Table of Contents
The global search volume for cloud computing is over 300,000! Cloud computing is the most commonly used generic term today. However, this is a relatively recent phenomenon. Dell tried to trademark the term “cloud computing” in 2008, and no one opposed it.
Dell applied for the trademark in context with:
“Custom manufacture of computer hardware for use in data centres and mega-scale computing environments for others” and “design of computer hardware for use in data centres and mega-scale computing environments”.
— ZDNet
The US Patent and Trademark Office sent a preliminary notice that Dell could own the term. However, USPTO withdrew the permission notice within a month.
Registration is refused because the applied-for mark merely describes a feature and characteristic of the applicant’s services.
— Statement of US Patent and Trademark Office
Fast forward to 2022, businesses now get to use and offer “cloud” as a service. The popularity of cloud computing services continues to increase as businesses are consistently defining new cloud initiatives. Here are some of these initiatives according to the Flexera Cloud report:
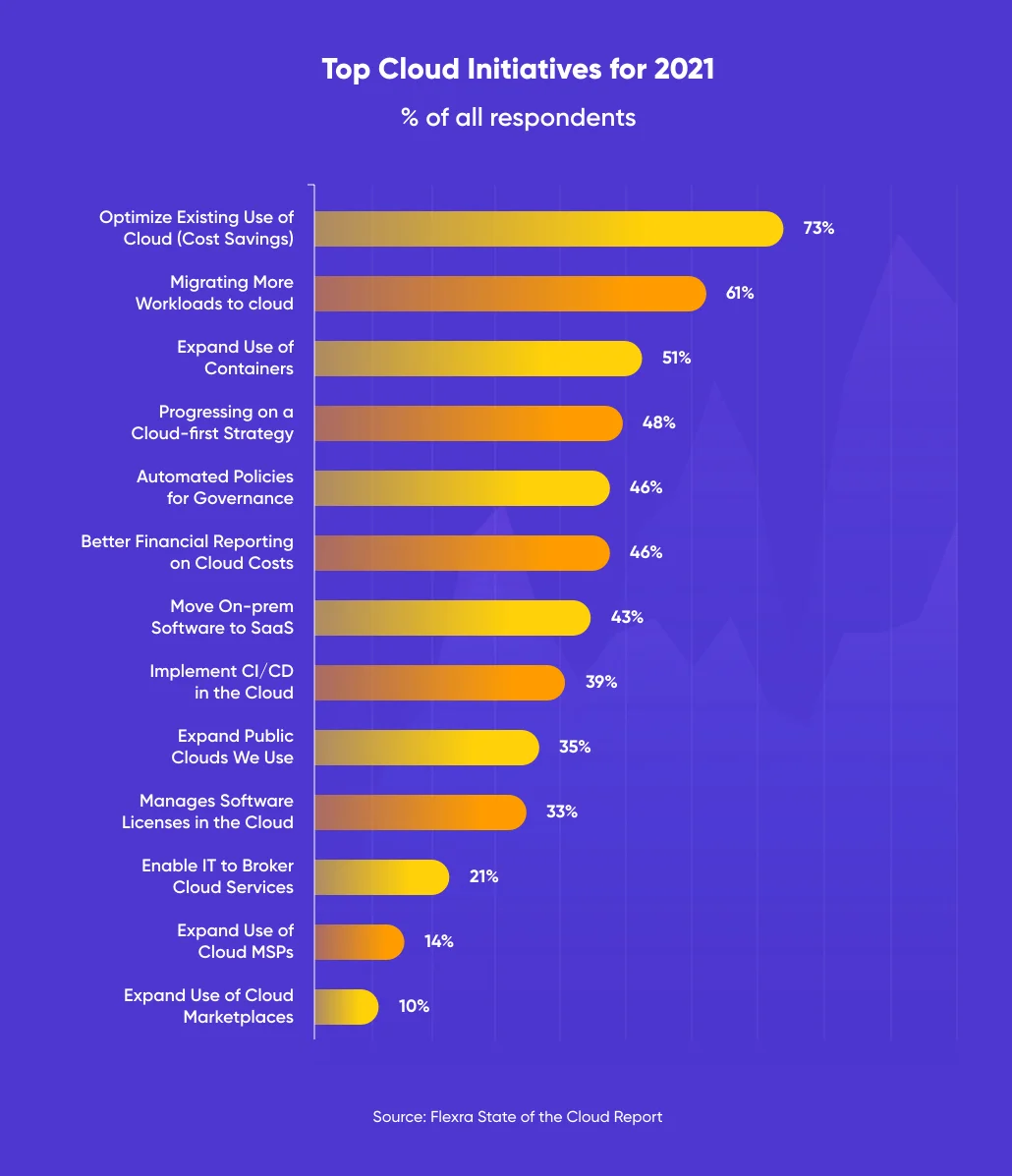
This guide will help gain knowledge about the A-Z of cloud computing. Time to get started.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud is a metaphor for the internet. Cloud computing is the on-demand availability of computing resources such as computation and file storage anywhere and anytime. The user does not have to manage the resources actively, and new resources can be added at any time, making it easy to scale operations.
Cloud computing is nothing but renting out someone else’s computer to run business operations.
Large-scale enterprises that require large clouds have data and functions distributed across multiple locations, with each of these locations representing a data center.
Fun Fact: Google has a floating data center, where they have a portable data center facility located on the ships. This system is water-cooled making it environmentally innovative.
History of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is not modern technology. It has continued to evolve since the early 1950s. In 1955, John McCarthy created a time-sharing concept that enabled users to use an expensive mainframe simultaneously. McCarthy’s theory of mainframe timesharing is said to have had a significant impact on the development of the internet.
With the evolution of technology, the concept of cloud computing took a giant leap in the mid-1960s, when an American computer scientist Joseph Carl Robnett Licklider, described a theory of interconnected computing systems. This idea gave birth to the predecessor of the internet: ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network).
Licklider’s contribution is considered to be the most valuable in the creation of cloud computation; thus, he is believed to be the father of cloud computing.
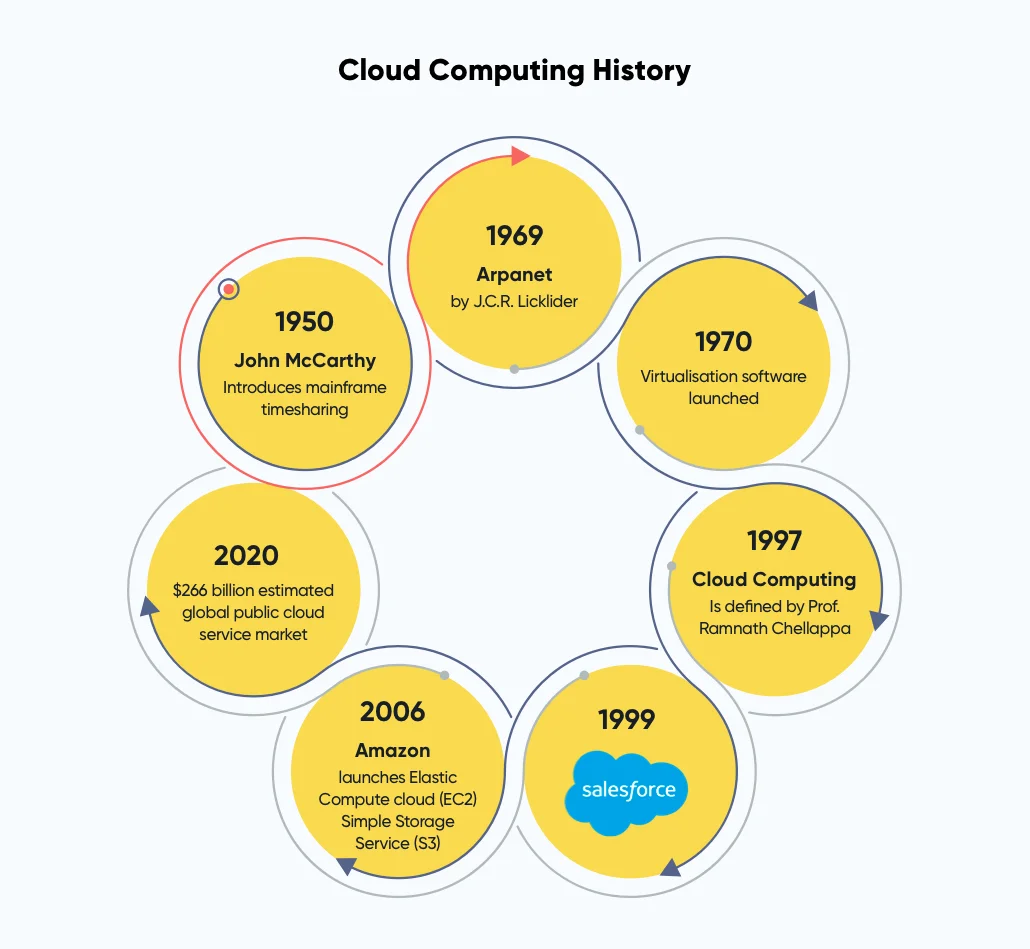
From the 1970s to the 1990s, the cloud evolved at break-neck speeds because of advancements in technology. In 1972, IBM released the VM (Virtual Machine) operating system, exhibiting the behavior of dedicated hardware, giving users the same experience on a VM. In the 1990s, telecommunications companies started offering “Virtualized” Private Networks (VPNs) as rentable services.
As businesses started to acquire a better understanding of the term cloud, it gained popularity. In 1999, Salesforce emerged as an ideal example of a successful cloud computing adoption.
However, cloud computing became extremely popular in 2006 when Amazon released its Elastic Compute Cloud product.
Primary Characteristics of Cloud Computing
The primary characteristics of cloud computing include:
- Pay-as-you-go Basis: customers only pay for resources that they use, which, in turn, reduces the overall cloud expenditure
- Device, Time, and Location Independent: Users can access the cloud-based applications from anywhere, any time, and from any device
- Scalability: Businesses can scale their operations by requesting more resources whenever required. This makes it easy to expand operations without much delay.
- On-the-Go Updates: The cloud vendor handles the management and the updates. For a vendor, this poses an added responsibility to meet the changing needs of the customers.
Cloud Computing: Use Cases
Cloud computing is beneficial for:
- Developing applications
- Storing, recovering, and backing up data
- Delivering software to the customers
- Streaming services such as audio and video
- Testing applications
- Running data analytics services
Advantages of Cloud Computing
The rate at which data is exploding has pushed digital businesses to embrace cloud computing as the platform for innovation. Businesses across all industries are leveraging cloud solutions for various use cases such as digital security, disaster recovery, big data analytics, and data backup.
Today, cloud solutions help businesses navigate the challenges of the digital era, enabling them to quickly respond to a complex and fast-paced business landscape. Adopting the cloud allows businesses to run more effectively, serve customers better, and boost their revenue. In fact, companies that invest in cloud, big data, and mobility see 53% faster revenue growth than their competitors.
Apart from helping businesses transform, differentiate, and gain a competitive advantage, the benefits of cloud computing are:
- Cost Optimization
- Scalability
- Security
- Efficiency
- Automatic Upgrades
- Disaster Recovery
- Mobility
Types of Cloud Deployment: Public vs Private vs Hybrid Cloud
A single type of cloud computing service is not fit for every business requirement. Different cloud deployment models and services have evolved with time to offer the right solution for every business need. Thus, before migrating to the cloud, it is essential to determine the types of cloud deployment: Public Cloud, Private Cloud, or Hybrid Cloud.
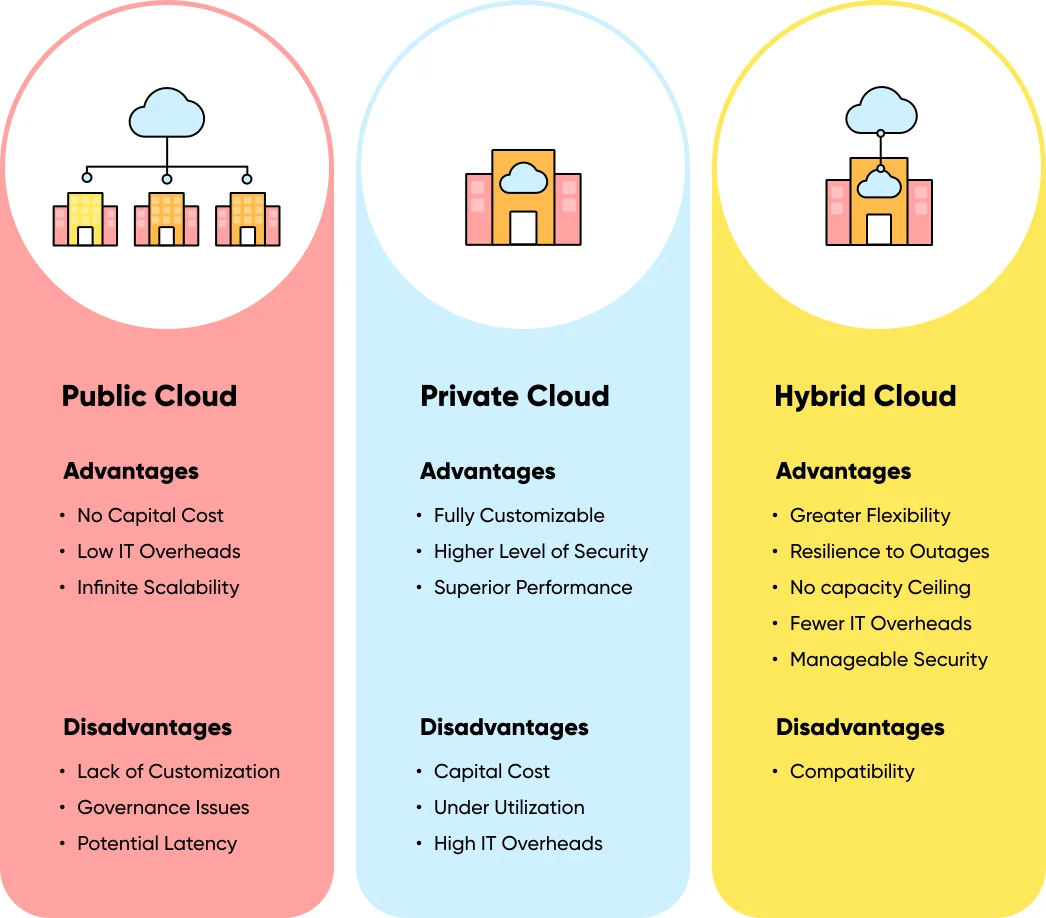
- Public Cloud Public clouds are operated and owned by third-party providers. In the case of a public cloud, the services offered by cloud providers are over a network that is open for public use. This implies that an organization shares the same hardware and network devices with other companies of the same cloud service provider. Microsoft Azure is an example of a public cloud.
- Private Cloud A private cloud is a cloud deployment model that a single organization exclusively uses. In the case of a private cloud, the services and infrastructure are maintained on a private network, either located physically at the organization’s on-site data center or hosted by third-party service providers.
- Hybrid Cloud The combination of private and public clouds gives rise to a hybrid cloud. A hybrid cloud deployment model enables businesses to move applications and data between public and private clouds, leading to an agile, secure, and flexible digital business model.
Types of Cloud Computing Service Models: IaaS vs SaaS vs PaaS
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), PaaS (Platform as a Service), and SaaS (Software as a Service) are the types of cloud computing services that help businesses transform their digital experience while, in turn, reducing the infrastructural costs. All of these cloud services differ primarily in what they offer to the end-user. Each of these cloud services has its benefits depending upon the business and functional requirements.
Here is a breakdown of the different cloud services (Iaas vs PaaS vs SaaS):
- Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS/software as a service refers to cloud-based applications, often developed by a SaaS development company, that are hosted online by a company. SaaS products are typically made available for purchase on a pay-as-you-go pricing model.
According to Gartner, the end-user spending forecast for the Software as a service (SaaS) model will be around $171,915 million in 2022.
Key Reasons Businesses Should Adopt SaaS Business Model
Adopting a SaaS Business model provides many benefits over traditional on-premise software installations. Some of them are as follows:
- Speed of Innovation
- Reduced Marketing Efforts
- Faster Time to Market
- Reduced Churn Rates
- The Anytime, Anywhere Access
- Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS/ platform as a service refers to a cloud-based platform service that offers a robust framework for developers to build, test, and manage custom applications. Unlike SaaS, PaaS does not provide software over the Internet. Instead, it offers a platform to businesses where the software is built. Google App Engine and OpenShift are common PaaS examples.
According to Gartner, the end-user spending forecast for the Platform as a service (PaaS) model will be around $100,636 million in 2022.
- Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS/ infrastructure as a service refers to a cloud-based infrastructure service that offers virtual data centers to businesses, which help them build and manage their operating systems, servers, data storage, and network infrastructure. The common IaaS examples are Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services (AWS).
According to Gartner, the end-user spending forecast for the Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) model will be around $121,620 million in 2022.
Comparison of Best Cloud Computing Platforms: AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud
The cloud computing market is flooded with several cloud computing platforms; however, Amazon (AWS), Microsoft (Azure), and Google (Cloud) are the three clear leaders, according to their market share and Gartner’s Magic Quadrant report.
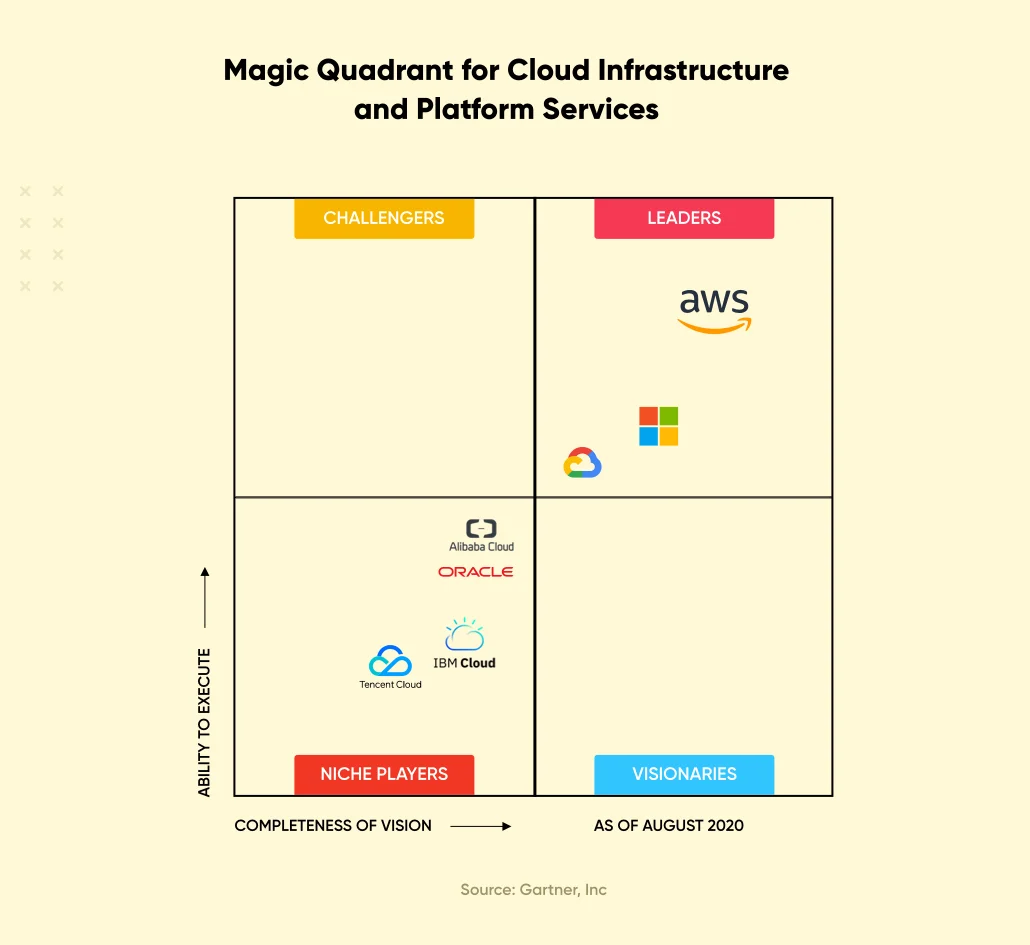
How should someone decide which cloud computing platform to choose? Here is a breakdown of the different cloud computing platforms (AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud):
- Google Cloud Platform
As the name suggests, Google Cloud Platform is a cloud service offered by Google. The Google cloud platform allows the user to build, deploy, and scale cloud-based services, applications, and websites on the same infrastructure that Google uses for its end-user products. Big brands like Twitter, Spotify, and Forbes use Google cloud to run their operations.
Key Advantages of Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform is a significant technological development and is being adopted by large enterprises and small businesses because of the following benefits:
- Higher productivity owing to quick access to innovation
- Less disruption when users adopt new functionality
- Employees can work from anywhere
- Allows quick collaboration
- Robust security
- Fewer data are stored on vulnerable devices
- Higher uptime and reliability
- Flexibility
- Amazon Web Services
AWS is the world’s most adopted cloud platform. This cloud service works on a pay-as-you-go model and dominates the public cloud services market with a 39% share. AWS is spread across 190 countries and serves millions of customers like GE, Samsung, Coca-Cola, Slack, and Netflix, offering benefits like reduced costs, agility, and faster innovation.

Why Consider Amazon Web Services?
For the ninth year in a row, AWS is positioned at the top in the Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for Cloud IaaS across both the axes of measurement (i.e., Ability to Execute and Completeness of Vision). Following are a few benefits that the AWS cloud computing platform offers:
- Enhanced Security
- Cost-Effectiveness
- Flexibility and Openness
- Elasticity and Scalability
- Azure Web Services
Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing platform that was released in 2010. Azure offers cloud computing services to build, test, deploy, manage, and scale service applications via Microsoft-managed data centers. 80% of Azure’s customers are from Fortune 500 companies such as Apple, Fujifilm, Honeywell, and HP.
Why is Azure Web Services Right for Digital Business?
According to Microsoft, “Azure is a growing collection of integrated cloud services — analytics, computing, database, mobile, networking, storage, and web — for moving faster, achieving more, and saving money.” Following are some other benefits that the Azure cloud computing platform offers:
- IaaS and PaaS Capabilities
- Autoscaling
- Flexibility
- Personalized and Timely Customer Experiences
AWS vs Azure vs GCP: Comparison
When it comes to choosing a cloud provider, which one fits the bill? Here’s a comparison chart to help clarify the options:
| Parameter | Amazon Web Services (AWS) | Microsoft Azure | Google Cloud Platform (GCP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gartner Peer Insights Reviews | 4.6 | 4.4 | 4.5 |
| Market Share Percentage as of Q4, 2020 | 32% | 20% | 9% |
| Suitable for | Businesses looking for a wide range of cloud services and tools | Businesses running their operations on Windows and Microsoft | For a small, web-oriented startup or a business that is keen on leading digital transformation with machine learning |
| IaaS Services | Amazon Elastic Cloud Compute | Virtual Machines | Google Compute Engine |
| PaaS | AWS Elastic Beanstalk | App Service and Cloud Service | Google App Engine |
| Containers | Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud Container Service | Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) | Google Kubernetes Engine |
What is Cloud Migration?
Migration in cloud computing is about transferring data, processes, and business workloads from an on-premise setup to the cloud. Alternatively, cloud migration can also be defined as shifting data, processes, and business workloads from one cloud provider to another. The latter is better known as cloud-to-cloud migration.
Some of the benefits of cloud migration include:
- Cost-Optimization
- Agility and responsiveness
- Remote Access
- Increased focus on core business operations
- Scalability
How to Build and Implement Enterprise Cloud Strategy?
An enterprise cloud strategy is defined as a well-thought-out strategy for implementing the cloud at the organizational level.
A 5-step plan for implementing an enterprise cloud strategy includes:
- Form a Team or Outsource The cloud team is headed by the CTO and usually comprises IT and networking team members. Alternatively, a business can consider hiring a cloud consultant company that can help create a fool-proof enterprise cloud implementation roadmap.
- Analyze Existing Applications
The second step is to decide which applications stay on-premise and which applications need to move to the cloud. For instance, mission-critical applications need to be maintained on-premise, while applications that are not mission-critical or have gone obsolete need to be scrapped.
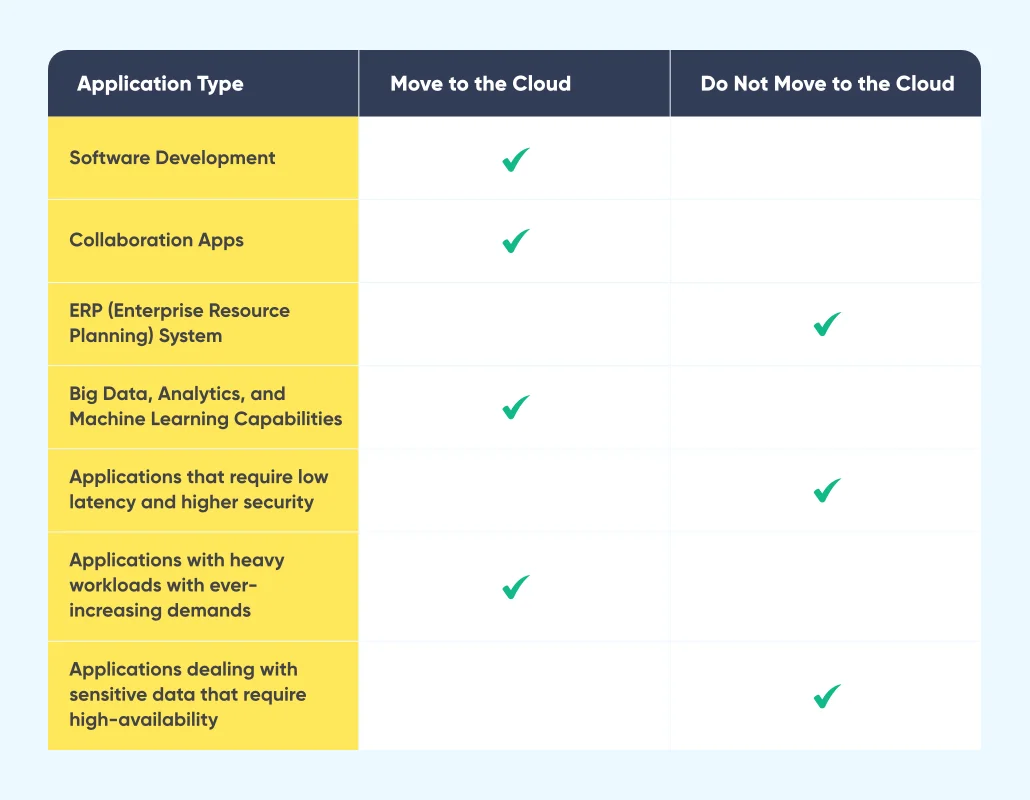
- Build a Hybrid or a Multi-Cloud Strategy
The next step is to build a hybrid or multi-cloud strategy. What cloud services does the business want to invest in? What cloud vendor would they choose? What are the business and functional requirements?
Answers to all these questions help in forming a robust, hybrid, or multi-cloud strategy.
- Reskilling and Upskilling
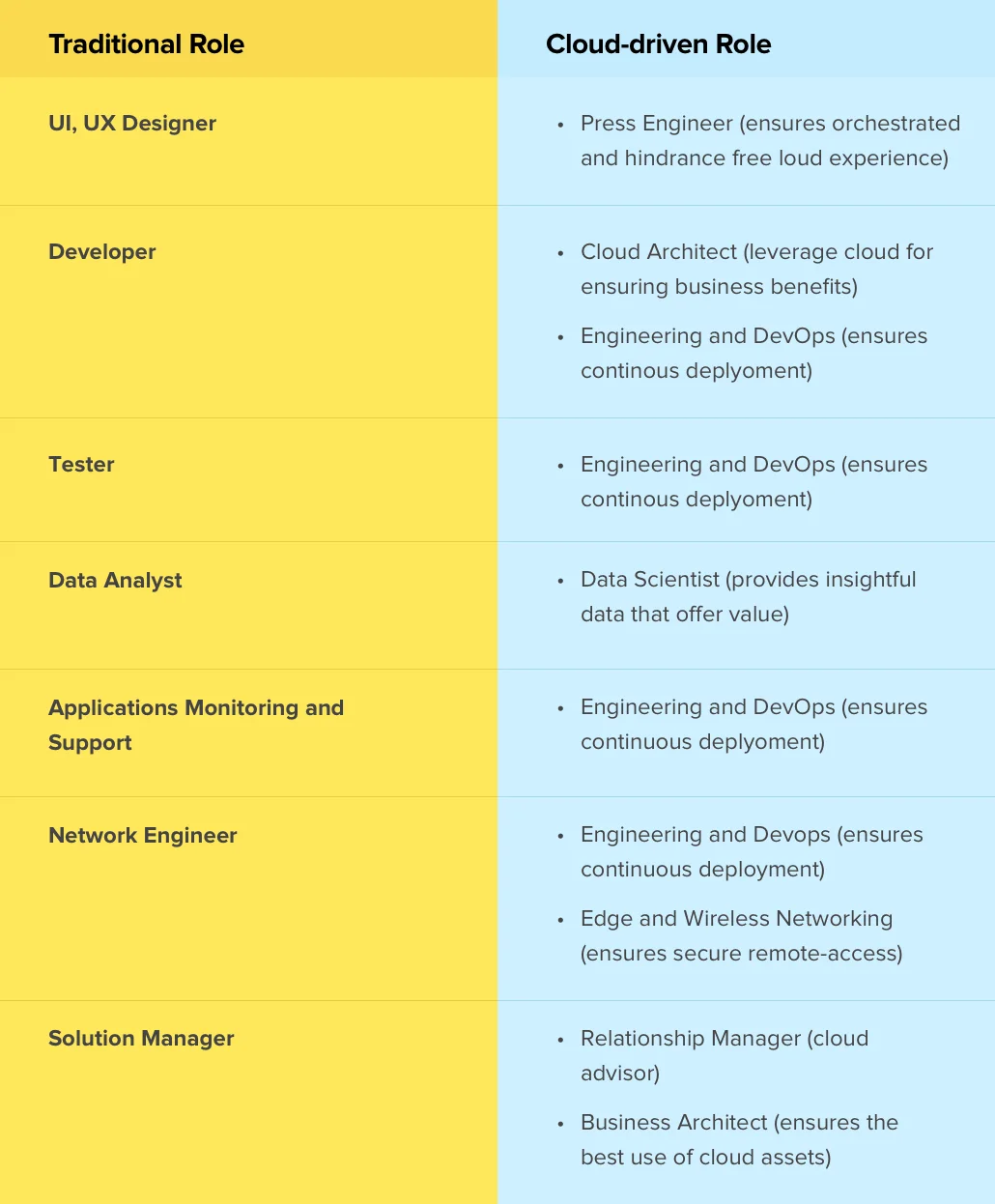
Preparing the workforce for the change is another essential step towards adopting cloud services. It is necessary to focus on upskilling and reskilling to enhance the cloud-driven roles at the organization.
Here is an overview of the traditional roles vs the respective cloud-driven roles:
- Implementation
Data should be moved to the cloud in phases rather than moving it all at once. The three prominent phases include:
- First Phase: Development and Testing (DevTest) environments, Web apps, new products, and redesigns of these products and solutions
- Second Phase: Regulatory solutions, High Input/Output online transactional processing systems (OLTP)
- Third Phase: Secure high-value assets (HVA) systems, public key infrastructure (PKI) systems, and legacy source control systems
FAQs on Cloud Computing
1. What is the Cloud-First Approach?
The Cloud-first approach states that any business, no matter their age or size, should prioritize investing and shifting their operations to the cloud. Also, do not confuse cloud-first for cloud-only.
2.What is the Multi-Cloud Approach?
A multi-cloud approach means investing in more than one cloud service, often from multiple cloud vendors. According to Statista, 79% of small businesses, 84% of mid-sized businesses, and 94% of large enterprises will be adopting a multi-cloud strategy by 2023.
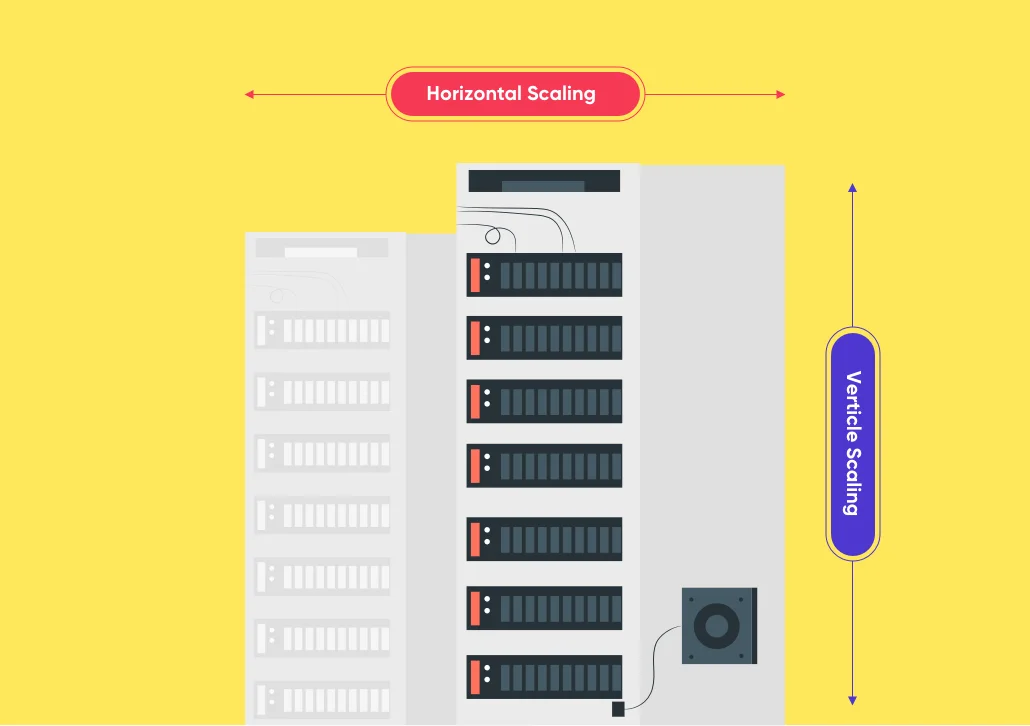
3.What is Horizontal vs Vertical Scaling in the Cloud?
Horizontal scaling means adding more machines to the existing resources. On the other hand, vertical scaling means expanding power with respect to RAM or storage to the existing machines.
4.Is the Cloud Secure?
Cloud security is about implementing strategies to safeguard data and applications residing on the cloud.
Cloud breaches are common. However, that does not imply that the cloud is not secure. Cloud computing security depends on how securely a business builds the cloud environment and how they use it.
Some risk is always going to remain. An organization should draft a well-defined enterprise cloud strategy to mitigate those risks in the best possible way. Recommended practices include:
- Implement stringent cloud ownership policies
- Rely on backup plans and recovery strategies
- Implement a cloud firewall across the network
- Rely on data encryption strategies
5.What are the Emerging Trends in Cloud Computing?
The top cloud computing trends for 2022 include:
- Optimization of the cloud budgets
- Rise of edge computing
- Adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud strategy
- The emergence of cloud automation
- Introduction of AI (Artificial Intelligence) in cloud computing
- Evolution of Kubernetes
6.What is MBaaS and FaaS?
MBaaS stands for Mobile “backend” as a service. According to the MBaaS model, mobile app developers can link the apps to the cloud environment through application programming interfaces (APIs).
On the other hand, FaaS stands for Function as a Service and is also known as serverless computing. According to this model, the cloud provider manages the virtual machines entirely to serve the customer requests.
7.What is Security Governance in Cloud Computing?
Cloud security governance refers to rules and policies that aim at implementing and managing security in the cloud environment. The model comprises cloud infrastructure performance expectations, operational strategies, security policy, backup recovery services, programming standards, etc. The benefits of cloud governance include:
- Enables efficient and safer use of cloud
- Reduces efforts to manage the cloud manually
- Helps maintain a check on Shadow IT
Conclusion
Cloud computing is growing massively. 61% of organizations plan to upscale cloud usage and make it a top initiative for driving growth. With that in mind, every business should implement a smart cloud strategy that fulfills their business and functional requirements.
This write-up covers what cloud computing is and everything about its related concepts. Before deploying the cloud, it becomes essential to understand the ins and outs of this growing digital transformation trend.

