Summary: In today’s Digital Darwinian world, when there’s tremendous pressure on enterprises to adapt and deliver quickly, Cloud computing can help you leverage innovative ways to grow and achieve your business goals. However, there’s a lot you need to know before you hop on the cloud computing bandwagon. This cloud computing guide will be a reference for everything you need to know before you adopt cloud computing.
The global cloud computing marketplace is expected to reach US $1,554.94 billion by 2030. –
Grand View Research
The world would be different without cloud computing. The OTT platforms, work-from-home, and IT outsourcing would still be a dream. Cloud computing has allowed businesses to have bolder visions for the future. Not only has it taken a load of IT resource management, but it also boosted ROI and brought down business operations costs.
Although the cloud has turned out to be the foundation of a successful digital enterprise, only a few organizations have been able to optimize this powerful tool — less than one-third of businesses have a documented cloud strategy.
Therefore, the question for entrepreneurs and interested prospects isn’t whether to avail of cloud solutions but how to. If you’re facing a similar dilemma, this cloud computing guide is for you. Read on as we learn what cloud computing is and how it can take your business to greater heights:
We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.
What is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is renting out someone else’s computer to run business operations.
Despite being the new norm for the current business environment, Cloud computing is often misunderstood and underutilized. What exactly is cloud computing?
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources like computation and file storage over the internet anywhere, anytime. It operates on a pay-as-you-go model without the direct involvement of users. Also, the resources on the cloud can be easily scaled up and down based on the business needs.
We have also covered a detailed hub page on what cloud computing is. You can refer to it to learn more.
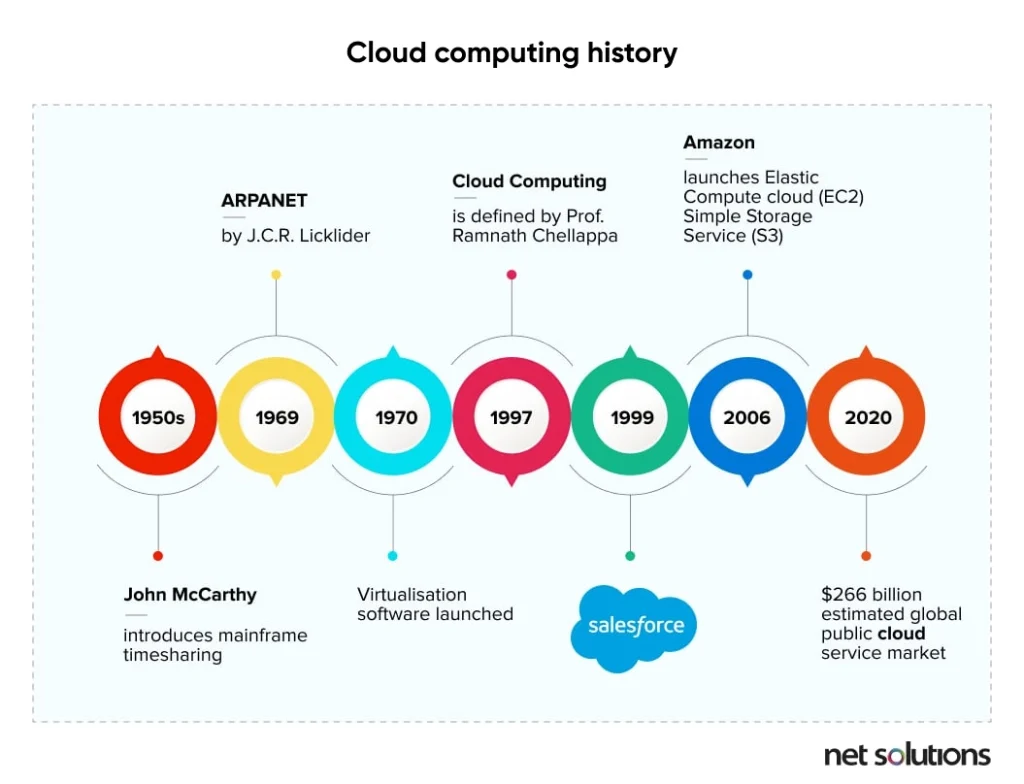
Here’s a brief image explaining the evolution of cloud computing over the past few years:
Cloud Computing Examples
Cloud computing examples surround us from all four sides: from messaging apps to productivity apps and audio streaming services. You can leverage cloud computing at work through business email or other communication applications.

Many cloud computing use cases range from productivity to data analysis, communication, file backup, software testing and development, and cloud storage. Most businesses use cloud computing apps through a subscription model, which is relatively cost-effective.
Following are a few cloud computing examples and uses:
- Communication: Skype, Whatsapp, Slack
- Productivity: Microsoft Office 365, Gmail
- Data Storage: Dropbox, Facebook, Gmail
- Business Processes: Salesforce, Hubspot
- Application Development: Amazon Lumberyard
- Big Data Analytics: Hadoop, Cassandra, HPCC
- Social Networking: MySpace, LinkedIn, Twitter
Types of Cloud Services: IaaS vs. SaaS vs. PaaS
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS are the types of cloud services that help businesses transform their digital experience while reducing the infrastructural costs in turn. All these cloud services differ primarily in what they offer to the end user. Each cloud service has its benefits depending upon the business and functional requirements.
Here is a breakdown of cloud services: Iaas vs. PaaS vs. SaaS.
1. Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS/ software as a service refers to cloud-based applications, often developed by a SaaS development company. These applications are hosted online by a company that makes them available for purchase on a pay-as-you-go pricing model.
The global SaaS market will be worth $186 billion by 2022 and is expected to reach $344.3 billion by 2028 with a CAGR of 11.0%. Grand View Research
Key Reasons Businesses Should Adopt SaaS Business Model
Adopting a SaaS Business model provides many benefits over traditional on-premise software installations. Some of them are as follows:
- Speed of Innovation
- Reduced Marketing Efforts
- Faster Time to Market
- Reduced Churn Rates
- The Anytime, Anywhere Model
2. Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS/ platform as a service refers to a cloud-based platform that offers a robust framework for developers to build, test, and manage new custom applications. Unlike SaaS, it does not provide software over the Internet; instead, it offers the platform to businesses where the software is being built. Google App Engine and OpenShift are common PaaS examples.
The global PaaS market will be worth $74.5 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach $206.30 billion by 2028 with a CAGR of 19.0%. – Grand View Research
Why should I adopt the PaaS business model?
With PaaS, businesses can quickly deploy, run, and manage custom cloud applications without building and maintaining their own servers and infrastructure.
3. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS/ infrastructure as a service refers to a cloud-based infrastructure service that offers virtual data centers to businesses, which help them build and manage their operating systems, servers, data storage, and network infrastructure. The common IaaS examples are Microsoft Azure and Amazon Web Services (AWS).
The global IaaS market is worth $115.74 billion in 2022 and is expected to reach $150.25 billion by 2023. – Grand View Research
Why should I adopt the IaaS business model?
- IaaS is easy to access and can be customized to meet your business needs.
- You get the storage, backup, and recovery of all essential data. It means you don’t have to worry about finding a storage space or investing in data management or maintenance. This significantly reduces costs.
Types of Cloud Deployment: Public vs Private vs Hybrid Cloud
A single type of cloud computing is not fit for every business requirement. There are different cloud deployment models and services, which have evolved with time to offer the right solution for every disparate business needs. Thus, before going into the process of cloud migration, it is essential to determine the types of cloud deployment — Public Cloud, Private Cloud, and Hybrid Cloud.

1. Public Cloud
Public clouds are operated and owned by third-party providers. In the case of a public cloud, the services offered by cloud providers are over a network that is open for public use, implying that an organization shares the same hardware and network devices with other companies of the same cloud service provider. Microsoft Azure is an example of a public cloud.
2. Private Cloud
A private cloud is a deployment model exclusively used by a single organization. In the case of a private cloud, the services and infrastructure are maintained on a private network, either located physically at the organization’s on-site data center or hosted by third-party service providers.
3. Hybrid Cloud
The combination of private and public clouds gives rise to a hybrid cloud, allowing the sharing of data and applications between both of them. Using a hybrid cloud deployment model enables businesses to move applications and data between public and private clouds, leading to an agile, secure, and flexible digital business model.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
The rate at which data is exploding has pushed digital businesses to embrace cloud computing as the platform for innovation. Enterprises across all industries are leveraging cloud solutions for various use cases, like digital security, disaster recovery, big data analytics, and data backup.
Today, cloud solutions help businesses navigate the challenges of the digital era, enabling them to respond quickly to a complex and fast-paced business landscape. Adopting the cloud allows businesses to run more effectively, serve customers better, and boost their revenue: companies that invest in cloud, big data, and mobility see a 53% faster revenue growth than their competitors.
Apart from helping businesses transform, differentiate, and gain a competitive advantage, the benefits of cloud computing are:
- Cost Optimization
- Scalability
- Security
- Efficiency
- Automatic Upgrades
- Disaster Recovery
- Mobility
Cloud Computing Platforms: AWS vs. Azure vs. Google Cloud
The cloud computing market is flooded with several cloud computing platforms; however, Amazon (AWS), Microsoft (Azure), and Google (Cloud) stand out as three leaders, according to their market share and Gartner’s Magic Quadrant report.
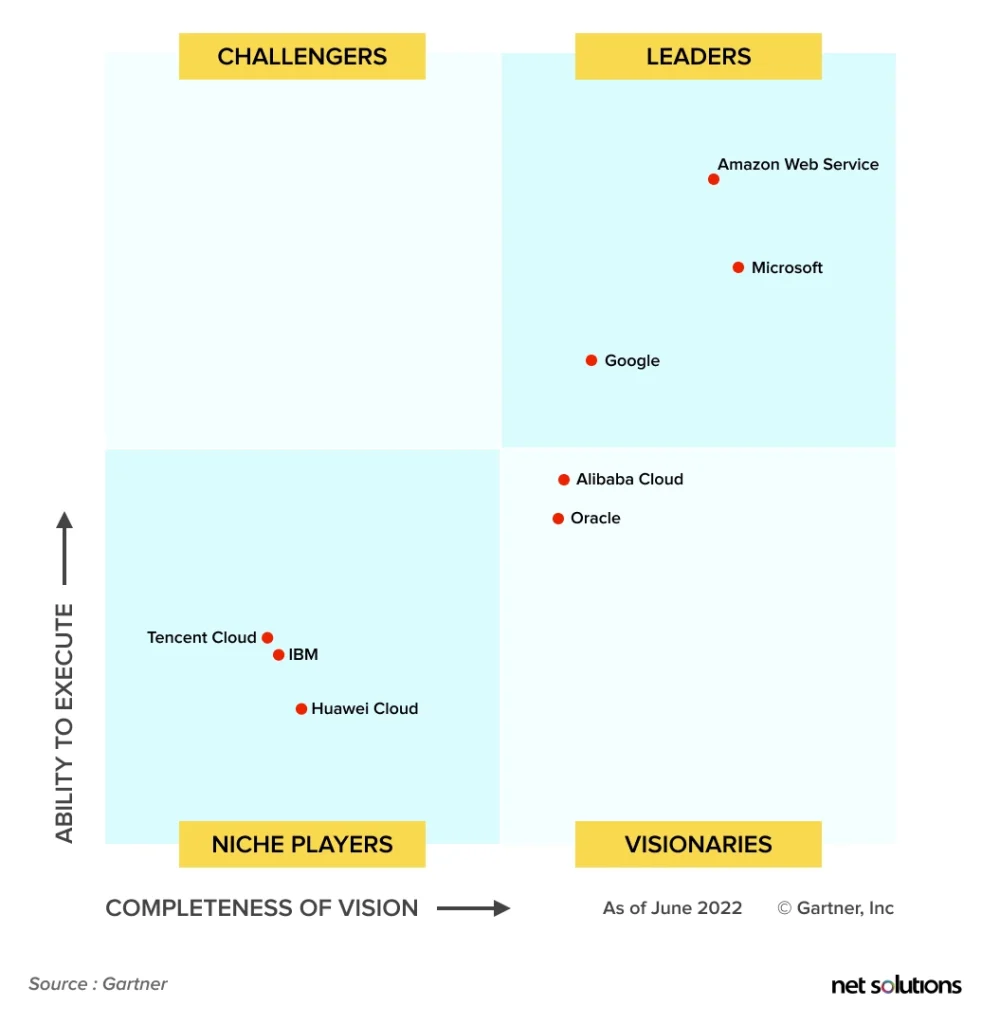
So, how do you decide which cloud computing platform to choose? Here is a breakdown of the different cloud computing platforms: AWS vs. Azure vs. Google Cloud
1. Google Cloud Platform
As the name suggests, Google Cloud Platform is a cloud service offered by Google to build, deploy, and scale cloud-based services, applications, and websites on the same infrastructure that Google uses for its end-user products. Big brands like Twitter, Spotify, and Forbes use Google cloud to run their operations.
Key Advantages of Google Cloud Platform
Google Cloud Platform is a significant technological development and is being adopted by large enterprises and small businesses because of the following benefits:
- Higher productivity owing to quick access to innovation
- Less disruption when users adopt new functionality
- Employees can work from anywhere
- Allows quick collaboration
- Robust security
- Fewer data stored on vulnerable devices
- Higher uptime and reliability
- Flexible
2. Amazon Web Services
AWS is the world’s most adopted cloud platform, working on a pay-as-you-go model, dominating the public cloud market with a 39% share, spreading across 190 countries and serving millions of customers like GE, Samsung, Coca-Cola, Slack, and Netflix, offering benefits like reduced costs, more agility, and faster innovation.

Why Should You Consider Amazon Web Services?
AWS is positioned at the top in Gartner’s Magic Quadrant for Cloud Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) across the measurement axes: Ability to Execute and Completeness of Vision. Following are a few benefits that the AWS cloud computing platform offers:
- Enhanced Security
- Cost-Effectiveness
- Flexibility and Openness
- Elasticity and Scalability
3. Azure Web Services
Microsoft Azure, a cloud computing platform released in 2010, offers cloud computing services to build, test, deploy, manage, and scale applications via Microsoft-managed data centers. 80% of Azure’s customers are from Fortune 500 companies: Apple, Fujifilm, Honeywell, and HP.
Why is Azure Web Services Right for Digital Business?
According to Microsoft, “Azure is a growing collection of integrated cloud services — analytics, computing, database, mobile, networking, storage, and web — for moving faster, achieving more, and saving money.” Following are some other benefits that the Azure cloud computing platform offers:
- IaaS and PaaS Capabilities
- Autoscaling
- Flexibility
- Personalized and Timely Customer Experiences
Difference between cloud strategy and cloud migration
Cloud Strategy
Cloud is a buzzword, but 37% of cloud migrations fail. Big brands like Twitter and Pinterest have experienced a cloud migration failure. TSB witnessed a cloud migration fiasco, forcing them to increase interest payments to cover customer losses. Why?
“Good tactics can save even the worst strategy. Bad tactics will destroy even the best strategy.”
– General George S. Patton Jr.
One of the key reasons for cloud migration failure is the business’s inability to frame out a cloud strategy before embarking on a cloud migration journey. There are a few necessary steps that every enterprise cloud strategy should follow.
- Creating an Enterprise Cloud Strategy Team
- Analyzing Applications Thoroughly
- Building A Hybrid Cloud Strategy Roadmap
- Reskilling and Upskilling
- Implementation
Cloud Migration
On their road to digital transformation, organizations face various challenges — digital security, digital vision & strategy, and organization readiness. To navigate these digital transformation challenges, businesses are turning towards cloud solutions.
However, organizations face many complications when they begin their cloud migration journey. One of the common questions regarding cloud migration is, “How do we even start?”
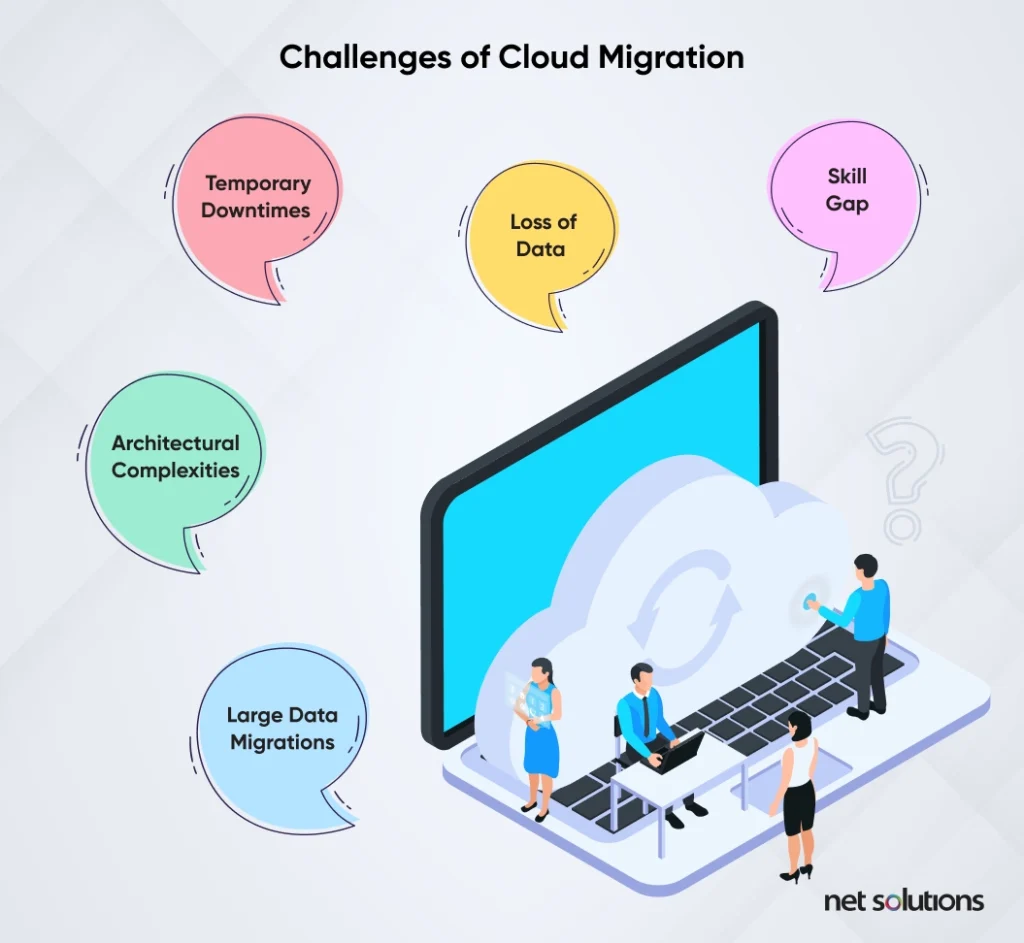
Following are the 5 R in cloud migration strategy that helps businesses embark on a successful journey.
- Rehost
- Refactor
- Revise
- Rebuild
- Replace
Cloud computing use cases
1. Serverless computing
The serverless computing approach takes the complete worry of setting up, managing, and maintaining resources off users’ shoulders. Vendors take care of everything, such as bandwidth allocation, software updates, and scalability. AWS, GCP, and Microsoft Azure are typical examples of serverless computing.
2. AI-as-a-Service (AIaaS)
Earlier artificial intelligence was accessible only to cash-rich businesses. The machines were expensive, AI programmers were in short supply, and companies didn’t have enough budget for hiring specialized talent and building AI capabilities into their infrastructure.
However, the AI-as-a-service (AIaaS) approach is completely changing the game. You can easily access fully managed AI and machine learning frameworks by paying a fee. It means you can access advanced infrastructure at a fraction of the cost or even scale them based on your business requirements.
3. Fault-tolerant systems
Even the most successful businesses took a hit at some point. However, Cloud computing can help you create fault-tolerant systems that withstand the test of time and ensure your operations never go down.
Netflix is a famous example. In 2008, it suffered a massive setback when database corruption affected its DVD shipments. Learning from the experience, the media streaming platform switched to cloud servers. These cloud servers duplicate data through multiple clusters to ensure it keeps operating even if one server goes down for some reason.
4. Scalable applications
Scaling a mobile application was a big challenge before. But with cloud computing, you can quickly build high-performance applications that you can easily host and scale on the cloud. This reduces the turnaround time for startups looking to raise funds and offers them the advantage of being first over their competitors.
What are the limitations of Cloud Computing?
Like other technologies in the IT industry, Cloud Computing isn’t picture-perfect. It has some limitations, despite the compelling benefits. As a newbie cloud computing enthusiast, you must be aware of them:
- Cloud computing has limited customization options. You will get repurposable templates that make your life easier, but you can only go this far. You need to depend upon your cloud provider to want anything specific.
- Cloud providers have complete control over the moderation policies of the platform. Without a regulatory understanding, you’ll have little control over the terms and conditions of the SLA. It may also hamper productivity or limit you in areas like data privacy, confidentiality, or technical limitations of the cloud provider.
- Even if you have developed and hosted applications on the cloud, you’ll only have partial control over them. Cloud providers will still control the app as they own the platform that hosts them.
What is the future of Cloud Computing?
We learned what Cloud computing looks like today and how businesses can benefit from it. But what does it have in store for the future?
1. Data will be processed much faster with edge computing
With a sudden spike in devices interconnected with the Internet of Things (IoT), there’s immense pressure on cloud service providers to process it faster. These providers are tackling it with edge computing, a new yet high-efficient cloud computing technique in which we process data locally as close as possible to the source of the network.
Since data doesn’t have to travel faster, processing it will be faster and easier. As a result, edge computing has become a mainstream trend, with a market worth $40.84 million.

2. Security becomes a priority with DevSecOps
Given the insane number of cloud computing risks like data theft, man-in-the-middle attacks, and denial of service attacks – data security is a significant concern for businesses hosting their assets on the cloud.
To overcome this, they use the DevSecOps approach to build security into the data pipeline right from the beginning. Many businesses see it as a game changer that can improve security levels in the cloud.
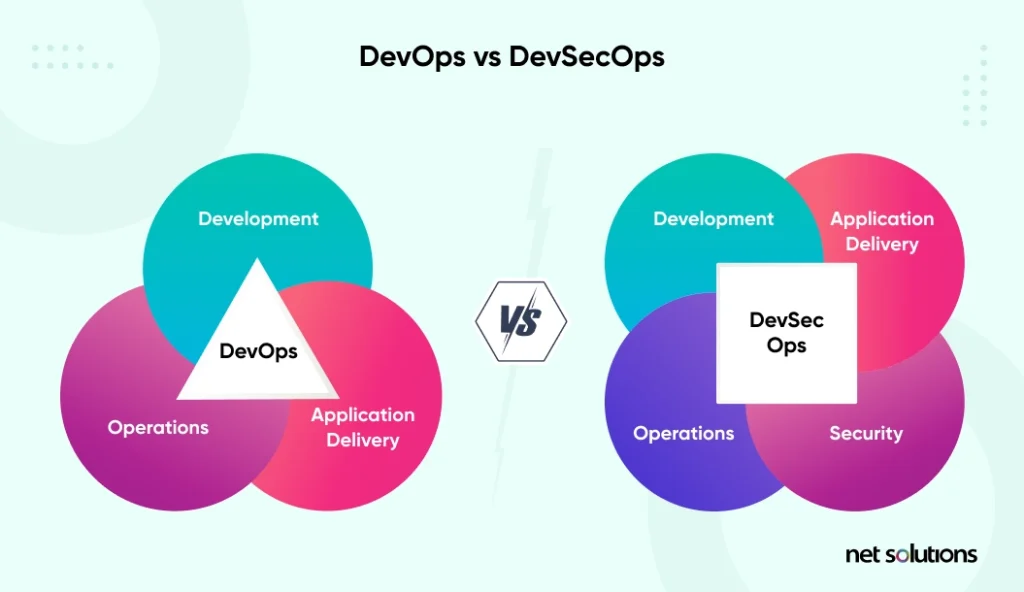
3. Using service mesh to foster secure communication between security layers
As businesses are creating robust enterprise applications using radical approaches like the microservice architecture, it is essential to ensure that individual services can securely communicate. Businesses are providing this by implementing service mesh, a platform layer on top of the infrastructure layer that aims to secure the communication channels between security layers. It plays a critical role in provisioning access to cloud tenants.
4. Cloud computing will lead to widespread AI adoption
Cloud computing is a key enabler for widespread AI adoption. – IBM
Every business looking to improve must include AI in its business processes. It is because some operations require 24×7 monitoring, and humans can never match the perfection of AI.
Cloud-centric ecosystems are integral to implementing these AI solutions because their cognitive abilities thrive on a large volume of data, which you can easily access on cloud computing ecosystems.
5. Open-source cloud ecosystems will come into prominence
While private cloud networks make up a large share of the cloud computing ecosystem, they’re often restrictive regarding features. That’s why most businesses are now moving towards open-source clouds built with free-to-access toolkits. The best part about these ecosystems is that you can easily customize them based on your business needs and use them without predefined limitations.
Frequently Asked Questions
Cloud hosting is better than traditional hosting because it can automatically scale up or down based on your business needs, thus removing the need to add or eliminate space manually.
Keeping the average cloud server pricing in mind, Cloud computing can cost anywhere from $400 monthly for one server to $15,000 monthly for the entire back-office infrastructure.
Data-centric organizations can benefit a lot from cloud computing because it allows them to store, manage, and scale data much more easily than on-premise data storage and management. It is also more logical, efficient, and economical.
Here’s why cloud computing is so secure:
- Cloud servers are located in locations that only a selected few can access.
- Cloud data is encrypted. It means even if cybercriminals get their hands on this data, they can’t read it without the digital key.