Summary: Collaborative product development (also known as collaborative product design, or CPD) is a business strategy, an approach to creating, and a combination of software tools that enables several businesses to collaborate on creating a product. Learn more about collaborative design in our blog to discover how it can help you create more successful products.
Have you ever felt stuck in the product development process, unable to develop truly innovative ideas?
It can be frustrating to hit a creative wall, especially when trying to build a product that stands out in a crowded market. But there is a solution: collaborative design.
Collaborative design involves bringing together a diverse group of people from different backgrounds and industries to work together and generate new ideas. By leveraging this diverse group’s unique perspectives and expertise, creating truly unique and effective solutions is possible.
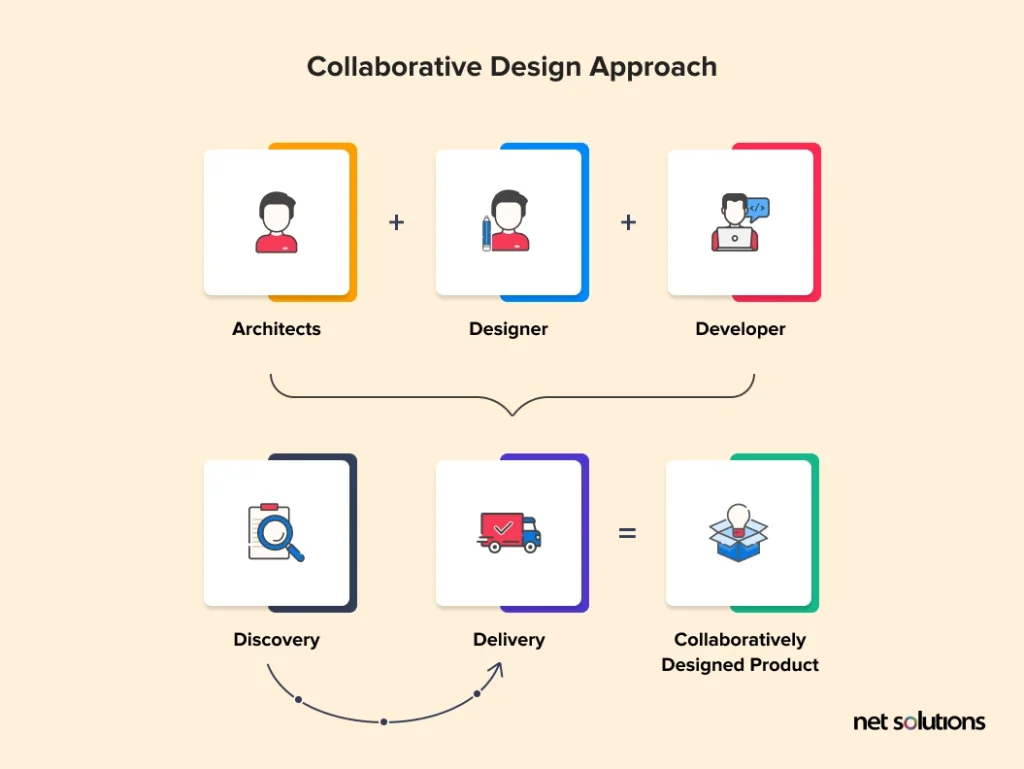
An architect will think of the software architecture, a designer will have an idea of how to make the product usable, the developer will know whether the proposed design is feasible, and the stakeholders will have opinions around the product design to make it invest worthy. Overall, the experience design process is a collaborative initiative undertaken by a product development company, not a one-person or one-team job.
In this blog, we’ll explore the benefits of collaborative design and why it’s worth pursuing product development. From improving the creative process to increasing the chances of success, there are many reasons why you should consider incorporating collaborative design into your product development strategy. So if you’re ready to take your product to the next level, read on to learn more about the power of collaborative design.
“Design is now too important to be left to designers.” — Tim Brown
What is Collaborative Design, and Why Is It Important?
Collaborative design, also known as participatory design, is a design strategy that helps foster effective collaboration among different teams of the product development team. i.e., the developers, designers, architects, and testers. But why need it?
Collaborative design is important in product development because it allows for the inclusion of a wide range of perspectives and expertise. By bringing together a diverse group of people, it’s possible to generate more creative and innovative ideas that may not have been thought of by a single person or a homogenous group.
Collaborative design can also improve the overall quality of the product by allowing for more comprehensive problem-solving. Additionally, involving diverse stakeholders in the design process can lead to higher buy-in and support for the final product. Overall, collaborative design can lead to more successful and well-received products.
By following this approach, everyone contributes towards designing the product, whether it is about — brainstorming ideas, giving feedback and suggestions, or validating and approving design ideas.
“Collaborative design is the process of involving people with distinct profiles in the design process to achieve non-linear solutions for various kinds of problems.” — Gustavo Pimenta, Managing Partners at SensesLab

We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.
How does Collaborative Design Work?
Collaborative design is a product development approach that involves bringing various stakeholders, such as designers, developers, and users, to develop a product. This approach allows a more diverse range of ideas and perspectives to be considered during the design process, leading to more innovative and effective solutions.
Collaborative design typically involves a series of meetings and workshops where stakeholders can share their ideas and discuss potential solutions to the problems being addressed by the product. This approach ensures that the final product is well-designed, effective, and meets the needs of all stakeholders.
Role of Collaborative Design in Product Development
The purpose of collaborative design is to integrate design and collaboration in the software development process.
The different stages of product development where collaborative design plays a role include-
1. Development of PoC (Proof of Concept)
Proof of concept is a process that applies to New Product Development to test the feasibility of innovative (untried) ideas.
Here the product development team, including the designers, developers, and architects, work together to check the practicality of the concept presented concerning development efforts and corresponding design requirements.
2. Development of Prototype
A prototype focuses on user experience design and is created to validate the look and feel of the product. In simpler terms, a prototype helps visualize how the product will look concerning UX design and also helps attract seed funding.
The designers, architects, and developers work together to build a prototype. The product owner conveys the product requirements to the team, and then the team brainstorms around the features and looks.
The designer’s team helps design the prototype while considering the recommendations from — developers, product owners, testers, and design architects. Hence, a collaborative design effort.
3. Building the MVP (Minimum Viable Product)
Minimum Viable Product is a basic launchable product version ready for shipping. The MVP is built with minimal must-have features, and once it passes all stages of the Software Development Life Cycle(SDLC), it is launched in the market. Further refinements and feature additions are based on user feedback.
When building an MVP, following collaborative design practices ensure shared ownership among the development team.
The stages of MVP development where collaborative design plays its part include –
a. Design Process
The designers work on the finalized design and tweak the design for changing requirements and opinions. Daily standups are conducted to check the team’s progress and collaborative work toward improving the design and development efforts.
b. Development Process
Developers and designers work in time-boxed sprint cycles where they simultaneously develop and design the features and the UX flow around them.
c. Design QA
Once the design is complete, the design QA team ensures that no “design debt” exists, i.e., no inconsistencies exist in the designed product and the idealized design.
It is a part of promoting collaboration in the design of your product as the developers and designers work together at this level to ensure design consistency.
- Designers review the UI code for the developed user story
- Work with the developers to make changes to the UI code if required
Agile Activities that Help Promote Collaborative Design
The common collaborative design approaches in the product development process include:

1. Retrospectives
A retrospective is a practice where the software development team, including designers, developers, and testers, revisit old product development projects to understand past best practices (what worked) and mistakes (what didn’t work).
For collaborative design, retrospectives can be conducted to validate the success of past product designs based on user feedback.
If the design falls short on parameters such as usability, findability, or discoverability, the entire team should brainstorm a new design that helps address the existing design issues.
2. Mob Programming
Mob programming is a practice where the entire product development team works on the same thing simultaneously and on the same system to solve a particular problem or complete a task.
For collaborative design, mob programming can help fix a design error or create a new design that everyone agrees with.
3. Swarming
Swarming is an activity where professionals with the same skill set work together to complete a task that a particular team member is having trouble with.
In collaborative design, swarming is referred to as an activity where the entire design team works to complete a design job that a particular designer is having trouble with.
Best Collaborative Design Strategies
The four common collaborative design techniques include — Whiteboard Sketching, Crazy Eights, Affinity Diagrams, and Design Sprints.
Here’s an overview of each of them:
1. Whiteboard Sketching
Whiteboard sketching is an informal session in which multiple team members contribute to one design on a whiteboard.
It works well for smaller groups or cross-functional teams aiming to compare design ideas using visualization.
Whiteboards are best suitable for solving complex design problems or developing innovative ideas.
2. Crazy Eights
The technique called the “Crazy Eights” is a sketching activity comprising three rounds, which include:
a. 5 Minutes, 8 Ideas.
Each participant must fold a sheet of paper thrice into equal halves, thus creating 8 rectangles in turn. Next, they unfold the paper. Now, the team members need to take no more than 5 minutes to sketch 8 ideas into each rectangle.
b. 5 Minutes, 1 Big Idea Now,
Each participant works towards sketching one big idea on a separate paper. This needs to be done in no more than 5 minutes. The plan is to either build one of the 8 ideas or combine various elements from any of those 8 ideas created in Round one.
c. 5 Minutes, 1 Storyboard/Wire Flow
Now that each participant has built a sketch around one big idea from Round 2, they must build a storyboard on a new piece of paper, along with the UX design flow concerning the idea generated.
3. Affinity Diagrams
An affinity diagram is a tool that helps gather opinions and ideas and organize them into common groups based on natural relationships among them.
Affinity diagrams are a prevalent collaborative design practice best suited for a team strength of 5-6 people.
The five steps in affinity diagrams are –
a. Idea Generation
The collaborative design project team writes the design ideas on post-its based on experience and creativity.
b. Idea Representation
Arrange all the post-its on a wall or a table randomly so that grouping can be done next.
c. Implement Grouping
The product development team manually arranges all the ideas into common groups. This arrangement is based on natural grouping and shared understanding among the team members.
d. Create Header Cards
At this stage, you need to look for a common idea that links all the ideas within a particular group. This idea can be a phrase or a sentence on a post-it and should be easily understandable.
You can also establish a group’s relationship with several other groups and categorize it under that common group (called a super header)
e. Draw a Complete Affinity Diagram
At this stage of collaborative design practice, you need to:
- Write the problem that the product is trying to solve
- Place headers and super headers in place for a proper grouping of design ideas
- Review and validate the groupings with the entire development team
- Document the affinity diagram
4. Design Sprints
A design sprint is a time-boxed process for working around design thinking, which, in turn, helps in reducing technical debt. This is a similar sprint cycle as that of any Agile project, but this one works around addressing design needs.
It is a collaborative design project process where developers, design architects, and testers are involved in the design process for validating, testing, revalidating, recommending, and approving ideas.
If Monday to Friday schedule is considered, the design sprint will include:
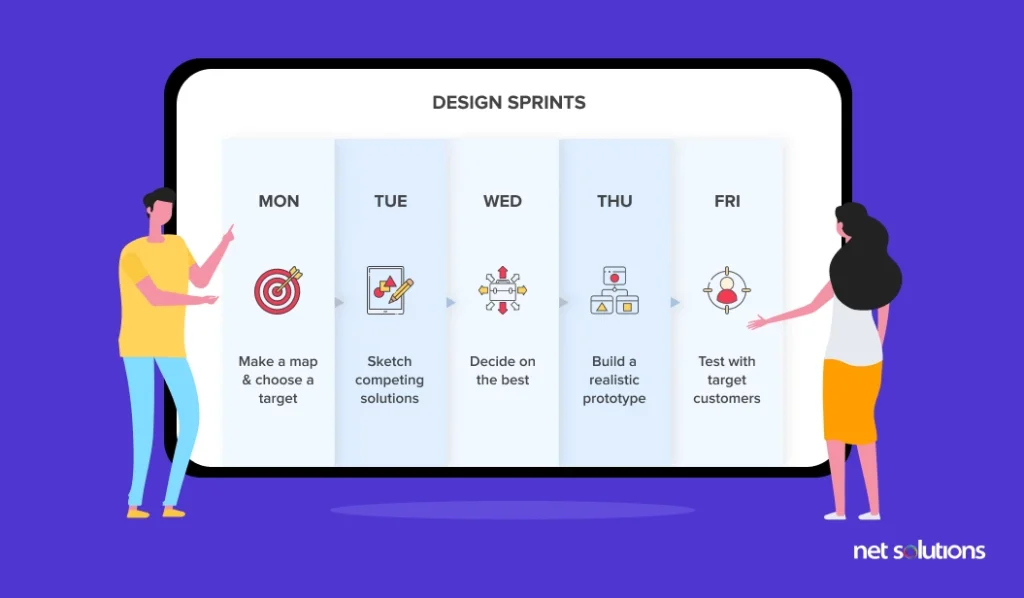
- Monday: Set goals, create maps concerning design priorities, seek expert validation, gather suggestions, and reset goals if necessary.
- Tuesday: Draft or sketch a rough design so the design team knows how to go about the actual design process.
- Wednesday: Create storyboards so that all the design elements connect to weave a complete and holistic story.
- Thursday: Convert storyboards into a prototype to create an early sample. This helps test and validate design ideas when it imitates a near reality.
- Friday: Test the design with your target customers. Iterative through the design sprints to improve the design based on user feedback.
Best Tools for Collaborative Design
Some good collaboration tools for designers and developers include
| 1. Figma (Our Personal Favorite) | A web-based vector graphics editor and prototyping tool. |
| 2. InVision | A prototyping tool for designers that can be shared across the product development team for reviews and suggestions. |
| 3. RedPen | A tool for creating design prototypes. Different members of the development team can then post feedback in the form of annotations. |
| 4. Mural | It is an intuitive collaborative design thinking tool for creating prototypes, building frameworks, images, gifs, etc. The team can then comment, chat, or even arrange a quick call for suggesting changes and presenting opinions. |
| 5. Zeplin | A cloud-based tool for the UI team to collaborate — for creating shareable design prototypes. |
| 6. Webflow | Allows users to create and publish professional-looking websites without writing code. It helps users design and builds their websites, including a drag-and-drop website builder, customizable templates, and various design tools such as typography, layout, and color palette options. |
Benefits of Collaborative Design
Collaboration is the most challenging part of the design process. But the payoffs are innumerable for those willing to take on the challenge.
So here is why collaborative design is important in design:
1. Breaks Siloes among the Teams
The collaborative design breaks the silos in the product development teams by nurturing inclusion. Productivity happens when everyone on the team works together for problem-solving or brainstorming ideas, irrespective of their roles.
The collaborative design promotes the idea that “Alone, we can do so little; together we can do so much.”
2. Helps Create Powerful, Fool-Proof Designs
The designers, the developers, the design architects, and the testers — everyone is involved in the design process, which means everyone’s perspective and opinion are considered before finalizing the product design.
Innovation happens, and robust designs are created that have a low probability of falling short on parameters such as — usability, intuitiveness, findability, discoverability, etc.
3. Gives Way to Shared Ownership
As different team members are involved in the collaborative design process, everyone feels invested and has a stake in the outcome. This creates a sense of shared ownership in the success of the project.
4. Faster Time to Market
If the final design is a visual representation that takes care of the suggestions from the entire product development team (designers, product owner, developers, testers) — there are fewer changes and to-and-fro changes in the design.
This, in turn, ensures faster time to market and work satisfaction among the team members.
When to Use Collaborative Design?
Here are some of the use cases where collaborative design can be usefully applied:
- Defining the vision of a product or service
- Gaining context on a specific problem
- Generating and discussing ideas in a practical yet fun way
- Solving a specific design problem
- Designing the life cycle of a product or service
Frequently Asked Questions
Designers from other disciplines contribute their expertise in both the design process and the design content through the collaborative design process. They do this to establish a common understanding of the design problem, a common design thinking technique.
- The developer is your audience
- Change is the only constant
- A design is never completed
- Less is better
- Design is a collaborative activity
Yes, collaborative design can be applied to any product development, from consumer goods and electronics to software and medical devices. The key is to assemble a diverse team with a range of skills and expertise and to create a collaborative environment that encourages idea-sharing and teamwork.
Product development teams can assemble diverse designers with various skills and expertise to implement collaborative design. They can then establish a collaborative design process that works for their team, including idea generation, brainstorming, and prototyping steps. Finally, they can create a supportive and collaborative environment that encourages idea-sharing and teamwork.