Embracing technology is the only way to stay relevant in the market and flourish. A digital transformation is no longer an option in most industries, and healthcare is not immune to this digital transformation. The potential benefits of a digital transformation in healthcare could be revolutionized with precision and personalized medicine, on-demand access to advanced telehealth, and streamlined clinical operations within reach. However, there are unique challenges that the healthcare industry – especially, telemedicine software development companies – must address to harness the full potential of a digital transformation.
These challenges have resulted in the healthcare industry lagging behind other industries in the adoption of technology. In fact, according to the State of Digital Transformation report, 80.8% of the respondents are geared up to accelerate technology spending in the healthcare domain.
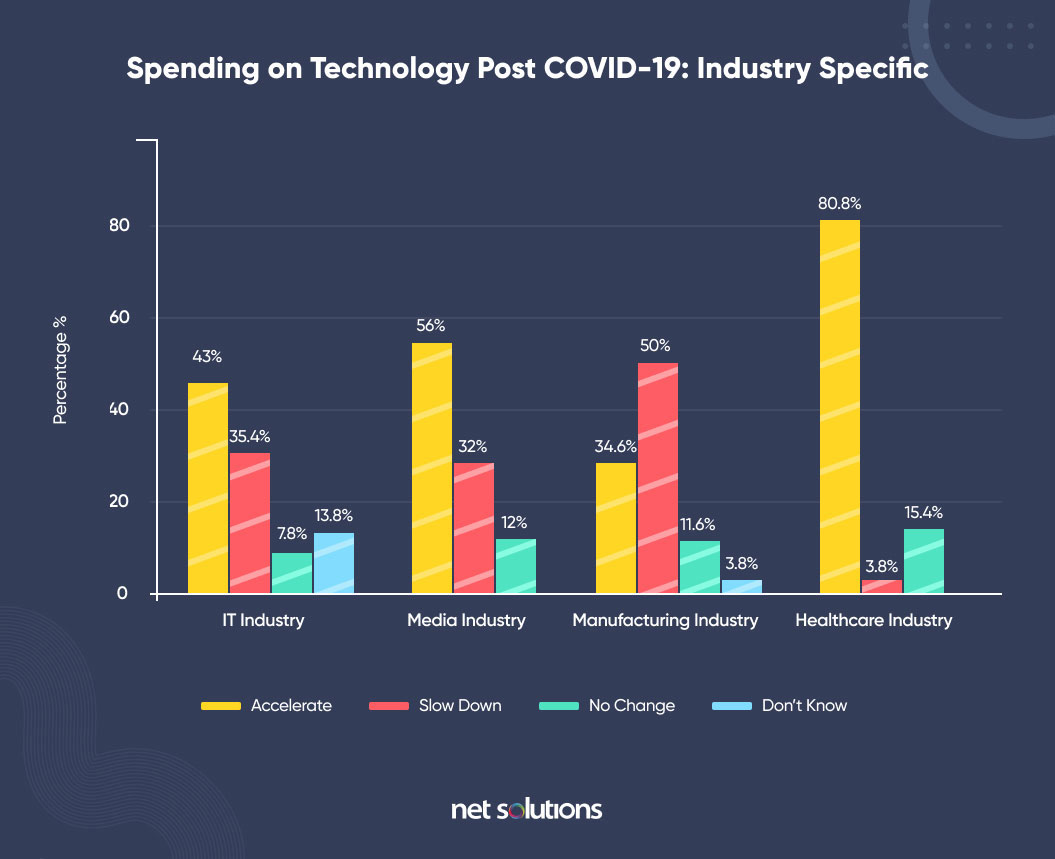
This, in turn, implies that a significant portion of the healthcare industry is still behind when it comes to leveraging the full power of technology.
This article examines the impediments hindering digital disruption in the healthcare industry as well as strategies to overcome these hurdles in a way that will lead to significant change.

We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.
What are the Benefits of a Digital Transformation in the Healthcare Field?
Benefits of digital transformation in healthcare include:
- Automatic management of patient and staff-related data
- Staying competitive in the healthcare sector
- Improved communication channels for better interactions between patients, healthcare providers, and other ecosystem partners
- Facilitation and advancement of remote care options to allow for business continuity when coming to the office is difficult and on-demand service options for patients
- Quick diagnoses and faster treatment leading to high levels of patient satisfaction and retention concerning the patient data
- Reduced risk of human errors and improved overall patient care
- Development of big data strategies to enable prognostic and diagnostic claims in a personalized manner
Specific technological developments might include:
- Telehealth advancements include the integration of health data from various sources to inform the physician of health conditions better (e.g., Fitbit, body composition scales, virtual reality tools, et cetera
- User-friendly platforms that allow patients and centers to seamlessly transfer data between providers and schedule appointments
- Improved speed in clinical decision making and risk assessments (e.g., quickly sorting MRI images so the physician sees the highest risk patients first)
- Precision and personalized medicine
Healthcare Industry: Challenges to Digital Transformation
- Access to healthcare data is incredibly complicated
- Healthcare data are not consistent across providers or centers
- Privacy concerns regarding patient data
- Security concerns regarding technology
- Budgetary restrictions for development
- The laws are not yet in-place that would address organizational concerns surrounding liability and patient autonomy
Organizational readiness
Healthcare Data: Access, Consistency, and Privacy
Many of the potential benefits listed above require data to be accessible and interoperable across centers. Although many centers have adopted systems to keep electronic health records, the accessibility and interoperability of these records has a long way to go before a digital health transformation can occur.
According to the department of Health and Human Services (HHS), “Without the capability to access multiple records across a population of patients, health care providers and payers will not benefit from the value of using modern computing solutions—such as machine learning and artificial intelligence—to inform care decisions and identify trends.”
For patients, this lack of efficient and electronic access to their own data in one, central location hinders their ability to transfer information between providers and shop for care within their insurance networks or at lower prices.
For providers, a lack of efficient, electronic access to their patients records means limiting the information available when treating the patient. This is especially true for longitudinal data that has been stored across many centers and IT systems. Further, secure systems are needed to transfer patient data to protect privacy.
This can limit the physician’s availability to real-time, 24/7 data such as metrics collected from a smartwatch to after-the-fact reporting by the patient. Transferring this type of data remotely would also advance the physician’s ability to offer remote, telehealth service.
For researchers, a lack of access to data that is interoperable across centers means limiting their ability to leverage the power of modern computing such as artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML). Aggregating datasets suitable for the application of AI/ML is the key for developing technologies able to assist with clinical decision making through prognostic, diagnostic, and optimized treatment strategy predictions. Ideally, these AI/ML technologies should give us the ability to learn from all past patients rather than the very limited scope of one provider or center, however, the interoperability across centers is further complicated by a lack of standardization across centers when it comes to clinical decision making which leads to inconsistencies in the type and amount of data available.
Potential Solutions:
Fully Adopting Blockchain in Healthcare
According to Precision and Strategic Intelligence, the market for healthcare-related blockchain applications will surpass $890 million by 2023.
Blockchain, the digital transaction technology characterized by a decentralized network of computers and known for its role in the financial world, could provide a solution to the data accessibility issues hindering healthcare’s digital transformation.
In healthcare, blockchain could serve as an efficient way to:
- identify inaccuracies or repeats in patient data
- prevent security breaches that leak private information
- allow patients to access and share their health records on a distributed ledger
- empower researchers to access and aggregate datasets suitable for AI/ML whether by directly sharing data or by sharing model parameters on the ledger and continually updating
Medicalchain is an example of an ongoing effort to implement blockchain as a solution for fragmented medical records.
Consortium Efforts to Standardize Data Collection and Increase Data Accessibility
Transforming Research and Clinical Knowledge in Traumatic Brain Injury (TRACK-TBI) is a large-scale effort involving 18 hospital systems in the US that is collecting detailed clinical data for thousands of brain injured patients. This effort standardizes the data sources and how they are recorded across centers. TRACK-TBI is also making the dataset publicly accessible for analysis by researchers and domain experts.
For other disorders and diseases, similar efforts are generating large, publicly accessible datasets. However, the siloed nature of these efforts may lead to concerns regarding inefficiency in terms of time and budget. Adopting ways to address the fragmented nature of health records such as blockchain technology may ease the strain that results from the current, brute force nature of these consortium studies.
In healthcare, consortium efforts could serve as a way to:
- Standardize data collection methods
- Aggregate and curate datasets suitable for AI/ML
- Increase accessibility of data
Technology Development: Best Practices and Trends
Once concerns regarding data accessibility, privacy, and security have been addressed, the healthcare industry needs to develop a digital strategy to accelerate its transformation and prepare staff for the incoming changes.
Digital transformation in healthcare goes beyond buying the latest IT system. Implementing digital transformation in the healthcare market will require massive investments in technology and hiring digitally savvy minds. This would require more funding and thoughtful strategizing for healthcare-driven businesses.
The following are a few ways that can set a smooth path toward creating influential healthcare technologies:
Agile Development
Agile software development introduces speed and flexibility to the process. Moreover, its iterative and incremental model enables the accommodation of newer additions and changes even in the later development stages.
When creating software that will fill the gap between healthcare and digital transformation, considering Agile Development or partnering with an outsourcing team that implements this process is recommended.
The right Agile Development team can also assist with accommodating big data analytics services in the product being developed. Big data analytics could assist the healthcare sector with:
- Predicting when there will be surges in patient demands and adjusting the staff availability accordingly
- Flagging inconsistencies or incompatibilities in patient records such as prescriptions that may be risky for a particular patient given their health history
- Facilitating the development of AI/ML-enabled technologies able to guide clinical decision making
Offer Digital Services to the Consumers
Today, digitization has successfully entered various industries like travel, banking, and entertainment. The impact of these digital transformations has integrated into consumers’ lives to the extent that they expect the same level of digital service delivery in healthcare systems.
A survey from McKinsey reveals that consumers are willing to use digital technology in healthcare, and they expect an omnichannel experience across all the touchpoints.
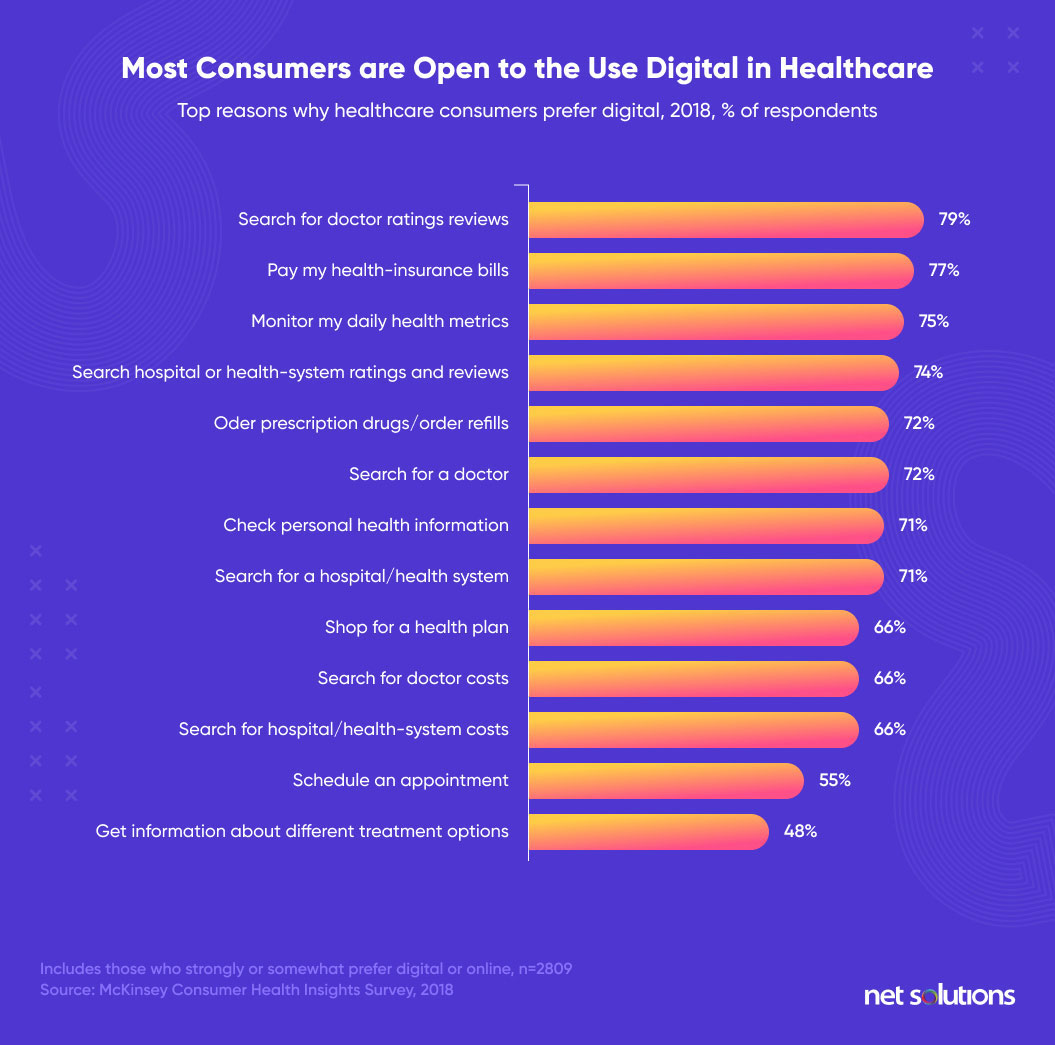
Leaders from the healthcare industry should leverage these unique digital identities to deliver more personalized digital services and build a trustworthy relationship with consumers.
Latest Trends around Digital Transformation in Healthcare
The latest healthcare technology trends 2020 include:
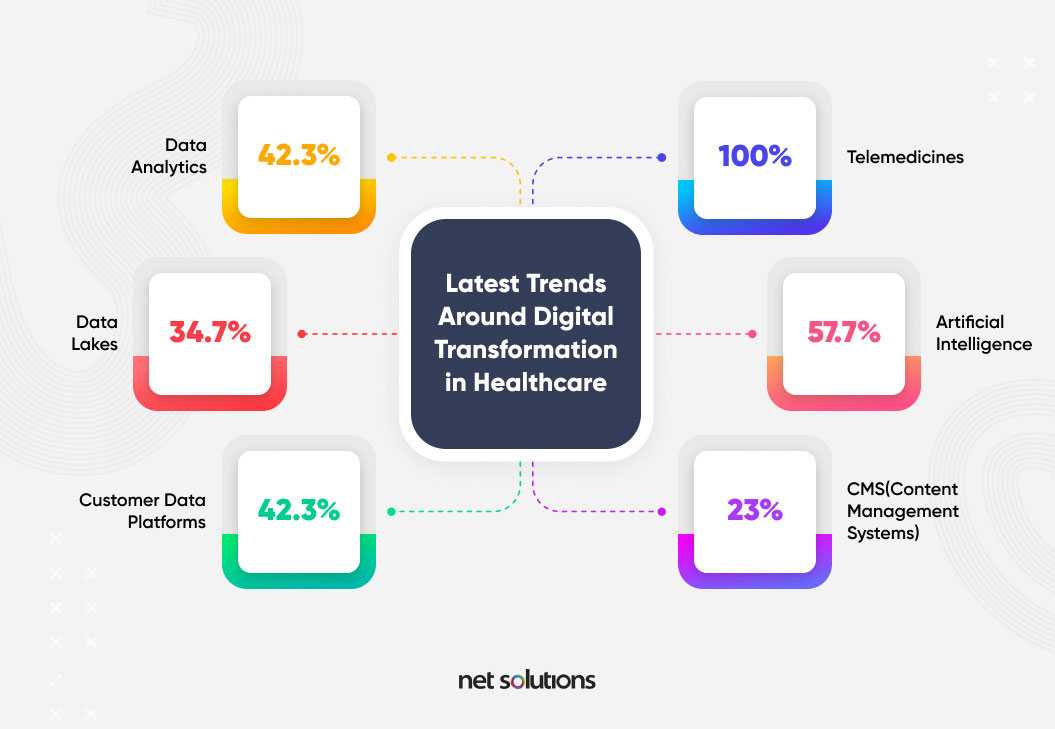
Although there are many benefits of digital transformation in healthcare, there is still a considerable gap in expectation between how patients want healthcare to be delivered and how it is being delivered. No doubt, consumers want their demands met; however, they do not want their privacy at the mercy of healthcare organizations.
Governance: Incentives, Liability, and Security
Incentives
Governments across the globe need to invest and promote the healthcare industry’s digital transformation. Many have been working towards the cause. For instance, according to a McKinsey report, the US government has introduced incentives for healthcare centers to use electronic health systems to maintain records.
However, there is room for improvement. In addition to providing incentives for the adoption of digital systems and funding mechanisms for the development of disruptive healthcare technologies, legislative bodies should reassess laws and regulations that currently limit the accessibility and interoperability of healthcare data.
Autonomy and Liability
It is not far-fetched to believe that AI-enabled devices may soon offer predictions regarding treatment strategies. When a healthcare setup chooses to adopt these technologies, there must be clear legislation that protects patient privacy and defines medical liability in a healthcare system. That is, the patient must be informed of what the technology is and what role it is playing in their care.
Additionally, in a case where the predictive system makes a mistake and a patient suffers, understanding where liability falls (e.g., physician, organization that implemented the technology, developers of the technology, etc) is vital.
Security
Developers of this technology must also incorporate the best practices for security. This is especially relevant for AI/ML-enabled devices that constantly update with new patient data. While constant updating is important for generalizability and addressing data drift concerns, model performance could be impacted by a data breach or data alteration. If model performance is affected and there is a span of time before the healthcare organization knows of the security concern, patients could suffer.
Organizational Readiness: Mindset, Culture, and Trust
The healthcare industry operates in a particular fashion and it would be unreasonable to expect an immediate and successful implementation of technology modernization in the sector. The resistance to change (both mindset and culturally) requires time and effort.
According to the State of Digital Transformation report, 23% of the healthcare sector respondents believe that lack of organizational readiness is the reason for lagging transformation in the healthcare domain.
There are a few ways to effectively address this resistance and accelerate the digital transformation in healthcare.
Address Skill-Gaps
Not everyone is digitally savvy. If a healthcare system aims to adopt technological solutions to address the concerns described above, training is required.
This training may be both taxing and expensive. To address this challenge, there needs to be a digital strategy implemented at the organizational level.
Mindset and Trust
Patient privacy and data security are at the center of technology improvements in healthcare; One leak too many (of PII or other sensitive information) will foster mistrust among stakeholders and impede progress.
There is a popular opinion that AI-enabled devices or droids will replace humans. This concern is accentuated in the healthcare space where data-trained systems cannot accurately capture the physician-patient interaction that influences healthcare treatment.
To mitigate these concerns and shift the mindset to a level that is supportive of digital transformation, the technology/healthcare fraternity needs to run awareness campaigns & highlight the positives a tech revolution can bring to healthcare.
Technology as an Assistant to Clinical Duties and Decision Making
Moxi, a robot with social intelligence, is being tested as an efficient way to handle duties such as grabbing and delivering items from the supply room. This initiative aims to reduce staff fatigue and turnover.
AI allows radiologists to accurately spot and diagnose diseases such as cancer from images even when the pathology is not yet visible to the human eye thus facilitating earlier detection. This technology can further be leveraged to help sort scans by risk and ensure the doctor reaches the most vulnerable patients first.
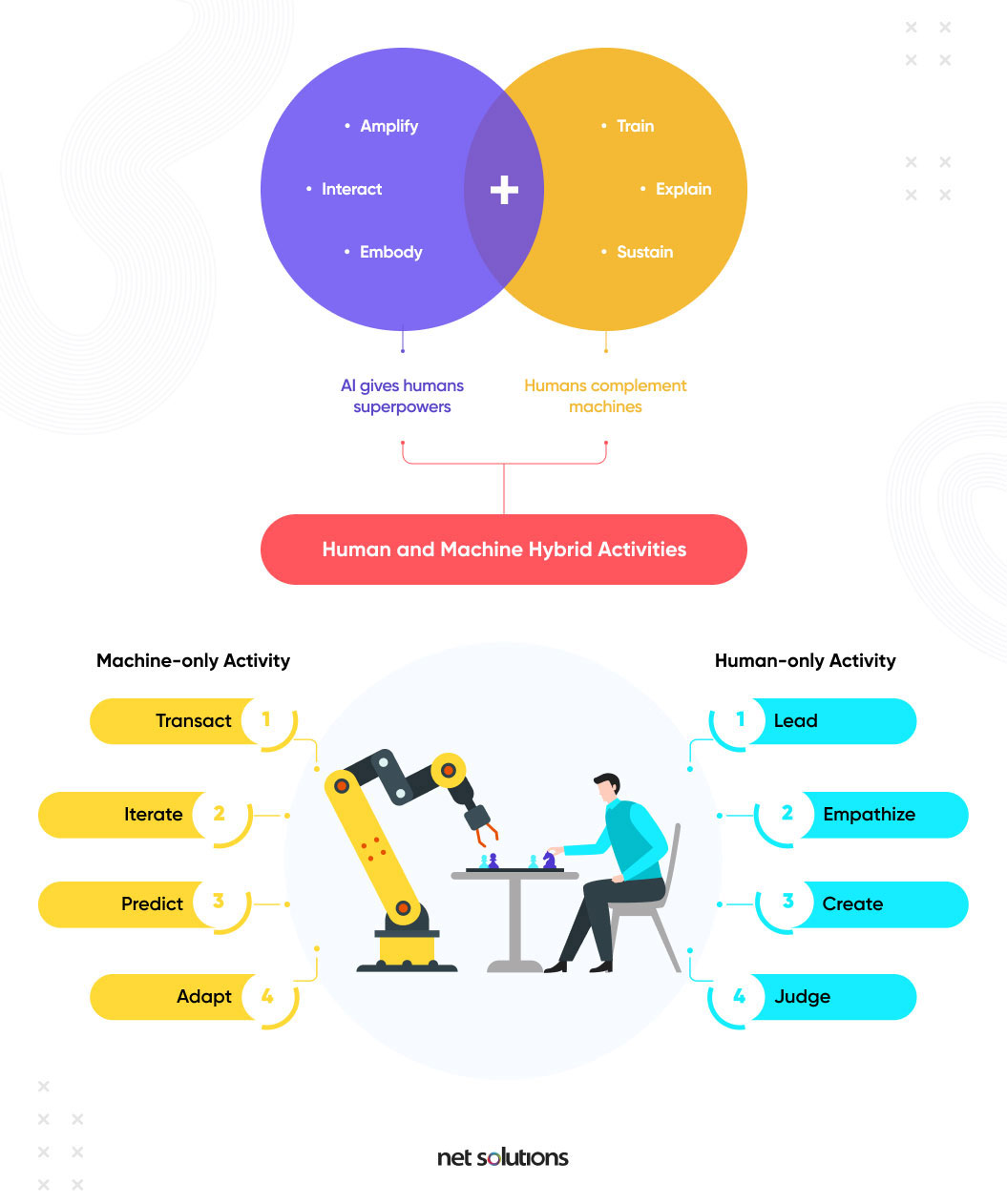
Human + Machine hybrid approaches often lead to better results than either alone further cementing the idea that technology is a powerful assistant in the healthcare field.
A collaborative study by Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC) and Harvard Medical School showcased that Artificial Intelligence is not just about Machines vs Humans.
To identify metastatic breast cancer, a deep learning algorithm was trained to interpret pathology images. The algorithm reached an accuracy of 92.5%, whereas pathologists reached an accuracy of 97%. However, when used in combination, the detection accuracy reached approximately 100% (99.5%).
Is Digital Health the Future of Healthcare?
Healthcare is learning, evolving, and growing when it comes to adopting the digital transformation that many other industries have faced. To adapt and focus on a customer-centric vision that leads to the best possible patient outcomes, the healthcare industry understands that technology must become a crucial part of its operations.
While investments in social, cloud, and analytics are progressing and adding value, the healthcare industry leaders should look towards more sophisticated ways to deliver technological solutions to the issues that are currently limiting advancement.
While many of these suggestions may seem easier said than done for organizations that are still dependent upon decades-old, legacy systems, strategizing today for the post-digital world is essential to promote and accelerate this incredibly important digital transformation.



