The product owner creates a product backlog, i.e., a list of user stories and bug fixtures that need to be worked on in the upcoming sprint cycles. This helps maintain a product roadmap that needs to be followed in the upcoming sprints. The items at the top are more descriptive and clear on intent compared to the less descriptive ones at the bottom. Further in the process, a backlog grooming session is conducted to reevaluate priorities, clean, and organize the product backlog for improving sprint planning productivity.
Though not an official Agile practice, backlog grooming is a widespread practice helping the product teams stay productive.
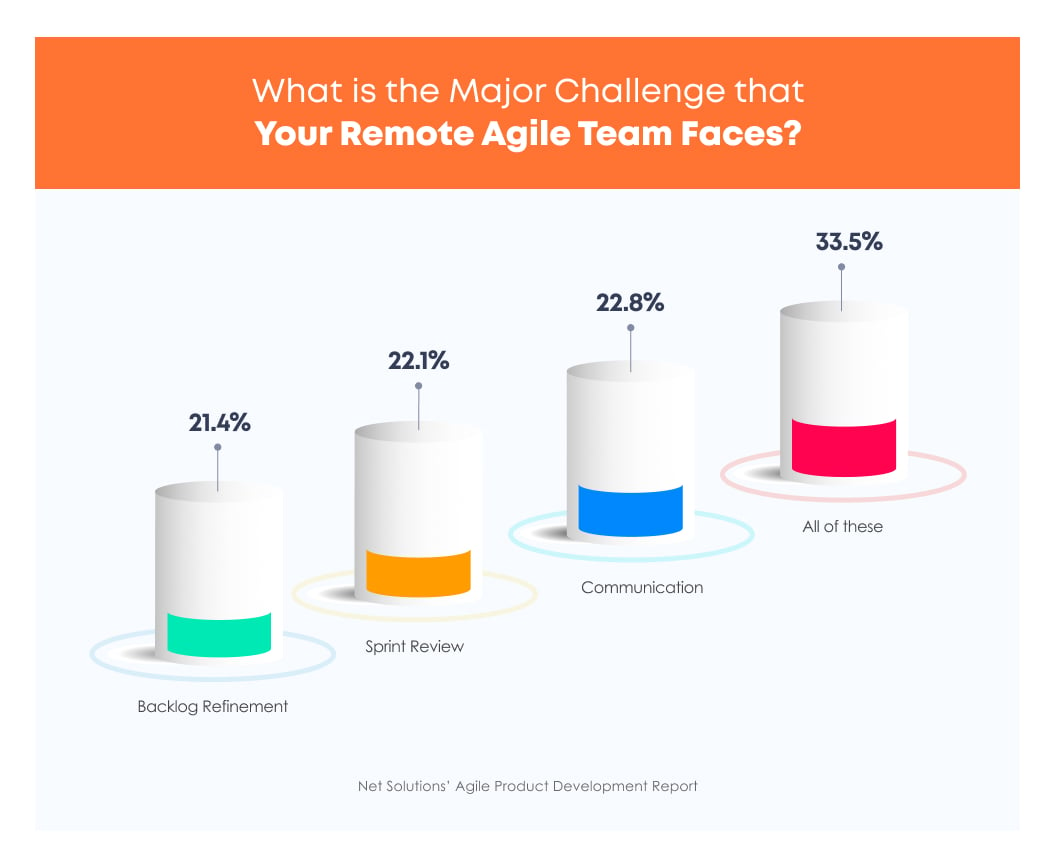
However, understanding how to conduct a backlog grooming session and how to conduct backlog management has been an ongoing challenge.
According to Net Solutions’ Agile Product Development report, 21.4% of the product development teams face challenges with backlog refinement.
Here’s a guide to help you understand and get the most of these backlog grooming sessions.

We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.
What is Backlog Grooming?
Other names: Story Time, Backlog Refinement
Backlog grooming is a recurring meetup of product managers, product owners, and the product development team to prioritize, refine, and discuss the top items on the product backlog before the sprint planning.
A nicely groomed backlog is the one that prioritizes work based on the most valuable tasks.
Backlog grooming is often considered a practice that adds granularity to the product backlog and helps create an actionable list of Agile user stories ready for sprint planning.
A good rule of thumb seems to be that about 10 percent of the effort in each sprint should be spent refining the backlog in preparation for future sprints. — Mike Cohn
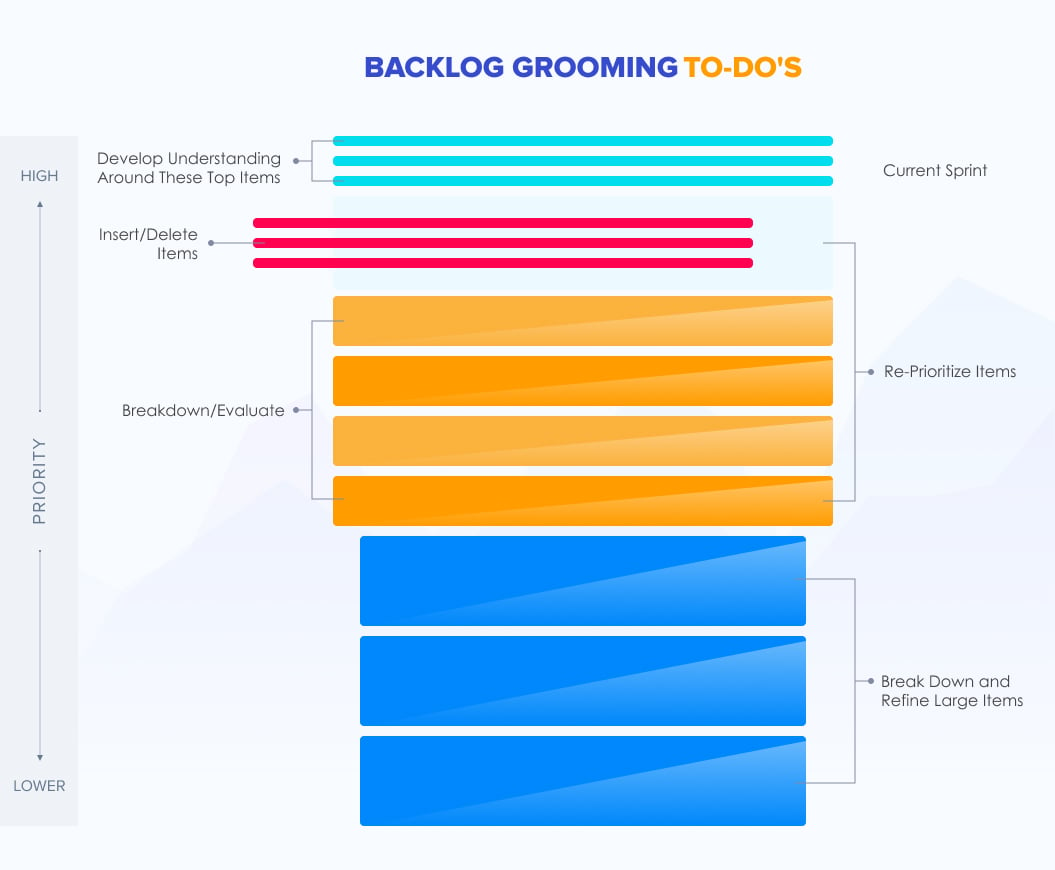
The to-dos of the backlog grooming process include:
- Eliminating user stories that don’t add value
- Reevaluating and prioritizing user stories
- Discussion around the top items in the product backlog for its fair understanding
- Breaking down large user stories to create smaller and manageable items
To understand backlog grooming, here is an overview of some related concepts.
What is a Product Backlog?
A product backlog is a prioritized central repository of all the to-dos for the product development team. These to-dos include — initially prioritized features, new feature requests, bug-fixtures to the developed features, and other activities.
In a product backlog, the high urgency, smaller and well-defined tasks are placed at the top, while the low priority, larger, and vaguely defined tasks are placed somewhere down the list.
The development revisits the product backlog before the next sprint cycle starts by conducting a backlog grooming session to reprioritize the backlog based on new learnings and ongoing product discovery.
The purpose of the backlog can be reduced to three simple goals:
- Develop a common ground to align stakeholders and teams with implementing the most valuable user stories.
- Provides flexibility to adapt and modify according to new needs and realities.
- Work on improving the accuracy of product release forecasts by creating a common denominator across many teams collaborating on one product.

What is Sprint Planning?
A product owner leads a sprint planning to help the development team develop a thorough understanding of the prioritized user stories that they are supposed to work on over the next sprint cycle.
These planning sessions are attended by the product owner, the scrum master, and the development team. Sprint planning helps the development team gain perspective into the:
- Sprint Goal: A short description of what the team will try to achieve in the upcoming sprint cycle. This can be done with the help of small cards (post-its) that describe the intent of the user story.
- Sprint Backlog: A list of items from the product backlog that the development teams commit to achieving in the discussed sprint cycle and the supporting tasks that will help deliver the prioritized deliverables.
Although entirely different, sometimes organizations confuse between sprint planning and backlog grooming. Here’s a table that highlights the difference between backlog grooming and sprint planning.
| Definition | Is an activity that helps revisit and reassess the product backlog items and reprioritize them based on new learnings, feedback, and ongoing product discovery | Sprint planning is an activity that helps the development team understand the sprint goal and create a sprint backlog, i.e., the items they commit to deliver in the discussed sprint |
| Attended By | Product manager, product owner, the development team | Product Owner, Scrum Master, the development team |
| Objective | To clean, refine, and rearrange the product backlog | To understand the objective of the user story and assign tasks for the upcoming sprint |
Thus, here’s the order of events that occur for improving productivity:
- Create a product backlog — a holistic list of tasks that need to be completed over the sprint cycles
- Conduct backlog grooming — prioritize tasks before the beginning of the sprint cycle based on urgency and value it offers
- Conduct sprint planning — describe the intent of the prioritized user stories, assign tasks based on how much the team commits to deliver
Backlog Grooming Benefits
Why should you focus on conducting backlog grooming sessions?
- Helps maintain a clean and organized product backlog
- Prioritizes user stories based on value and urgency
- Helps improve sprint planning productivity
- Assures that everyone on the team is on the same page
- Keeps the team informed regarding the new changes
- Decreases the time spent on sprint planning
Backlog Grooming Best Practices
Here are some best practices to follow when conducting backlog grooming sessions:
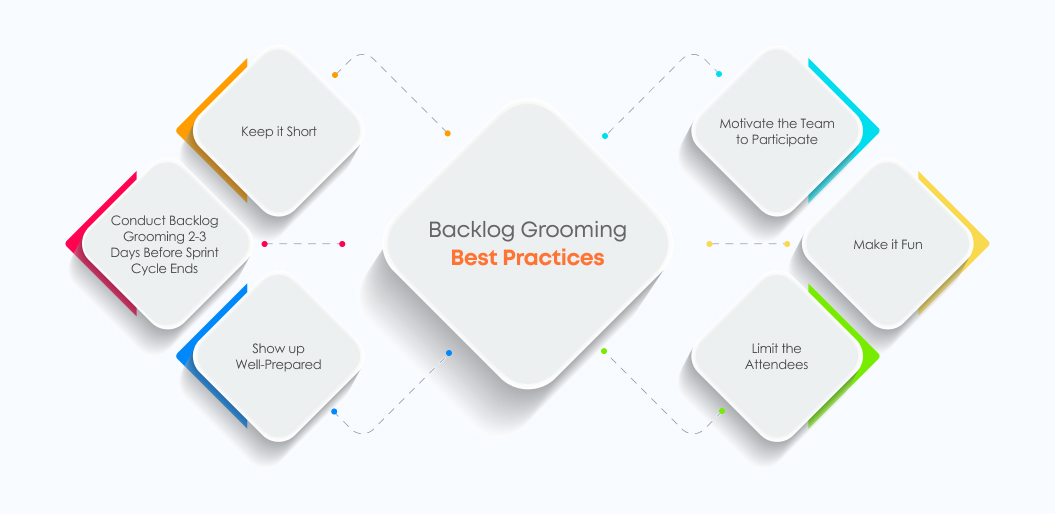
1. Keep it Short
Do not overstretch the backlog grooming sessions and convert them into sprint planning. The objective of the grooming sessions is to identify and eliminate waste, evaluate and prioritize new user stories, and clean and refine the product backlog.
2. Conduct Backlog Grooming 2-3 days Before Sprint Cycle Ends
It is good to conduct backlog grooming sessions two to three days before sprint cycle completion. The reasons to do so include:
- It helps track the team’s progress to see if they would need another sprint cycle to complete what they are already working on
- Prepare the team for the upcoming sprint cycle in advance
- The team has enough time to attend the sprint planning sessions before the next cycle starts
3. Show up Well-Prepared
The product owner needs to be well prepared and needs to have a plan before conducting backlog grooming. A few things need to be in place, such as:
- The product backlog is updated
- Should know the strategic objectives of the prioritized user stories
- Should know upfront what items need to be discussed
- Know team’s progress in advance
- Should be inviting the right people
- Talk to the stakeholders to get their feedback and expectations
4. Motivate the Team to Participate
Good leadership plays a vital role here. The product manager needs to ensure that no one feels left out and unheard.
The concerned individual should consider everyone’s opinion along with ensuring that everyone understands the top-priority items. Also, the product owner should be given time to ask questions about user stories under discussion.
In case the product owner is unusable to answer a particular query, they should be ready with the answers in the upcoming sprint planning meeting.
5. Make it Fun
Backlog grooming doesn’t need to be boring. While you need to stick to its purpose, you can always start by asking how everyone is doing and how everything is around. Starting on a positive note can also lead to more productive backlog grooming sessions.
Also, if someone shows up late for the meeting, do not make them feel bad about it.
6. Limit the Attendees
Unlike other Scrum meetings, I do not think the product backlog refinement meeting requires the participation of the whole team. Mike Cohn
There will always be someone who will be busy working on the sprint deliverables and will have to sit up late or have leftover tasks carried over the next sprint cycle.
It is thus a good idea to excuse those team members from the backlog grooming meetups. What you can do is — post the discussed items and the major takeaway on your communication channel. The takeaways will help them catch up and discuss any queries when they have time.
What is Product Backlog Prioritization
Product Backlog prioritization plays one of the most critical exercises in agile software development. Your backlog needs to be structured, organized, and arranged to favor your team’s most strategically important things to work on.
Effective and Consistent Prioritization of the requirements (user stories) leads to successful project completion.
When the stakeholders or clients, or business gets the most valued functionality at the earliest, we conclude the project being successful.
We require Backlog prioritization to organize the product backlog items (user story/Defects/Spike, etc.) to develop and deploy.
The scrum team further follows this sequence to select product backlog items during sprint planning or backlog grooming.
Why do we Need Prioritization?
We all prioritize our everyday life because we have limited time for every set of items to execute, and that’s why we choose the necessary actions to perform first and followed by lesser important.
Similarly, we prioritize functionality or tasks in software development because few functionalities are more important than others.
An efficient product prioritization process earns support from stakeholders, incites a vision in your team, and reduces the risk of working on something nobody wants.
Factors Influencing Backlog Prioritization?
- Customer Satisfaction
- Business Value
- Complexity
- Risk & Opportunity
- Cost
Scrum Team Members Role During Prioritization?
Scrum Master’s Role
The Scrum Master facilitates planning for the Sprint meeting to help the team develop the Sprint Backlog. They pick items for discussion from the top of the list and create their sprint backlog according to the capacity and complexity of parameters.
Development Team’s Role
The scrum team owns the sprint backlog, and they create their sprint board which consists of the user stories, bugs (if any), and spikes. It is the development team that determines the Sprint Backlog. The scrum team utilizes the sprint planning meeting to discuss the sprint goal and their commitment for the upcoming sprint.
Product Owner’s Role
Managing the product backlog is one of the most critical responsibilities for a Product Owner.
The product owner is responsible for creating and prioritizing the backlog items based on the overall strategy and business objectives. In addition, product Owners plan out the proper and necessary sequencing of project development.
The Product Backlog is a live document requiring continuous updating based on the evolving project requirements throughout the development phase.
Benefits of Backlog Prioritization?
Business Benefits
- Value-based delivery provides an early return on investment
- Enhanced supervision and guidance of dependencies
- Customer or Business satisfaction
- Keep focused on Value-driven development
Scrum Benefits
- Prioritized product backlog contributes to better sprint planning and story selection
- Better visibility to pick stories within current sprint scope, if there is bandwidth
- Helps in effective risk management due to first-hand information on problems during backlog grooming
- Effective Grooming by saving time of selection story
Product Backlog Prioritization Techniques
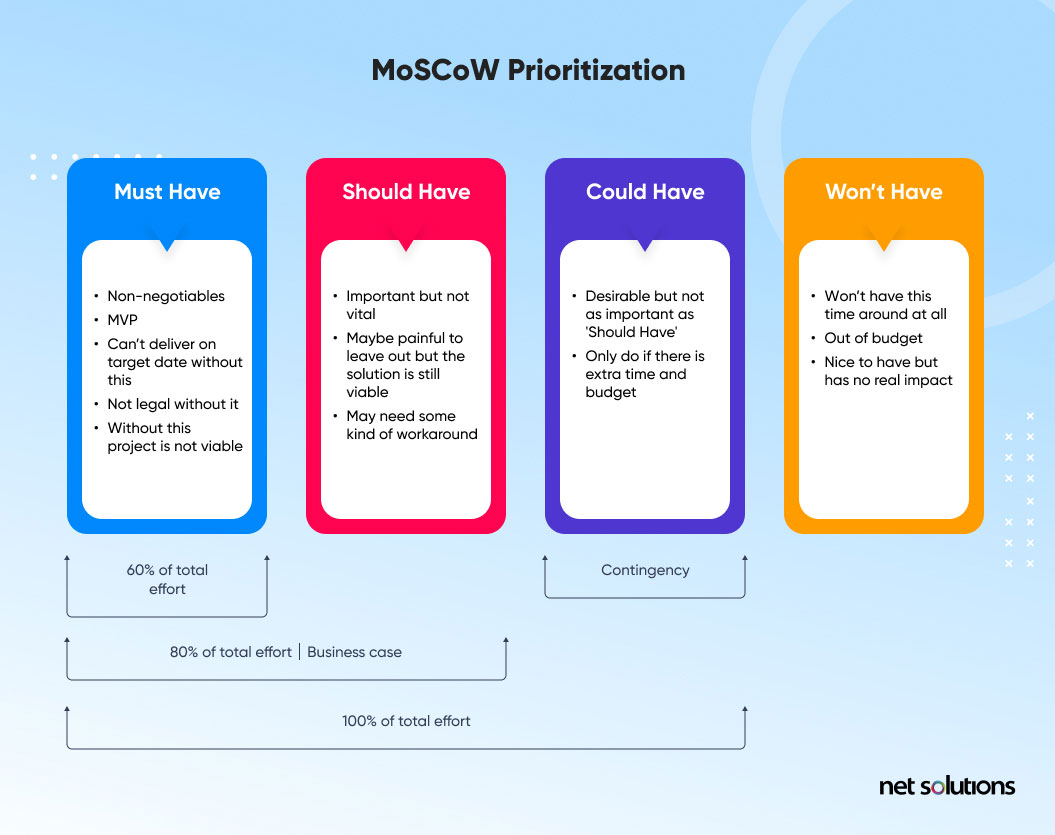
1. MoSCoW Method

MoSCoW is one of the easiest methods in prioritization.
The prioritization method allows in categorizing the list of requirements, ideas, or features into the following sets:
- M (must have): These features must be satisfied and non-negotiable at the final solution. The product will fail without them.
- S (should have): These features are not critical to launch but hold high priority. They come in 2nd place on the priority list.
- C (could have): Desirable but not mandatory conditions for the release. These are generally low-cost enhancements for the product.
- W (won’t have): These are the least critical and do not necessarily correspond to the product strategy. Usually not used in the current release but can be revised for future releases.
What are the Benefits of MoSCoW Prioritization?
The MoSCoW method helps to sort and organize your product items in a classified manner that yields successful results. This method is based on the expert opinion of any team. It is easy and quick to complete and defines the priorities of features that are in progress.
2. Kano Model
If prioritizing customer satisfaction and delight is your goal, the Kano model is one of the most excellent options you would want to consider.
Product managers often admit their feature backlog seems endless, but they sincerely want to create a product roadmap with the right features.
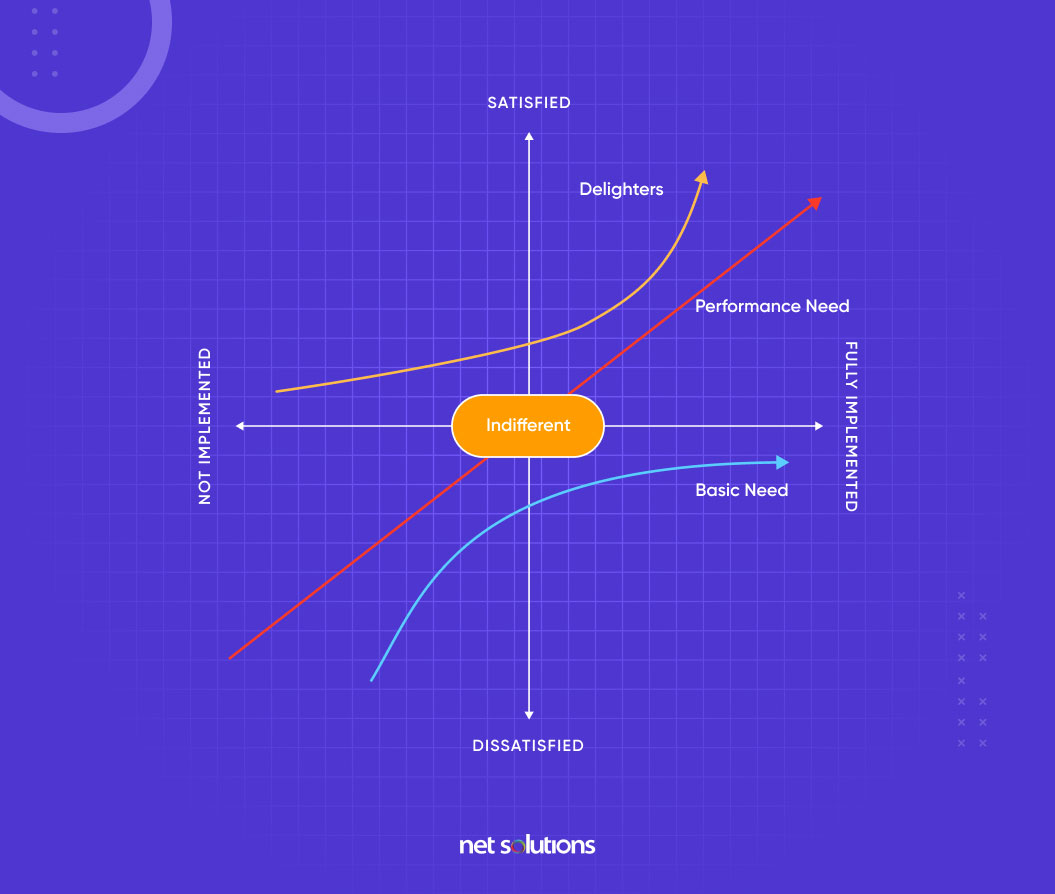
There are three premises, according to the Kano model:
- The satisfaction that resonates with client enjoyment product features depends on the level of functionality provided.
- Customer reaction. Categorization of features depends upon how customers react to the offered functionality.
- Customer feelings — it states how clients feel about a feature through multiple questionnaires.
Kano identifies three major components of the quality profile:
- Basic: That corresponds to the fundamental characteristics of the product.
- Expected: That compares to the “quantitative” attributes of the product.
- Attractive: This corresponds to the admirable qualities of the product.
They help in understanding customers’ perspectives on product features by assessing their satisfaction and sentiment.
3. Affinity Analysis
With the Affinity Analysis technique, development teams categorize user stories into different baskets like high, low, medium, etc.
Further, they pick backlog items to groom, plan or construct. Teams use this technique to prioritize groups as per their level of importance.
The idea behind this Affinity technique is simple. Participants brainstorm different ideas and possibilities together.
Then, the team maps out their new ideas and plans into thematic clusters. Afterward, teams vote and rank each group after establishing affinity analysis.
At the end of the activity, the team is set to have a prioritized list of new ideas.
4. Stack Ranking
In Stack Ranking, you examine each backlog item and place it in the order of priority. Starting with one, then two, three, and continue to n, followed by the total number of items in your backlog. You pick the first product backlog item first to groom, plan, construct, etc followed by the lower rank.
These two things set Stack Ranking aside from other methods:
- Possibility of only one number one- This provides the option of avoiding a familiar (and, frankly, stressful) product trap where everything becomes a high preference.
- Often more accurate, less confusing. You prioritize each and every item relative to all other items, simplifying the process and making it more transparent. This is usually a more specific and easier way to prioritize than to provide absolute values (such as “very high priority”).
FAQs on Product Backlog Prioritization and Backlog Grooming
What is Sprint Backlog?
The sprint backlog contains all the works which the team is committed to complete, either right away or as a part of the sprint (usually a one- to four-week period).
A much shorter list is picked from the product backlog list — particularly those items, which the team recognizes during a sprint planning meeting as the essential tasks to accomplish next in priority order.
Who owns the backlog grooming session?
A product owner owns a backlog grooming session.
However, there is no standard rule for who runs these grooming sessions. Sometimes a scrum master or the product manager can also arrange and run the backlog grooming sessions based on availability.
Who should attend backlog grooming sessions?
The product owner, the product manager, and the development team attend the backlog grooming meetings. Sometimes, a scrum master might also attend backlog refinement sessions for assistance.
How long does a backlog grooming session take?
The thumb-rule of running effective backlog grooming meetings is to keep them short. However, there is no standard time for how long it should be running.
To stick to an estimate, 45 minutes to a 1-hour time frame could be a good idea. Do not overstretch it to an extent where everyone feels exhausted and running out of time to complete the present sprint deliverables.
Why do we do product backlog grooming for the next sprint in the middle of the current sprint?
There are a couple of reasons for doing so, including:
- Product backlog items need to be ready for accurate sprint planning
- To prepare the backlog for the upcoming two sprints so that you can minimize the duration of the sprint planning session and increase productivity
- So that the team has an idea about the queued up user stories in advance and they can prepare them for the same and come up with any related queries from early on
- Postponing the backlog grooming session to the next cycle and the beginning of the week will delay the sprint planning, which, in turn, will delay the Agile product development efforts. On the other hand, arranging a grooming session in the middle of the week or later in the week is productive as work is somewhere near completion and the team has less workload to bear with.
How often backlog grooming occur?
It depends on the duration of the sprint cycle. If the team is working a one-week sprint cycle, running a backlog refinement meeting every week is a recommended practice.
On the other, if you are working on a two-week sprint cycle, running these meetings every alternate week should be considered.
What are some of the popular backlog refinement tools?
Having the right tools should always be a priority for product owners. And now that remote work is gaining momentum — having a remote tool stack is essential for a visual lookahead of the product backlog for effective grooming and planning sessions.
You could use tools like:
- Google Docs and spreadsheets
- ClickUp, Asana, Trello, etc
- Video Conferencing tools such as Zoom, Google Meet, Cisco Webex, etc.
What is Cost of Delay?
Cost of Delay (CoD) is a prioritization framework that helps businesses quantify the economic value of completing a project sooner than later.
Product teams quite perform this approach to calculate and compare the ongoing monetary costs that would result from delaying the completion of each initiative on the team’s backlog.
Conclusion
Backlog grooming helps ensure better project management. It is a good practice to refine the product backlog and prepare it for the sprint planning.
In this guide, we covered what a product owner should know before getting started with backlog grooming.
In all, consider working as a team and apply the best practices to keep your product development efforts on-track and going.