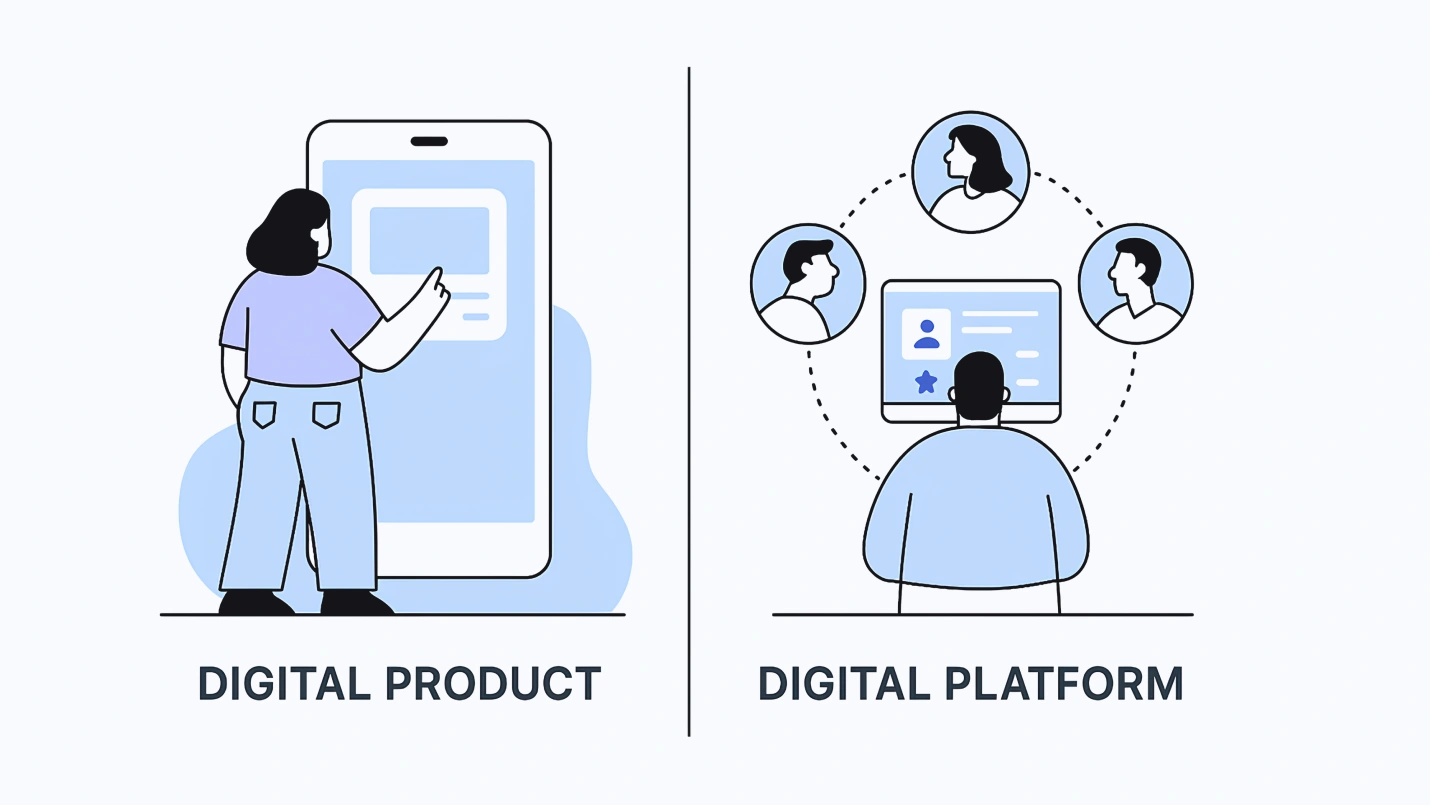
Summary: Both digital products and digital platforms have their share of robust features and significance. Hence, differentiating between them becomes difficult for most business owners. Can’t decide whether to build a digital product or a digital platform? This is the right guide for you.
Technology has paved the way for enormous business growth and curated memorable digital experience platforms in every way possible. The two popular and trending business ideas triggered by the changing needs of providers and consumers point to digital products and digital platforms. Entrepreneurs are often confused when it comes to digital products vs. digital platforms. While they both add value to a business, they both hold a unique stand in the market.
Digital platforms constitute a business model that attracts value by connecting two or more parties, usually producers and consumers. Digital product design is focused on the end-user entity in the form of content or services sold to individuals seeking to benefit from what the product offers.
This is exactly what the two business models primarily focus on:
Platform = Communication
Product = Production
A fair range of other differences significantly differentiates digital products from digital platforms. Let’s dive deeper into a meaningful analysis.

We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.
What is a digital product?
Any product you sell or distribute online is a digital product, such as an e-book, a mobile app, a website theme, a video game, etc. This product focuses on creating value for its buyers or users by solving their problems, spreading awareness about an important topic, or increasing their knowledge.
Facebook app, Google search, Uber app, and WordPress themes are popular examples of digital products.
What is a digital platform?
A digital platform allows communication between a supplier and a consumer. It also helps facilitate activities between businesses and customers and within enterprises. A platform can become the most powerful tool for a company to enhance its customer experience.
Here are a few examples of various digital platforms:
- Media sharing platforms like Vimeo, Spotify, and YouTube.
- Social media sites like Twitter, Facebook, LinkedIn, and Instagram.
- Knowledge-based platforms like Quora, StackOverflow, and Reddit.
- Service-based platforms like GrubHub, Uber, and Airbnb.
Digital product vs. digital platform: The dissimilarities
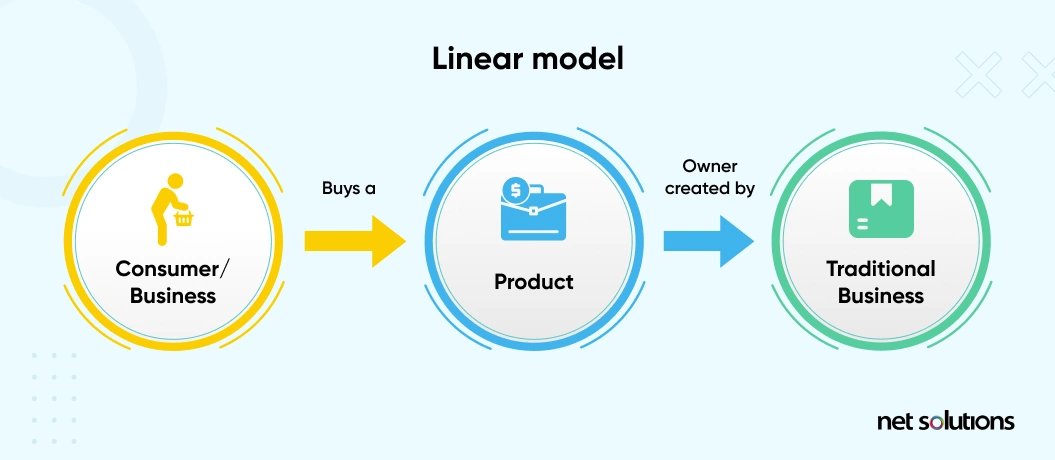
1. Linear Model Vs. Circular Model
Digital products follow the linear model, i.e., they attract value by producing products that are, in turn, sold to consumers/clients down the supply chain. Here are two brilliant examples of the linear model:
- The vehicle manufacturing company Toyota produces cars and sells them directly to users.
- The video streaming content production company Netflix creates content and sells it directly to end-users.
On the other hand, digital platforms follow a circular model that adapts to a better system where a business provides value by offering communication between consumers and third-party businesses.
For example, YouTube allows content creators worldwide to share content with their users. In a way, platforms have proved to be highly valuable. Even a study by Statista states that the top 10 companies by market capitalization are platforms.

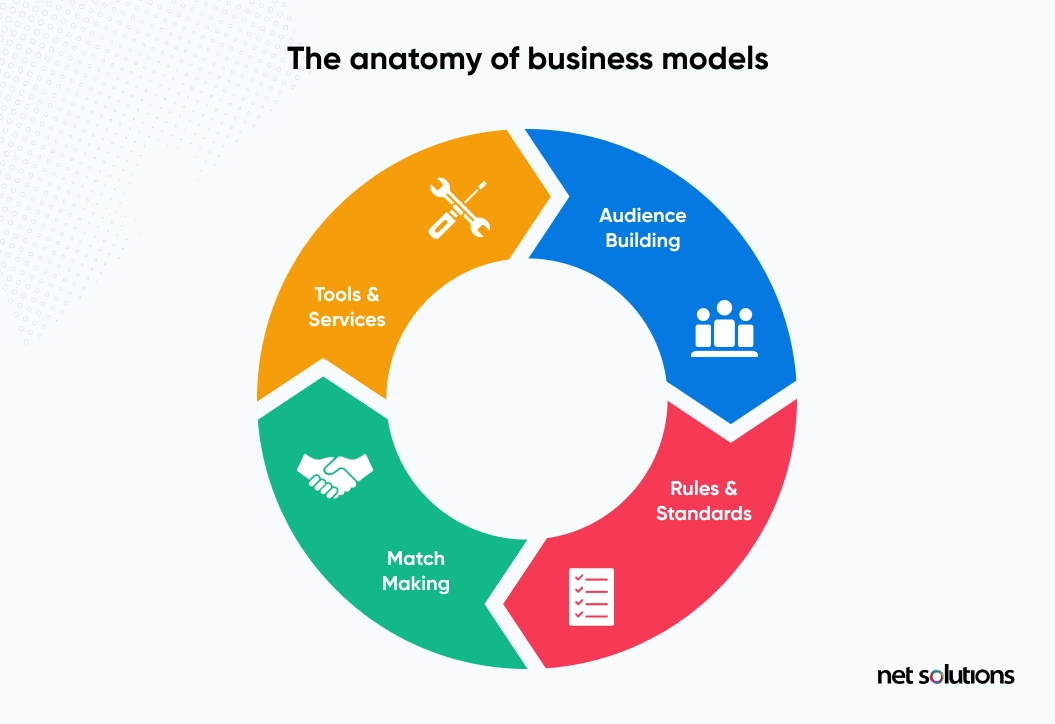
2. The Anatomy of Business Models
A digital product has a much easier job at hand. It doesn’t have to worry about anything except product development. A business only needs to plan how to offer content/service to its end users and advance the product according to the trending technology.
This condenses its role to three main vital functions:
- Building an audience base (consumer)
- Providing core services or content to the audience base
- Creating standards and T&Cs for maintaining authenticity
On the other hand, the primary purpose of a digital platform is to ensure perfect communication between the concerned parties. Everything revolves around the smooth facilitation of transactions to produce and exchange value among the actors.
The four essential functions to execute a transaction include:
- Building an audience base (provider and consumer)
- Connecting the right provider with the right consumer
- Provision of core services and features for a great UX
- Creating standards and T&Cs for maintaining authenticity
A digital platform must master the above core functions to facilitate a fruitful transaction.
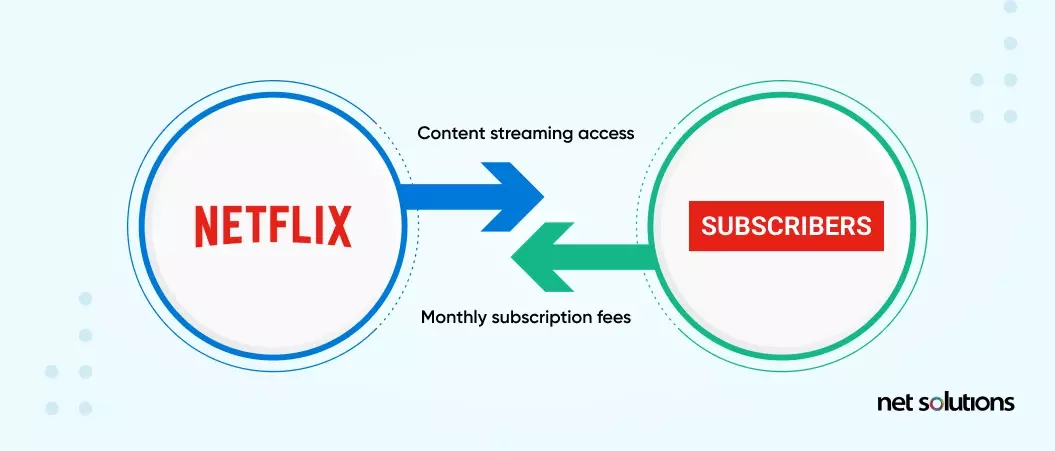
3. The Complexity of Operations
Both digital products and digital platforms operate in distinct ways. Digital products drive value by providing one product to a single end-user. The process is simple: the business offers a product, and the user consumes it, thus creating a single revenue stream. But users can’t resell the product further as the individual or the digital product development company who made it remains the rightful owner.
One famous example is Netflix. It offers content streaming access to consumers for a monthly subscription fee. Users can buy, watch, and enjoy the content but can’t resell it as Netflix remains the rightful owner.
On the other hand, a digital platform focuses on multiple revenue streams. Both creators and consumers are involved in a transaction on it. Also, a digital platform operates on demand and supply-model where the consumer has a requirement, and the creator fulfills it. Neither the creator nor the consumers are the owners of the platform.
YouTube is an excellent example of how digital platforms function. Here, both content creators and content consumers are involved in a transaction. Content creators benefit from the number of views, while consumers benefit from watching the content. None owns the platform; they’re engaged in a mutually beneficial transaction.

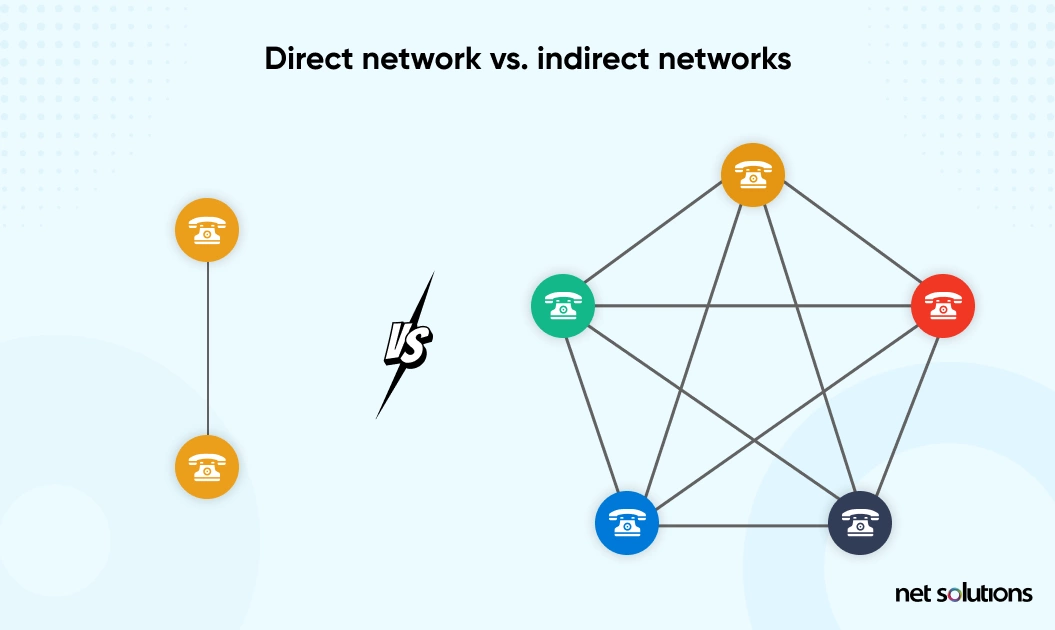
4. Direct Network Vs. Indirect Networks
The incremental benefit of every new user joining the bandwagon of connected networks is called the network effect. For example, if you have a smartphone but your friend doesn’t, there is no value associated with your phone as you cannot communicate.
Looking at the different types of digital platforms, we can say that two or more groups exchange value with one another. This is thus a similar scenario where everybody has a cell phone and can contact everybody.
Uber is an example of an indirect network. As more riders join the network, the value it adds up to the drivers also escalates exponentially, and better profits lie ahead of them.
5. The Economics of Products/Services
Digital products may not offer significant disruptive value in the times to come, while digital platforms are deemed much more valuable. It is because businesses need more financial resources and human resources to sell more digital products.
Here’s a graph that depicts the average cost curve for linear and platform businesses:
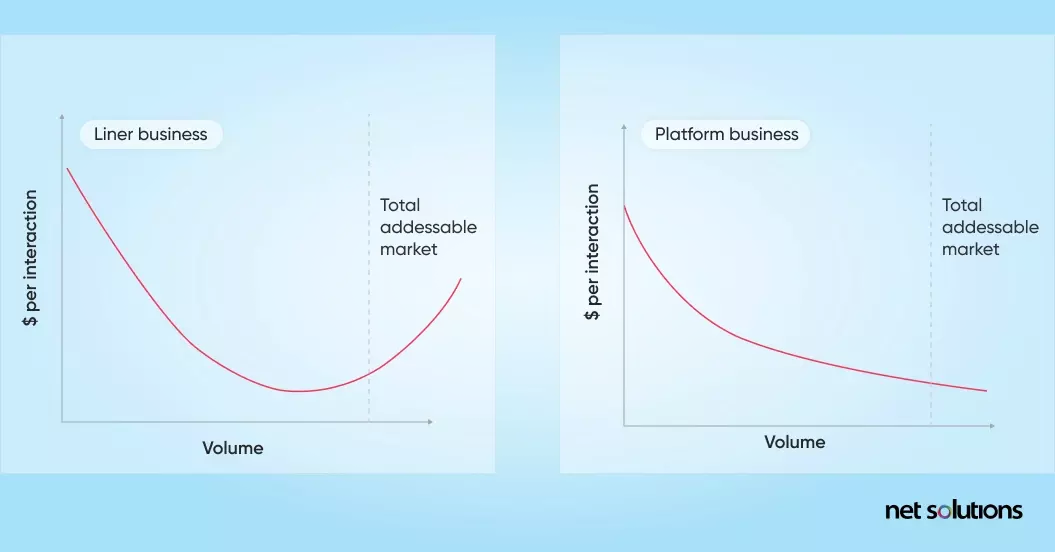
For example, when Netflix needs to add new content to the portal, they need to spend more on its creation, production, launch, marketing, etc. If the content created is excellent, profits will reap, or all the money spent will go waste.
On the other hand, the marginal cost of production and distribution in digital platforms is considerably low. This means expenses are less, and revenues turn out to be manifold. Taking YouTube as an example, the cost to add new videos and content to the platform is negligible, as the platform only needs to add new users to produce new content to its digital experience solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Subscription fee: Digital platforms like Netflix and Hulu let users consume content for a monthly subscription fee.
- Advertising: Digital platforms that don’t charge a subscription fee run ads, making them the most significant source of revenue in digital platforms.
- In-platform purchases: You can rent or buy content within the platform by paying some fee. Kindle is an example.
- Online courses
- Web-based applications
- Video games
- NFTs and tokens
- Music and Audio
- eBooks
- Videos
- Graphics and digital art
- Mobile applications