Between 2023 and 2025, AI in the retail market is expected to grow from $7.30B to $29.45B to support brick-and-mortar, omnichannel, and online retailing. It is forecasted that 325,000 retailers will implement some form of AI within 2023 and that retail spend on chatbots alone will reach $12B globally within 2023.
AI is getting much attention because it delivers results, including boosted productivity, improved customer satisfaction, and optimized product decisions. Walmart has, for example, used conversational AI to reduce the time care agents need to spend with customers, while Amazon’s AI initiatives are partly responsible for an 8.5% revenue growth.
“Digital transformation in retail is about more than connecting things. It’s about converting data into insights, which inform actions that drive better business outcomes. AI in retail—including machine learning and deep learning—are key to generating these insights.” – Intel.
What is AI?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a machine’s ability to perform cognitive tasks typically assigned to human intelligence, such as learning, perceiving, or problem-solving. These so-called “smart machines” have become smarter and more complex, able to perform complex calculations quickly, interact with their given environment, and ultimately assist humans in some way.
How is AI Used in the Retail Industry?
To answer how AI is used in retail, we need to understand that AI impacts all aspects of the business, from planning and forecasting to inventory management, sales, and fulfillment.
- Responsive R&D: Analyze trends (competitive, celebrity, market, etc.), customer sales, and feedback history to identify innovations.
- Demand Forecasting: In optimizing inventory, use historical and predictive analytics to anticipate demand for the entire brand and by store location (if relevant).
- Supply Chain Optimization: Use data analytics to know how much product to order, where to ship it, and when to optimize driving routes, avoid over or under-purchasing inventory, and reduce duplicative, unnecessary shipments.
- Inventory Management: With demand forecasting, avoid under and overstocking and reduce carrying costs. The use of robotics can also spot product loss.
- Operational Optimization: Identify process improvements (people and machines), identify bottlenecks, and replace manual or time-consuming tasks with automation. Further, analysis of customer service interactions can positively improve performance.
- Fraud Detention and Security: Analyze purchase patterns and unusual purchases or returns to spot for fraud. Leverage AI in cybersecurity efforts to reduce the risk of breach or fraud.
- Pricing Optimization: Know what the market and competitors are doing to set and change pricing, including real-time adjustments.
- Visual Merchandising: In-store or online, visual merchandising optimizes how products are displayed to gain attention. In-store decisions include lighting, space, sounds, smells, interactive displays, and even how different colors boost aesthetics. Trends can influence what is displayed, how, where, with what lighting, and any other seasonal display or product information is added. Online ads and product groupings can adjust in real time to customer behavior.
- Virtual Try-On and Augmented Reality (AR): Help visualize purchases to close sales.
- Customized Selections and Personalized Marketing: Use browsing behavior, preferences, and past purchases to display personalized information or use personalized marketing techniques (email, text, in-app, on social, etc.).
- Customer Sentiment Analysis: Analyze chat data, emails, and social media to gauge customer satisfaction.
- Seamless Customer Service & Engagement: Leverage chatbots and virtual assistants to provide real-time interaction, recap conversations for live agents, spin out new help articles, or adjust product recommendations.
- Interactive Chat: When designed with the right strategy and tactics, Chatbots hold the potential to understand and respond to user questions naturally and do a great job of handling simple customer queries or pre-screening queries to speed up human response. Chatbots rely on conversational AI, such as ChatGPT.
- Voice Commerce and Virtual Assistants: Support voice commands to assist in retail, a growing trend not just for accessibility but as a preference for users who prefer to ditch keyboards and screens.
- Cashierless Technology: Use cameras and sensors to support checkout and billing without needing retail staff or cashier processes.
AI Technology in Retail
There is a variety and constantly shifting landscape of AI technology in retail and AI applications in retail, including:
1. Machine Learning
Machine learning (or ML) is a form of AI based on algorithms trained using data, typically to make predictions based on a data set. Given the advance of “big data” in many industries, machine learning is helping make decisions and recommendations based on more data than humans can process. Machine learning can estimate demand, product freshness, product placement, markdown optimization, and bundling opportunities.
2. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing is the technology behind conversational AI and chatbots, allowing the computer to respond to commands, summarize text, and even translate languages.
3. Computer Vision
Computer vision enables computers to derive intelligence from visual information (images, videos), often used in combination with other AI, e.g., to make beauty recommendations based on facial features to make product recommendations based upon an image.
4. AI-powered recommendation systems
An AI-powered recommendation system is the cornerstone technology of many retail efforts at personalization. Usually associated with machine learning to suggest or recommend products based upon known information such as shopping patterns, browsing patterns, preferences, location, or more.
5. Robotics and Automation
Robotics is a technology utilized in retail to take over manual tasks that are either repetitive or hazardous, autonomously with intelligence or semi-autonomously with some intervention. Automation is a process that uses either software or robots to replace or improve processes (technology or human processes).
6. Predictive Analytics
The use of data to predict future trends or to better understand customer behavior through the customer journey.
7. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
Augmented reality (AR) overlays the real world with superimposed virtual elements, practical to “try” on products (e.g., clothes, furniture, art). In contrast, virtual reality creates an artificial environment, such as walking customers through a “store” or joining a runway show.
Benefits of AI in the Retail Industry
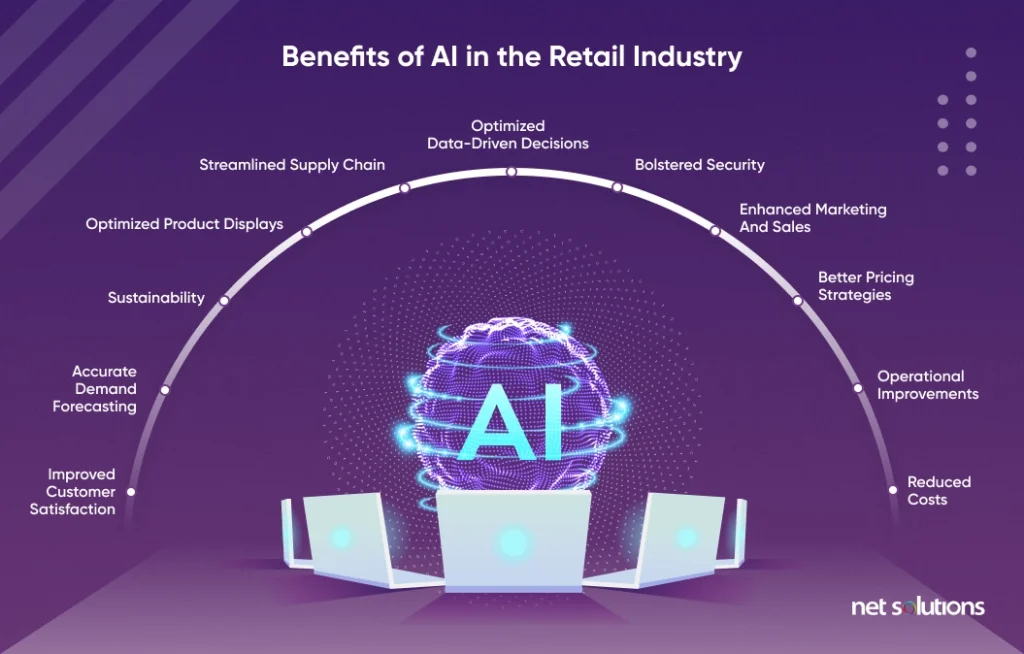
There are many benefits of AI in retail, including:
- Improved customer satisfaction: Improve the customer experience with fast, responsive chatbots, personalized recommendations, streamlined checkouts, and better marketing.
- Accurate demand forecasting: Better understand how much product to order and when / where to ship or restock it. With consumer and competitive data, decisions can be made in all stages, including merchandising, marketing, pricing, and in-store optimizations.
- Sustainability: Leverage data to monitor emissions, optimize shipping, and promote recycling.
- Optimized product displays: Anticipate trends to prioritize product displays or learn from purchase behavior what products work well together.
- Optimized supply chain: Based upon demand forecasting, inventory management optimizes ordering and shipping, helping to reduce the cost of product purchased and how it is shipped and stored.
- Optimized data-driven decisions: Analyze large data sets to identify patterns, forecast the future, and provide insight on what products to purchase, what to price them, how to market them, how to improve operations, where to open new retail locations, how to optimize staffing, and more.
- Bolstered security: Prevent shoplifting, log suspicious shoplifters.
- Enhanced marketing and sales: Leverage customer insights to personalize marketing and sales opportunities via newsletters, text, and omnichannel in-store, social media, or in-app. This could include recommendations, sales, new product alerts, and more.
- Enhanced pricing strategies: Competitive and demand insight can be used to determine an optimal price, when to mark down, and when to promote.
- Operational improvements: Use to streamline or automate mundane tasks such as inventory scanning, customer service, forecasting, inventory management, staffing levels, and delivery schemes.
- Reduced costs: Many of the above efficiencies help cut costs with less product loss, better forecasting, better customer service, and more.
Examples of Big Giants Using AI for Retail Experience
Some AI in retail examples include:
1. Walgreens Uses AI To Track Flu Spread
The Walgreens Flu Index is an online, interactive tool that ranks flu activity across the United States. The Index uses retail prescription data for antiviral medications to create a picture of flu activity, where it may be hitting hardest, and trends that show if the activity is higher than average to help inform people about their activities and need for an annual flu shot.

2. Neiman Marcus Uses AI For Visual Search
Neiman Marcus is prioritizing personalization and experience for its customers with visual search capabilities to help customers find products they’re looking for. The capability enables users to enter a 3D image and have suggestions that would be similar. The “Snap. Find. Shop.” capability is excellent at taking suggestions for photos taken or found on the web and can extend to clothes, makeup, and more.
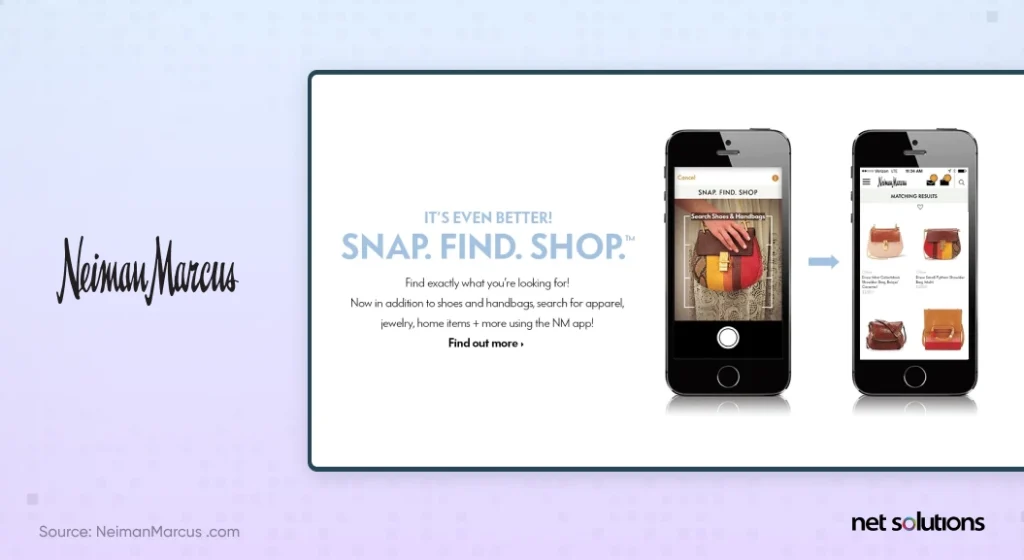
The brand also utilizes customer information, including favorites, history, and preferences, to curate suggestions and in-store alerts of new products or promotions.
3. Walmart is a Leader in Generative AI
The retail giant Walmart has been a leader in AI and robotics, although not all projects go to plan. While there was much news about using mobile robots to scan inventory, that pilot project was on par with associates in terms of cost and efficiency. However, the pilot was key to Walmart’s understanding of how AI “can assist associates, make jobs easier, and provide better customer service.”
Just recently, Walmart’s CEO Doug McMillon shared its continued excitement about AI, noting they were developing their generative AI language models and others to improve the shopping experience and support its associates. Walmart recently announced giving this “My Assistant” app to 50,000 non-store employees to boost productivity related to content.
“Our approach to new tools like generative AI is to focus on making shopping easier and more convenient for our customers and members, and helping our associates enjoy more satisfying and productive work.” – Doug McMillon, CEO, Walmart
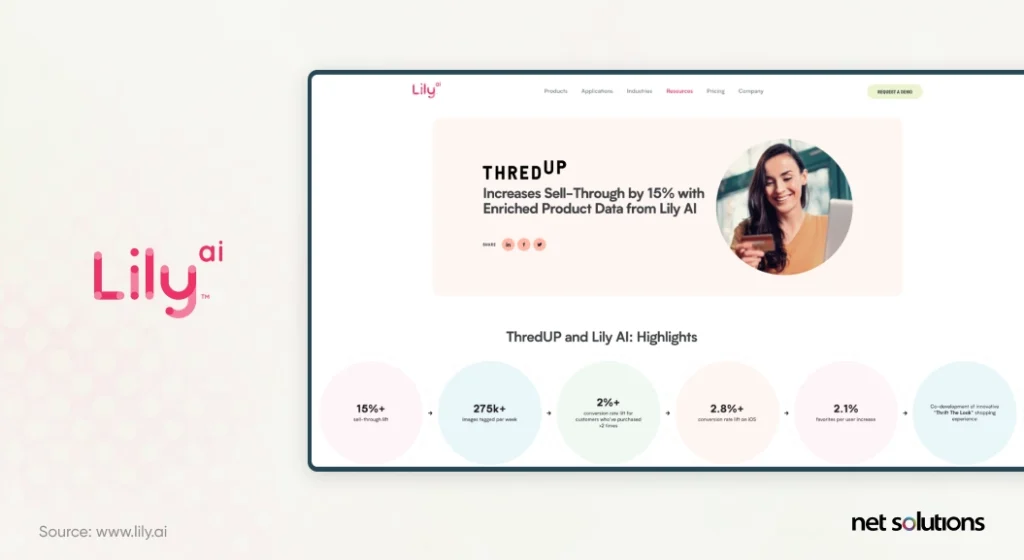
4. thredUp Uses AI To Remember Customer Preferences
thredUp uses AI to help get thrifted and secondhand clothing back into circulation in a way that supports sustainable fashion and helps glamorize items and outfits to inspire re-use. Processing over 100k items and 4.4M items on thredUP daily, thredUp uses AI to position goods better and generate recommendations, including creating custom ‘Goody Boxes’ matching interest profiles. The result is a 15% increase in sell-through.
5. Amazon Eliminates Cashiers With AI
Amazon helped develop cashier-less checkout, which it’s used to open stores that leverage its sensor and camera “Just Walk Out” technology to bill shoppers after they’ve left. This technology is now being sold to wider third-party retail audiences.

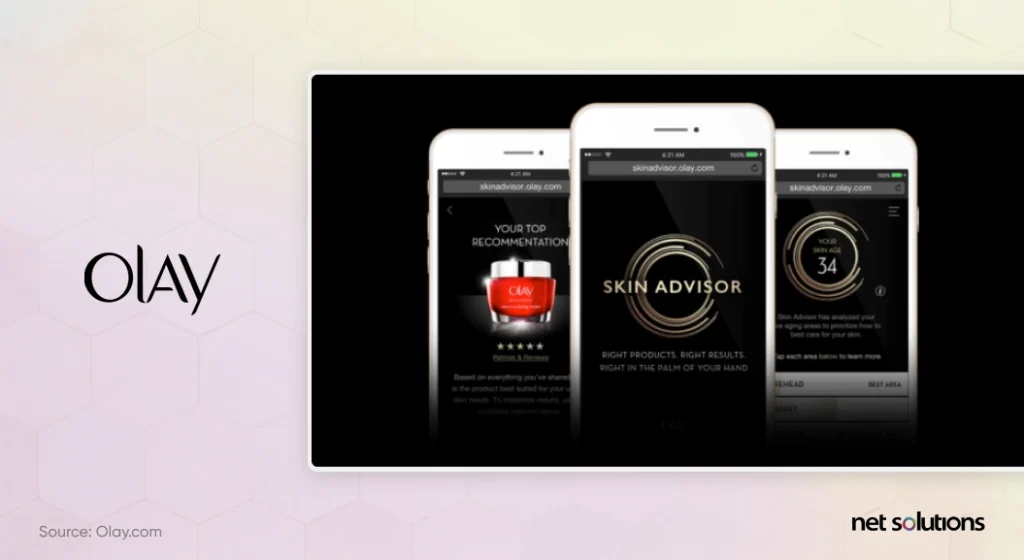
6. Olay Uses AI To Personalize Skincare
Leveraging deep learning, Olay is taking the guesswork out of beauty. Knowing consumers often put together their skincare regimes, mixing chemicals with sub-optimal results, Olay uses AI to analyze skin from photos to suggest the optimal beauty regime.
7. H&M Uses AI To Keep Popular Items Stocked
As a fast fashion retailer, H&M is using AI to optimize its supply chain to help get trends to consumers faster than before, leveraging insight from search engines and blogs, fashion week, and celebrity influence to inform how much, when, and what they buy and where to place it in stores. When stock sells quickly, AI also informs how to restock items. The result has also helped the brand reduce waste and make more sustainable decisions.
8. Zara Streamlines Order Pickup With Robots
Although Zara also uses AI to predict trends, it’s also a brand that utilizes robotics and AI to automate order pickup for its buy online, pick-up in-store (BOPIS) orders, allowing its AI Robots to search for and fulfill requested orders from the back-of-store warehouse.
Challenges of Implementing AI in Retail
Some of the most common challenges in retail, at least perceived challenges, include:
1. Worker Displacement
One of the top concerns, one report predicted “significant net employment reductions” across wholesale, retail, finance, and public administration. Still, these displacements may be offset long-term by switching employees into more value-generating positions.
2. Data Quality and Accessibility
Limited, inconsistent, or incomplete data or data locked behind a paywall (e.g., trend reports) can hinder the effectiveness of AI analysis. Data preparation is key to removing biases, removing inaccurate or irrelevant information, and (in some cases) standardizing formats where input systems format the same data differently.
3. Cost and Infrastructure
Training an AI to be knowledgeable can cost millions of dollars, which is why off-the-shelf AI systems have some advantages. However, any AI will need an investment and a team to operate it successfully.
4. Integration With Existing System
To provide AI inputs or refine processes, AI must be integrated into existing systems, which can pose challenges for legacy systems.
5. Ethical and Privacy Concerns
Data can inadvertently introduce bias or ethical considerations, requiring teams to look closely at data and rules to eliminate potential bias, which has emerged in a number of situations. Further, organizations must (and sometimes this is a legal must) disclose data processing by clarifying that AI is being used and that any data shared with third-party processors follows privacy regulations.
6. Not Enough ROI
AI is still nascent, and some applications of AI in retail do not yield anticipated returns, as demonstrated above in the Walmart robot example. Unless you’re looking for a leading edge, look to success stories as a barometer for what kind of AI to adopt.
7. Skill Gap and Workforce Transition
Workforces must change skill sets when automation replaces work, and new technologies require knowledge of AI expertise or elevated services. In many cases, more skilled IT workers must be needed to help retailers take advantage of new AI opportunities.
8. Consumer Adoption and Trust
While there is some general consumer mistrust of AI, most consumers are excited about AI’s new opportunities for the retail experience (and their personal lives!) As with any initiative, transparency and communication can help foster trust in new services.
9. Complexity of AI Models and Interpretability
As the output of AI models is the insight upon which decisions are made, complexity can get in the way of understanding and action. Model maturity will likely improve the interpretability while also keeping models accurate.
10. Continuous Monitoring and Maintenance
To maintain data quality, monitoring and maintaining both the data and the algorithms supporting the model and refining the model if biases emerge is essential. After all, intelligence will ‘learn,’ sometimes, the learning takes a less ideal path (e.g., if gender bias arises on facial recognition).
11. Risk of Overreliance and Unforeseen Impacts
Adverse side effects are often unintended and unforeseen if an algorithm is incorrect or bias emerges from data, damaging reputation, leading to operational losses, and impacting the bottom line. In some cases, bias could also have legal consequences.
12. Cybersecurity
47% of retail business leaders consider cybersecurity breaches a top concern with AI and the need to comply with data security and privacy regulations. How you set up AI is as important as Why you set up AI.
Future of AI in the Retail Industry
- AI-Enabled Social Commerce – using AI to support social shopping (purchase via social media)
- AI-Powered Virtual Fitting Rooms – expanding use of VR and AR to ‘try on products
- Hyper-Personalization with AI – an ever-tightening level of personalization in shopping experiences
- AI-Driven Market Trend Analysis – expanding how trends emerge and inputting this into AI models (e.g., use of TikTok for trends)
- AI-Powered Dynamic Store Layout Optimization – use an in-store camera and sensor footage to heat map stores, combined with sales, to optimize the layout
- AI-Enhanced Automated Returns and Exchanges – streamline the return/exchange process to improve customer satisfaction
- AI for Socially Responsible Product Sourcing – focus on ethical sourcing and delivery to meet ESG goals
- AI-Enabled Sustainable Retail Practices – focus on ‘green’ efforts such as optimizing package size and shipment numbers, optimizing fulfillment, truck routing, inventory management, sales optimization to reduce waste, and other opportunities
How Net Solutions Can Support Transformative AI
78% of retail business leaders express difficulty staying on top of AI evolutions. A trusted partner can help you vet which advances suit your business outcomes. Net Solutions is your partner in AI-driven success, from chatbots and robust personalization systems to automation and supply chain optimization.
Ready to personalize and enhance customer shopping experiences with AI solutions? Our experts can help.
Frequently Asked Questions
Although the better question may be, “How is AI disrupting the retail industry?”retailers using AI have enhanced the customer experience with personalization, optimizing the supply chain (from trends and ordering to shipping), and improved operational processes. These changes are the new baseline for success in retail.
The use of AI can generate results that are not accurate or biased in some way, additionally raising some privacy concerns and concerns that employees will lose their jobs to machines or AI.
Significant and wide-reaching benefits include improved operations, more sustainable purchasing decisions / optimized demand forecasting, and better customer experience.



