Adobe Commerce (previously Magento) is a full-featured eCommerce platform to help you build and scale an online store, but pricing is variable based upon which version of Adobe Commerce you use and the size of your business. The four versions we will feature are:
- Adobe Commerce Pro (Adobe Commerce on Cloud)
- Adobe Commerce Managed Services
- Adobe Commerce on-Premise
- Magento Open Source
In this guide, you will learn everything you need to know to estimate how much it will cost you to operate a fully functional Adobe Commerce or Magento Open Source website.
How Does Adobe Commerce (Magento) Pricing Work?
Adobe Commerce (previously Magento) operates four versions of its eCommerce software, a platform that delivers rich out-of-the-box capabilities paired with a wide range of third-party integrations to extend the platform and its capabilities.
Magento Open Source is free and open-source, designed for early entrepreneurs or developers, but suitable for enterprises of all sizes to self-manage an online store. Adobe Commerce, built on Magento, adds comprehensive new functionality to appeal to enterprise customers and includes two all-in-one packages to help enterprises build scalable omnichannel customer experiences for B2B and B2C. Learn more about Magento Open Source vs Adobe Commerce.
Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) is defined as the total USD value of all transactions processed through any customer sites during a contract year, excluding shipping, handling, customs, taxes, or financing charges.
Average Order Value (AOV) is defined as the GMV divided by the number of transactions during the contract year.
A store view refers to each store available to customers. Additional store views can support different languages or for other purposes.
What Factors Affect the Cost of an Adobe Commerce Store?
In general, there are shared factors between Magento Open Source and Adobe Commerce (previously Magento Commerce) when it comes to determining the final price. Let’s examine some of the general costs, which we’ll provide a full breakdown of when speaking later about each version.
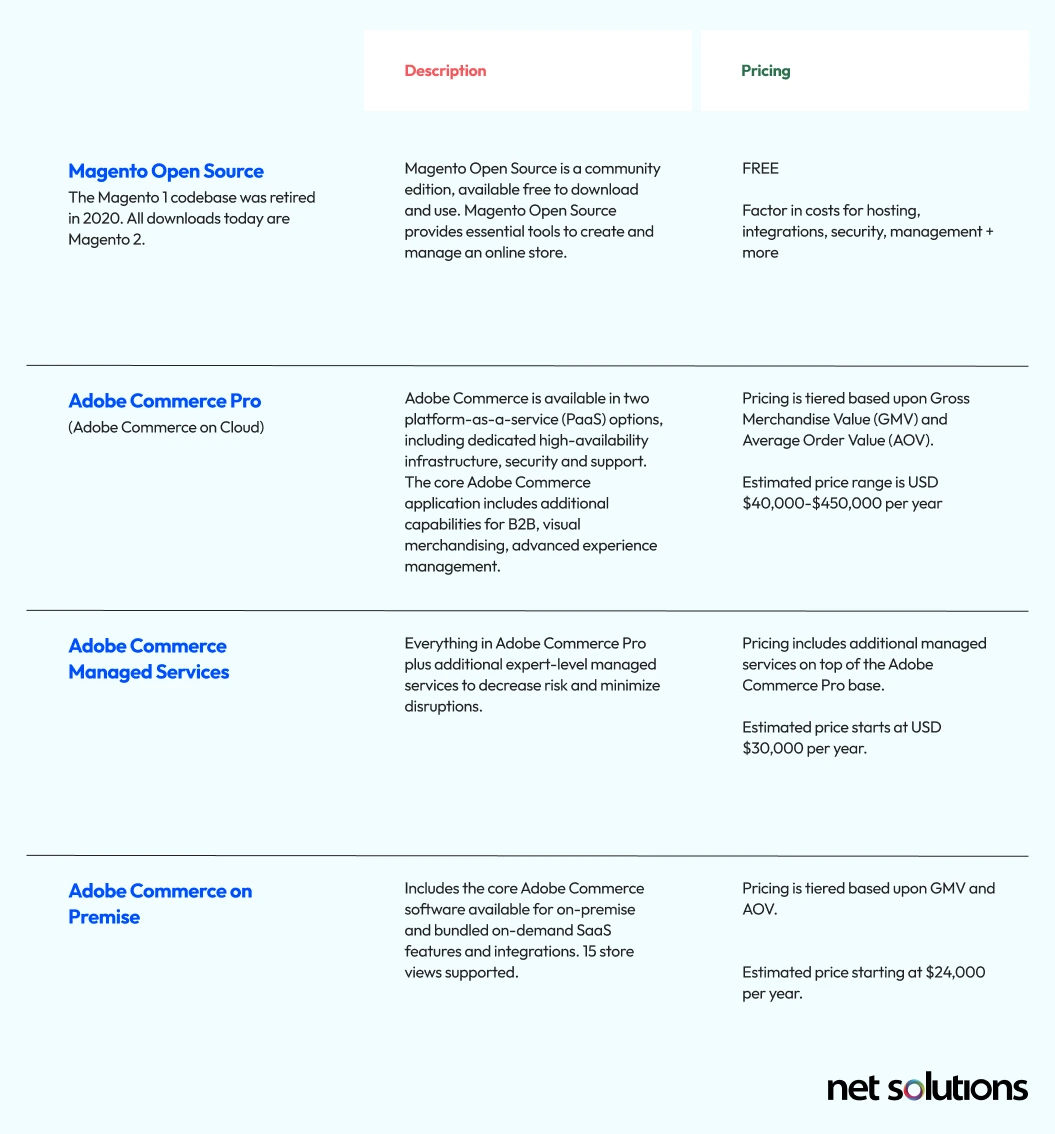
1. Adobe Commerce license fees
Adobe Commerce is a licensed software package and bundled services and capabilities. The cost of the license is determined based on GMV and AOV.
2. Adobe Commerce Hosting
Adobe Commerce Cloud consists of two products: Adobe Commerce Pro and Adobe Commerce Managed Services. Both of these are hosted platform-as-a-service (PaaS) products.
- Adobe Commerce Pro includes dedicated, high-availability infrastructure that includes infrastructure security and a 99.9% SLA for infrastructure.
- Adobe Commerce Managed Services includes 99.9% application level SLA, a designated cloud infrastructure customer success engineer and 30-minute SLT for P1.
Adobe Commerce on-Premise is self-hosted and includes bundled SaaS services, so is ideally deployed to the cloud (e.g. Amazon Web Services / AWS or Microsoft Azure). The hosting environment must include Linux OS, an Apache web server with PHP, MySQL and a search engine. Web hosting fees are directly tied to traffic and are variable based on the quality of the host (which impacts uptime).
3. Domain name
All Adobe Commerce websites require a custom domain name. Premium names that have been purchased already may come with a hefty price tag.
4. Adobe Commerce themes
You have the option to deploy Adobe Commerce with the default theme (included), or one found in the marketplace. These themes may be customized with minimal design + development time.
For a custom theme, factor in considerable web design and development (see next).
5. Web design
You have the option to create a custom web design for your Adobe Commerce store to better align with your branding. Custom-designed websites vary based on scope.
You can expect large enterprise websites to have more sophisticated user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) work. Further, web design costs may increase based on any custom channel variability in a headless deployment (see next).
6. Development
Adobe Commerce is a full-featured platform featuring advanced capabilities in personalization and search. As a result, Adobe Commerce eliminates the need for some third-party services, as well as the development time to use them. Furthermore, as an all-in-one solution, Adobe Commerce (cloud) does not require development time to install, secure or maintain the infrastructure.
However, there is always some development time to customize third-party services, integrate with internal systems, implement custom designs and more. The number of customizations significantly impacts the final cost. Development time may include an in-house development team or external development agency.
Adobe Commerce can be deployed in different architectures, which impact the overall development time and cost:
- As a traditional coupled storefront
- As a hybrid or decoupled solution with a progressive web application (PWA) using PWA Studio (with fee)
- As a fully headless solution, which would require custom front-end development (+ potential license fees) for each supported channel.
Adobe Commerce on-Premise would require additional development costs and time related to infrastructure, security, maintenance and technical support for an eCommerce site.
7. SSL Certificate
All websites need an SSL (secure sockets level) certificate to prove the site’s identity and that it has an encrypted connection. Adobe provides one certificate for both the production and staging environments of Adobe Commerce on cloud plans, with the option to use your own SSL certificate. For Adobe Commerce on-Premise, SSL certificates are an added cost, based on various levels.
8. Security
Adobe Commerce (cloud) operates on a shared security model, with merchants obligated to follow security best practices. However, Adobe applies hundreds of security processes and controls to protect its software. Further, Adobe Commerce Managed Services comes with additional application monitoring assistance to help reduce risk.
For Adobe Commerce on-Premise, depending on whether you are self-hosting on your own server or relying on some level of security with a cloud service provider, you may incur additional costs related to security such as security tool licenses for things like firewalls and antivirus software, vulnerability scans, security patches, PCI DSS compliance, and more.
Note, headless implementations of Adobe Commerce on Cloud would require hosting the front-end outside of Adobe, which has security implications similar to the above.
9. Content Delivery Network (CDN)
A CDN is a network of global servers designed to help deliver content at greater speed and connectivity. Adobe Commerce (cloud) uses Fastly to optimize and secure content delivery. Adobe Commerce on-Premise users would need to contract with Fastly or another CDN for these services.
10. Extensions
The Adobe Commerce marketplace includes 2,840 extensions for Adobe Commerce (cloud) and 3,101 extensions for Adobe Commerce (on-premises) across a wide variety of categories, from payments & security to marketing, customer support and shipping & fulfillment. The number of extensions you need depends on your business and goals. Integrations to internal systems (e.g. SAP, Salelsforce, Sage ERP) have the highest price tags.
11. Payment fees
Adobe Commerce includes built-in payment methods that do not require third-party services, including zero subtotal checkout, cash on delivery, bank transfer, check / money order, purchase order, and payment on account (B2B only).
For additional payment methods, payment gateways offer services that support credit and debit card payments, e.g. Stripe, Amazon Pay, PayPal and Square. These payment gateways may operate with a monthly fee or a per transaction fee (% + fee). These can vary by volume.
12. SEO & digital promotion
While large enterprises likely have teams dedicated to sales and marketing, it is very common to also contract with specialized copywriters, PR & content agencies, and SEO experts to optimize on-site content for growth. Factor in the cost of internal staff and external support, consultant hourly rates vary.
Now let’s examine these cost factors for Magento Open Source.
What Factors Affect the Cost of a Magento Open Source Store?
Magento pricing is influenced by many factors, including hosting and website development:
1. License fees
Magento Open Source has no license fee, but overall Magento costs will be influenced by the below.
2. Magento Hosting Cost
Magento Open Source is self-hosted, which you can do on your own server or with cloud hosting. Hosting fees are directly tied to traffic and are variable based on the quality of the host (which impacts uptime). If you self-host on your own server, build in a large budget for maintenance and eventual replacement costs.
As enterprises scale, self-hosting becomes more complicated, costly and introduces greater security and uptime risks, often prompting the decision to switch to Adobe Commerce.
3. Domain name
All Magento Open Source websites require a custom domain name at an annual fee. Premium names may also have a high initial purchase cost.
4. Magento Open Source themes
Magento Open Source has a default theme for a traditional coupled storefront. Any additional Magento themes can be purchased in third-party marketplaces or created custom.
5. Development
Magento Open Source includes all the basic features for an online business, but lacks the advanced features or bundled services of Adobe Commerce. As an open-source platform, Magento Open Source is infinitely customizable, requiring significant web development to set up infrastructure, set up architecture (traditional, hybrid or headless), integrate with systems, add capabilities, extend with third-party systems, and maintain. In terms of Magento development costs, very simple, non-customized start-up stores will have the lowest amount of development time.
6. Web design
The cost to create a custom Magento website can vary. When not using standard templates, expect the cost to reflect the size and complexity of your eCommerce store.
7. SSL Certificate
The SSL certificate verifies your site’s identity and enables an encrypted connection, with different SSL certificate types and costs based on levels of validation, encryption strength and features.
8. Security
Although some security is built into the core platform, Magento Open Source is a self-hosted platform, meaning a greater burden of security falls on the store owner. Security cost depends on where you host and the number of precautions you take to protect your site.
9. Content Delivery Network (CDN)
If you do not use a CDN, your content is served by your main hosting provider, which can be subject to downtime. If you choose to use a CDN, this is an extra cost.
10. Extensions
There are over 4,000 Magento extensions in the Adobe Marketplace that work with Magento Open Source. Third-party extensions are available at variable prices.
11. Payment fees
Magento Open Source offers the same basic payment options of zero subtotal checkout, cash on delivery, bank transfer, check / money order, and purchase order, but all other payment gateways would be subject to monthly fees and/or transaction fees (% + fee).
12. SEO & digital promotion
Small start-up online stores will likely run most sales & marketing efforts internally, while stores with goals of scalability will likely contract with specialized copywriters, PR & content agencies, and SEO optimization experts to optimize on-site content for growth.
Given the variability in prices, let’s break down all these variables with actual estimates for the different versions of Adobe Commerce and Magento Open Source to make an eCommerce website.
Detailed Breakdown of Adobe Commerce and Magento Open Source Pricing
In order to facilitate comparison between the different versions of Adobe Commerce, we’ve broken down the estimated cost of each of the points above to help you estimate what your eCommerce website cost will be. Where the cost is zero (the capability is built into the Adobe Commerce platform), we will indicate this with a “-” symbol. All prices are in USD.
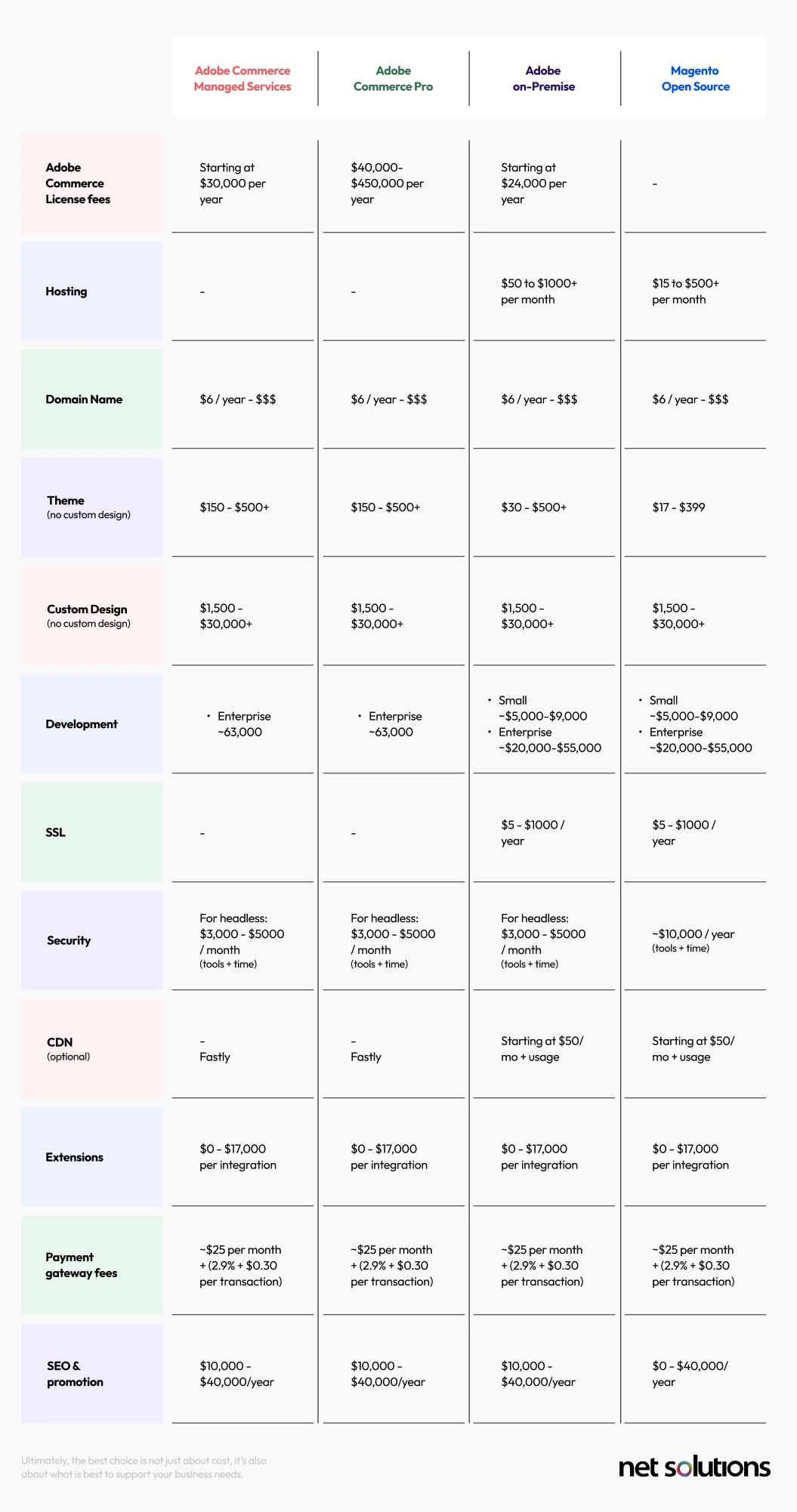
Ultimately, the best choice is not just about cost, it’s also about what is best to support your business needs.
How Does Adobe Commerce Compare With Other Platforms in Terms of Pricing?
Here’s a look at how Adobe Commerce compares with other platforms, in terms of total cost. Please note, each platform may have additional limits that push you into higher price tiers or require add-ons, which could be related to bandwidth, number of users, number of locales, API calls, environments or more.
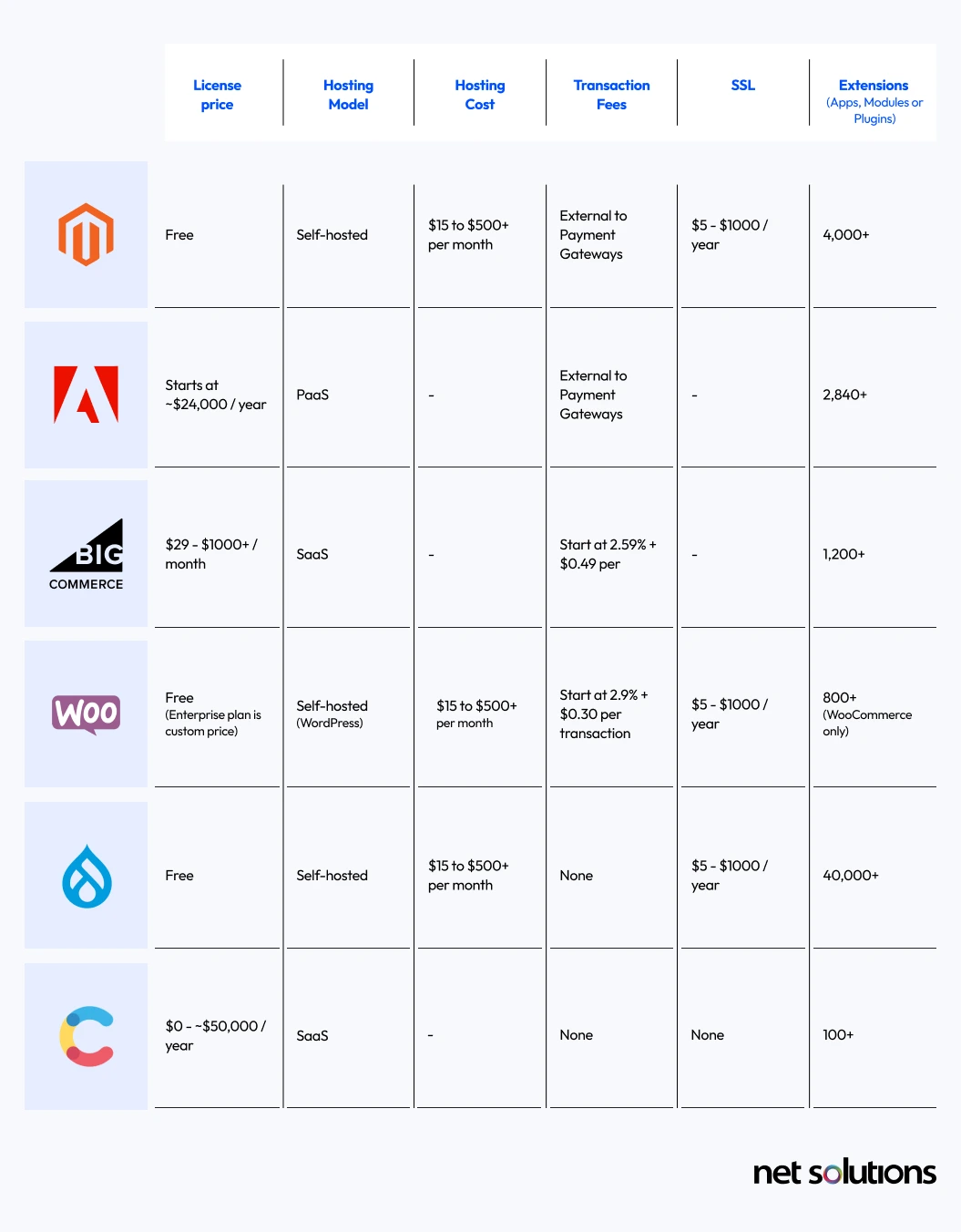
There are many other eCommerce solutions that you can also choose, from Shopify to Sanity and more. Look at our posts for the top enterprise eCommerce platforms, top open-source B2B platforms, and top B2B eCommerce platforms overall.
The Bottom Line
Magento Open Source is an ideal solution for developers and small stores looking to explore creating an eCommerce store for the first time, while Adobe Commerce is designed to take you to the next level, as an enterprise solution with full-featured capabilities across B2C and B2B to offer personalized omnichannel shopping experiences.
Net Solutions is an award-winning Magento Development Services company, offering project-based services to help you start your store or migrate from Magento Open Source to Adobe Commerce. Net Solutions also offers a more affordable (vs Adobe Commerce) Managed Services solution.
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, all versions of Adobe Commerce are licensed, starting at an estimated $24,000 per year. Magento Open Source is available for free (no license cost).
Adobe Commerce prices are based on Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) and Average Order Value (AOV), which will scale to new price tiers. There could be additional costs related to store views. Furthermore, while not ‘hidden’, eCommerce business owners should always estimate sufficient budget for development, design, marketing and costs related to integrations and extensions.
Adobe Commerce (cloud) provides one SSL certificate to each license for production and staging.



