuomorphism describes designing for familiarity. That is, the structure of content and the graphical elements should be similar to real-life counterparts. For example, a real-life calculator and a digital calculator are identical in design and usability.
Skeuomorphism is the key to retaining customers. The product needs to follow design standards when creating products over experimentation. For instance, if an app has a different option for the drop-down menu other than a hamburger icon (which everyone recognizes), people will feel confused and leave immediately.
UX Design Process
The five-step UX design process includes:
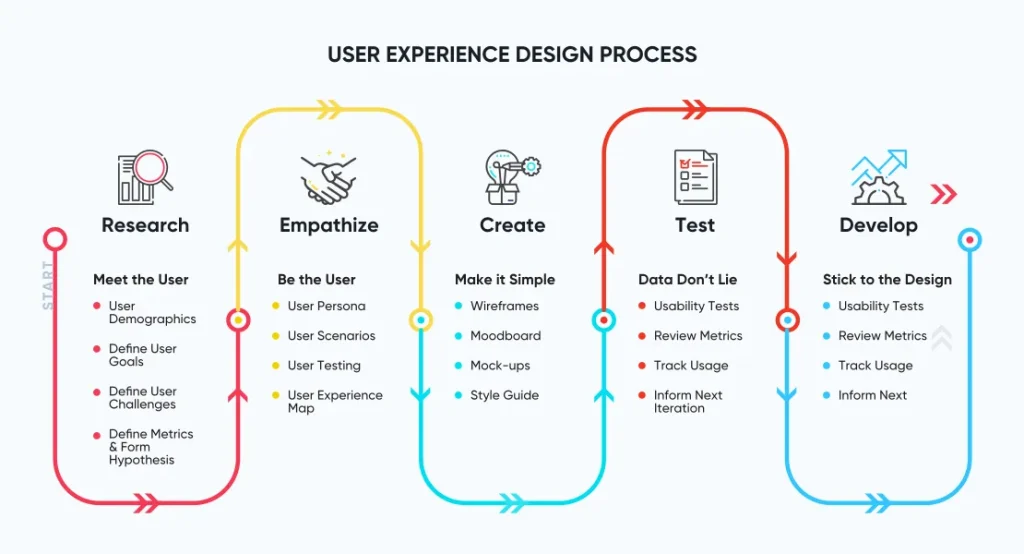
- User Research
Conducting user research is the first and the most crucial step towards creating a wonderful user experience. User research helps both with understanding the problem the app will solve and with inferring the functional and business requirements of the product.
There are a handful of user research methods. Some of which include:
- User Surveys Creating and distributing surveys among the target audience is the easiest and most inexpensive way to understand user needs.Here, the focus should be on creating intent-driven questionnaires that ask relevant questions about how the user interacts with the product.
- Stakeholder Interviews Stakeholder interviews are another easy method to conduct user research. Stakeholders’ approval and feedback is essential throughout the design process.Stakeholders help a business understand the user behavior and what they expect out of the system being designed. It is a good practice to record the stakeholders’ expectations early on for developing user-centric products.
- Ethnographic Research Ethnographic research helps in understanding the user’s needs for complex problems. In this method, a researcher spends time in the live environment of the target audience to understand how they interact with technology.The method helps in designing better user experience but is expensive and time-consuming. This is why businesses only consider ethnographic research methods when the problem is complex, and user requirements are unknown.
- Finalize Requirements
Once the user research is complete, the design requirements need to be narrowed down for a clearer perspective.
Run brainstorming sessions with the product development team (i.e., developers, UX designers, UX architects, business analysts) and create a set of final requirements.
For spot-on requirements analysis, here are some methods to follow:
- Create BuyerPersonas Segment the target audience based on common interests and perspectives. Next, create buyer persona charts that depict the users wants and needs from the product as well as any insights as to what delights and frustrates them.
- Creating User StoriesA user story is a description of the product’s feature/s that helps in understanding what the user wants in a simple and natural way. The format for defining a user story is “As a [User], I want to [goal] so that I can [benefit]”.
- StoryboardingStoryboarding is a technique that helps in representing the findings from the buyer persona charts and the user stories. Storyboards represent information graphically in the form of images and illustrations to demonstrate a narrative.This process helps with deciding the UX design of the interfaces in chronological order.
- Create Information Architecture/Wireframe
Strategizing around the information architecture will help plan an organized structure for the web/mobile design. This includes labeling content and organizing it in an understandable and intuitive format.
On the other hand, a wireframe is a skeleton of different interfaces. A UX wireframe represents the organization and structure of elements on product pages for different devices.
Creating information architecture and wireframes ensures that the content is neatly and cleanly organized, the interface looks attractive and user-friendly, and the navigation is intuitive.
- Create Prototypes
A prototype is a draft version of the product that demonstrates its UX/UI flow. Prototypes help analyze the look and feel of the product, which, in turn, validates the product’s design.
The goal of UX prototyping is simple — gain early feedback from the team regarding the design, and visualize how the product will look and feel when completed. Prototypes also play a vital role in attracting seed funding for the product being developed.
- User Experience Testing
Testing is an essential part of the UX design process as it helps validate whether the designed product meets the business and functional requirements. Different types of UX testing include:
- User TestingThe product is shared with a group of people who represent the target audience for testing. This helps get real-time feedback from the users, which helps to analyze the UX across touchpoints and rate users’ overall experience.
- Analytics (Qualitative Method)Various analytics tools can be leveraged to help analyze how the users interact with the product. For example, heatmaps are a great representation of how an audience interacts with technology.
- DogfoodingDogfooding implies that the business needs to use and test their own product (i.e., in-house testing of the product). This practice greatly helps with identifying flaws when the product is still inside the four walls of the organization and yet to be launched in the market.
What are the Benefits of User Experience Design?
According to UX Planet, a good UX design can lead to 400% conversion rates.
Here are some other amazing benefits of a good user experience design:
- Achieve customer loyalty
- Higher customer satisfaction rate
- Better brand reputation
- Higher market share
- Competitive advantage
- Costs cheaper in the long run
UX Design: Best Practices
Here are some best practices that will help infer how to enhance the UX of products or services:
- Maintain a consistent UI/UX across channels and touchpoints
- Embed clear, concise, and understandable CTAs that leverage the best of UX writing
- Thoroughly research user behavior before moving on with the actual design process
- Follow Hick’s Law when creating user interfaces and experiences. According to Hick’s law, the more choices represented to the user, the longer it will take to make a decision. This is why many apps minimize options and functionality to cut the clutter
- Place the control in user’s hand (i.e., introduce personalizations and remove all roadblocks they encounter when performing the desired action)
- Focus on creating an omnichannel experience across channels and touchpoints(i.e., a user can switch from one channel to another and carry out the task from the point they left on the prior channel).
- Regularize A/B testing. UX design is an ongoing process. Keep experimenting and testing what works for the target audience and improvise
Latest UX Trends
The latest UX trends that are disrupting the market include:
- Password-Less Login
This helps enable sign-in options such as through social media accounts, Google account, phone patterns, or QR code scans.
- UX Writing
Includes the words that a user reads when interacting with the product. These words should be short and understandable so that the user can infer the intent of the options and features included.
- Anthropomorphic Animations
These animations mimic human-like movements such as blinking of the eye. Businesses are experimenting with the design across the home page to create a delightful UX for website visitors.
- Voice-Activated User Interface
Designing for voice recognition is gaining traction. Voice-activated interfaces eliminate the need to type through the screens, which will significantly enhance the user experience.
- Personalization
Offering UI personalization options to users helps to modify the interfaces in a way that is preferential for every user. For example, many apps include a choice between dark theme and light theme. This is one of the elements that define personalization.
- Virtual and Augmented Reality
Design for VR and AR is the next biggest thing for UX designers. This not only helps improve UX but also helps in maintaining a competitive edge.
- Videos
Short and interactive videos that talk about the business model and its value proposition are good for improving the bottom line. Around 40% of the audience responds better to the video content as compared to a textual one.
Why Hire UX Design Agency?
Hiring a UX design agency is a fool-proof plan a business needs to implement from day one when designing products. The UX expert team understands the forward and backward of UX design and has up-to-date knowledge of the latest trends.
An experienced UX design agency helps in:
- Creating a powerful UX strategy
- Product Prototyping
- Organizing and implementing design sprints
- Usability testing and validation
FAQs Related to User Experience (UX)
1. How to Measure User Experience (UX)?
Google’s HEART framework is a good standard for measuring UX success. The five metrics used in the HEART framework include — happiness, engagement, adoption, retention, and task success.
This is a chart that depicts the goals of each of these UX metrics:

2. What is the Role of Accessibility in UX?
Accessibility aims for inclusiveness (i.e., when one and all can use the technology irrespective of their disabilities). When designing for improving UX, following the accessibility standards should be essential.
The seven principles of accessibility include:
- Design for the blind should be a priority as about 80% of the accessibility issues are associated with blindness
- Assigning ALT tags for all the images and graphical content is important
- Tag hamburger icons so that the screen readers can find them easily and can navigate across touchpoints
- Place the most important content and options at the top for easy accessibility
- Test for accessibility with real users facing accessibility issues
- Do not disable the zoom functionality when designing for mobile
- Design for accessibility from early on. This saves time, money, and efforts.
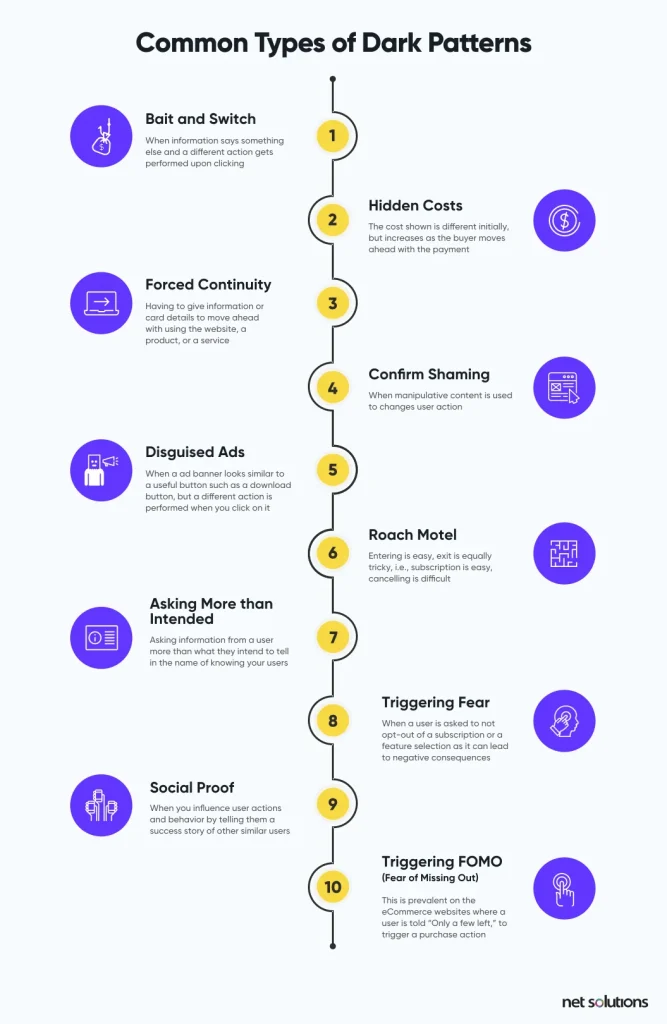
3. What are Dark Patterns in UX?
Dark patterns are tricks and gimmicks that are embedded into the user interfaces that instigate users to take action (that they did not intend). For example, the “Bait and Switch” dark pattern is when the text indicates one thing but a different action is performed when the option is selected.
Other types of dark patterns include:
4. What is Collaborative Design Practice?
Collaborative design is a practice that the product development team needs to follow for improving the design process. In collaborative design practice, the developers, the designers, architects, and testers come together to work on the design of the system.
Collaborative design is the process of involving people with distinct profiles in the design process to achieve non-linear solutions for various kinds of problems.
Gustavo Pimenta, Managing Partners at SensesLab
Conclusion
User experience (UX) design is all about how to make the users feel delighted with the product. For creating great UX design, it is essential to understand user needs and desires along with what delights and frustrates them. If done right, investing in UX is very likely to enhance the bottom line, potentially up to 400%.
This write-up covered everything about UX and its related concepts. Businesses need to thoroughly understand UX before creating a digital experience that will lead to positive impressions.
Concluding with the words of Don Norman, Director of Design Labs at the University of California — when the technology delivers basic needs, User experience dominates.


