If you are looking for a reliable cloud service provider for your business, you can’t miss out on AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud comparison. They’re the goliaths of cloud computing technology that dominate the cloud services domain with their safe, flexible, and reliable offerings.
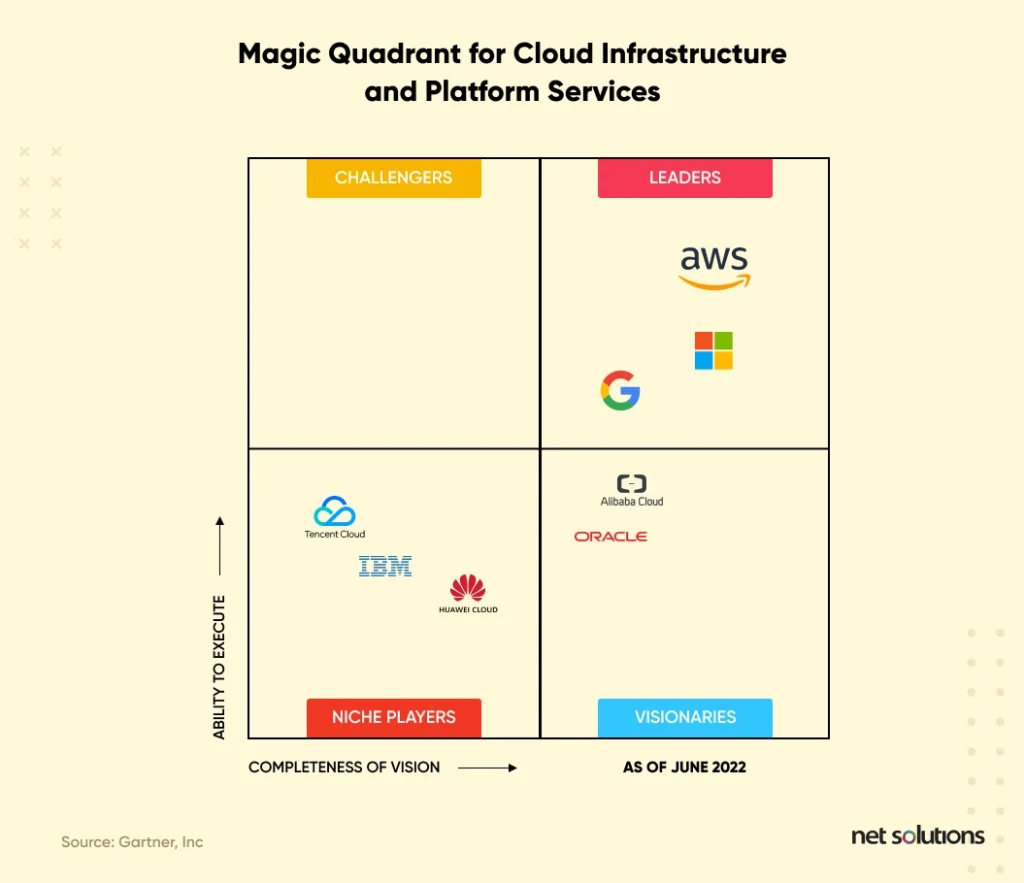
Even Gartner considered AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud leaders in its Magic Quadrant for Cloud Infrastructure and Platform services.
The three cloud providers serve the same purpose yet differ in features, functionality, pricing, and storage capacity. Whether AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud — an organization should always choose a provider that suits its business and functional requirements.
This blog will compare these three cloud services, highlighting the significant differences between AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud.
We respect your privacy. Your information is safe.
AWS vs Microsoft Azure vs Google Cloud: A Brief Introduction
To understand which is best among Amazon Web Services, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud – you must first know what they are, who uses them, and their upsides and downsides. Let’s begin:
1. Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Launch: March 2006
- Services: over 200
- Availability: 99 availability zones across 31 geographical locations
Amazon offers on-demand cloud services to organizations across the globe on a pay-as-you-go basis through Amazon Web Services (AWS). Like its other diversified businesses, Amazon’s cloud computing business is widely accepted and ranks first, i.e., its AWS market share is the largest.
“AWS had the unique advantage of a seven-year head start before facing like-minded competition. As a result, the AWS services are by far the most evolved and functionality-rich.” — Jeff Bezos
Who Uses AWS?
- Startups and small businesses use AWS to develop, launch, and scale their products and services quickly and cost-effectively.
- Large organizations like Netflix, Airbnb, Unilever, BMW, MI, Samsung, and Zynga use AWS for their cloud computing needs.
- Many government agencies, both in the US and around the world, use AWS for their cloud computing needs. For example, the US Department of Defense has a $10 billion contract with AWS to provide cloud services.
- Non-profit organizations also use AWS to support their operations and improve their ability to deliver services and programs to their communities.
- Many colleges and universities use AWS to provide students and faculty with cloud computing resources for research, instruction, and other projects.
In short, AWS is used by various individuals and organizations, from small businesses to large enterprises, from government agencies to non-profit organizations, and from education institutions to startups.
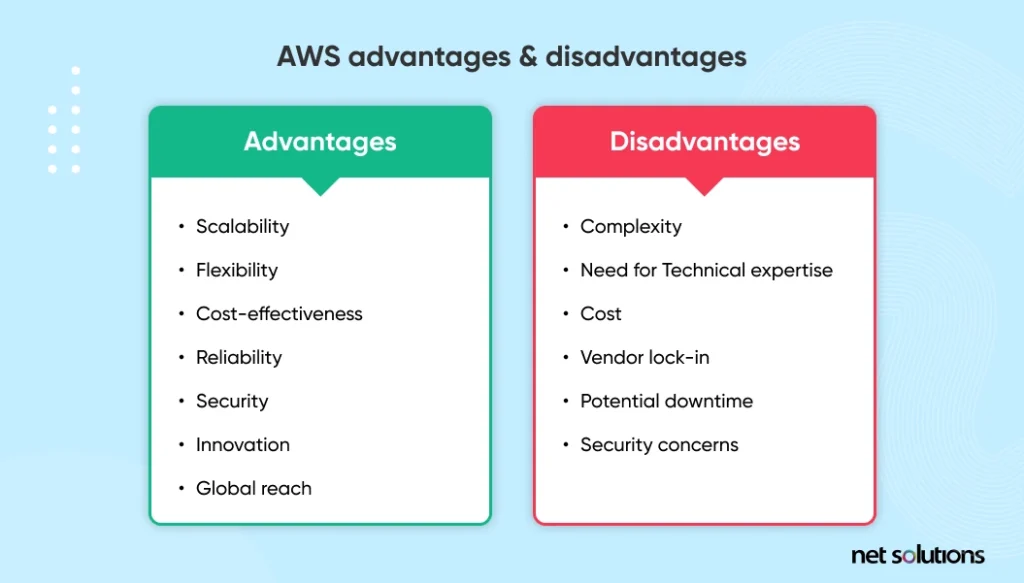
AWS Advantages
- Scalability: With AWS, you can quickly scale your computing resources up or down based on resource demands. It is especially beneficial for businesses with fluctuating resource demands.
- Flexibility: AWS offers various services and deployment options to meet your business needs.
- Cost-effectiveness: AWS offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which can help users save money by only paying for the resources they use.
- Reliability: AWS has a proven track record of providing highly reliable and available services with built-in redundancy and failover capabilities.
- Security: AWS offers several security features and certifications to protect user data and applications, such as encryption, access controls, and compliance certifications.
- Innovation: AWS constantly adds new services and features to its platform, enabling users to use the latest technologies and trends.
- Global reach: AWS has a global presence, with data centers located in regions worldwide, enabling users to deploy applications and services closer to their users for better performance.
Overall, AWS offers a powerful and flexible platform for organizations of all sizes to build, deploy, and scale their applications and services.
AWS Disadvantages
While AWS (Amazon Web Services) offers many advantages, there are also some potential downsides that you must consider:
- Complexity: With so many services and features available, AWS can be complex and overwhelming to navigate, especially for users who don’t have extensive cloud computing experience.
- Need for Technical expertise: To make the most of AWS, users may need certain technical expertise. Not every organization has the luxury and resources to train its employees.
- Cost: While AWS can be cost-effective for some users, it can also be expensive, especially for organizations that require a lot of resources or use high-end services.
- Vendor lock-in: Once an organization has invested heavily in AWS and its services, it can be challenging to switch to a different provider or platform, which can create a form of vendor lock-in.
- Potential downtime: Despite its reliability, AWS can experience occasional downtime or service disruptions, which can impact user productivity and performance.
- Security concerns: While AWS has several security features and certifications, there is always the potential for security breaches or data leaks, which can be a concern for some organizations.
While AWS offers many advantages, organizations should consider their specific needs and challenges before using AWS or any other cloud computing provider.
2. Microsoft Azure
- Launch: February 2010
- Services: Over 100
- Availability: 116 availability zones across 140 countries
Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing service for building and managing applications through Microsoft’s managed service data centers. Microsoft already has a substantial user base for its in-built applications, which gives it a competitive advantage because of the default preference.
Who Uses Azure?

A wide range of individuals and organizations use Microsoft Azure, including:
- Several enterprises across various industries use Azure for their cloud computing needs, including Johnson Controls, Polycom, Fujifilm, HP, Honeywell, Apple, Pixar, Dell, Xerox, Coca-Cola, BMW, and GE Healthcare. Salesforce has declared Microsoft Azure as its public cloud provider for its marketing cloud.
- Many government agencies in the US and worldwide use Azure for their cloud computing needs. For example, the US Department of Defense has a contract with Microsoft for cloud services.
- Small and medium-sized businesses also use Azure as it offers a range of services that lets them develop, launch, and scale their products and services quickly and cost-effectively.
- Non-profit organizations use Azure to support their operations and improve their ability to deliver services and programs to their communities.
- Many colleges and universities use Azure to provide students and faculty with cloud computing resources for research, instruction, and other projects.
In short, Azure is used by a diverse range of individuals and organizations, from small businesses to large enterprises, from government agencies to non-profit organizations, and from education institutions to startups.
Microsoft Azure Advantages
Microsoft Azure is a cloud computing platform offering several advantages for organizations seeking to leverage cloud services. Some of the key benefits of Azure include the following:
- Scalability: Azure enables users to scale computing resources up or down quickly and easily, which can be especially beneficial for businesses with fluctuating resource demands.
- Flexibility: With Azure, users can choose from various services and deployment options to meet their specific needs, including virtual machines, databases, and developer tools.
- Integration with Microsoft ecosystem: For organizations that already use Microsoft technologies, Azure can be an attractive option, as it integrates with other Microsoft tools and services, such as Office 365 and Visual Studio.
- Hybrid cloud capabilities: Azure enables users to integrate their on-premises data centers with cloud services, providing a hybrid cloud solution that can benefit both environments. You can save up to 40% on virtual machines when using Azure Hybrid Cloud.
- Cost-effectiveness: Azure offers a pay-as-you-go pricing model, which can help users save money by only paying for the resources they use.
- Reliability: Azure has a proven track record of providing highly reliable and available services with built-in redundancy and failover capabilities.
- Security: Azure has several security features and certifications, including encryption, access controls, and compliance certifications, that can help protect user data and applications.
Overall, Azure offers a powerful and flexible platform for organizations of all sizes to build, deploy, and scale their applications and services, with strong integration with the Microsoft ecosystem, hybrid cloud capabilities, and a wide range of Azure development services and features.
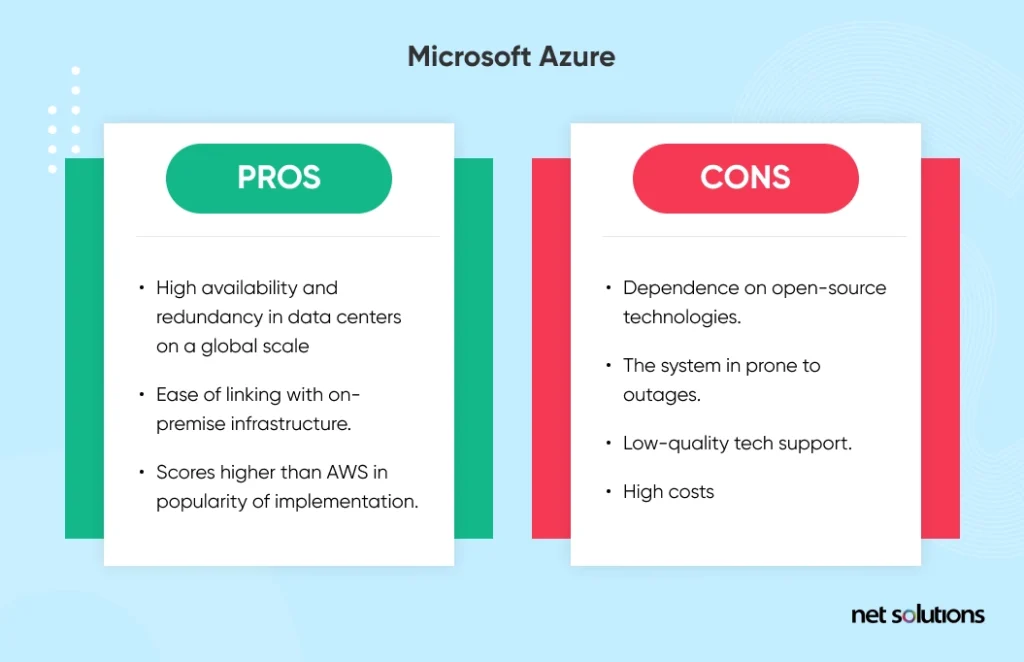
Microsoft Azure Disadvantages
- Microsoft Azure has shown reliability issues owing to the outage instances reported in the past.
- Microsoft Azure offers poor customer support, which, in turn, ruins the customer experience.
- Microsoft Azure has high expectations from its customers as its sales strategy has always been around, focusing on its already established customer base. They tend to overlook the challenges that non-Microsoft customers face while using Azure.
3. Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- Launch: April 2008
- Products: Around 60
- Availability: 106 availability zones in 35 regions
Google Cloud is a suite of cloud computing services that runs on the infrastructure that Google deploys for its user-centric products. Its cloud services include — computing, storage, analytics, and machine learning (ML).
Who Uses Google Cloud?
- Many startups use GCP as it offers cost-effective solutions for building, deploying, and scaling applications.
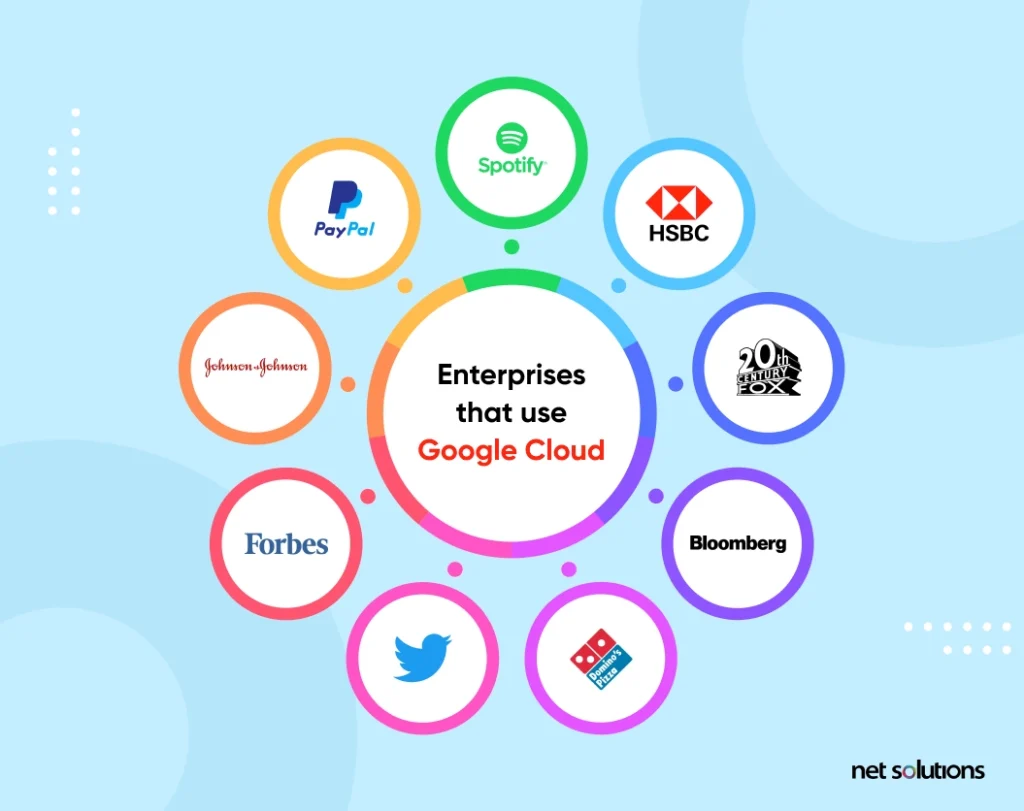
- Large organizations like HSBC, PayPal, 20th Century FOX, Bloomberg, Dominos, Twitter, Johnson & Johnson, Forbes, and Spotify use GCP for its robust infrastructure, scalability, and security features.
- Developers use GCP to build and deploy applications quickly and easily, leveraging its powerful tools and APIs.
- Data scientists use GCP to perform large-scale data analysis and machine learning tasks using its powerful analytics and AI tools.
- IT professionals use GCP to manage and automate their infrastructure and services, making their jobs more efficient.
- Gaming companies use GCP for their high-performance computing infrastructure and scalable storage solutions for game development and streaming.
- Healthcare organizations use GCP to securely manage and store sensitive patient data.
- Financial institutions use GCP to process and store financial data securely and compliantly.
Google Cloud Advantages
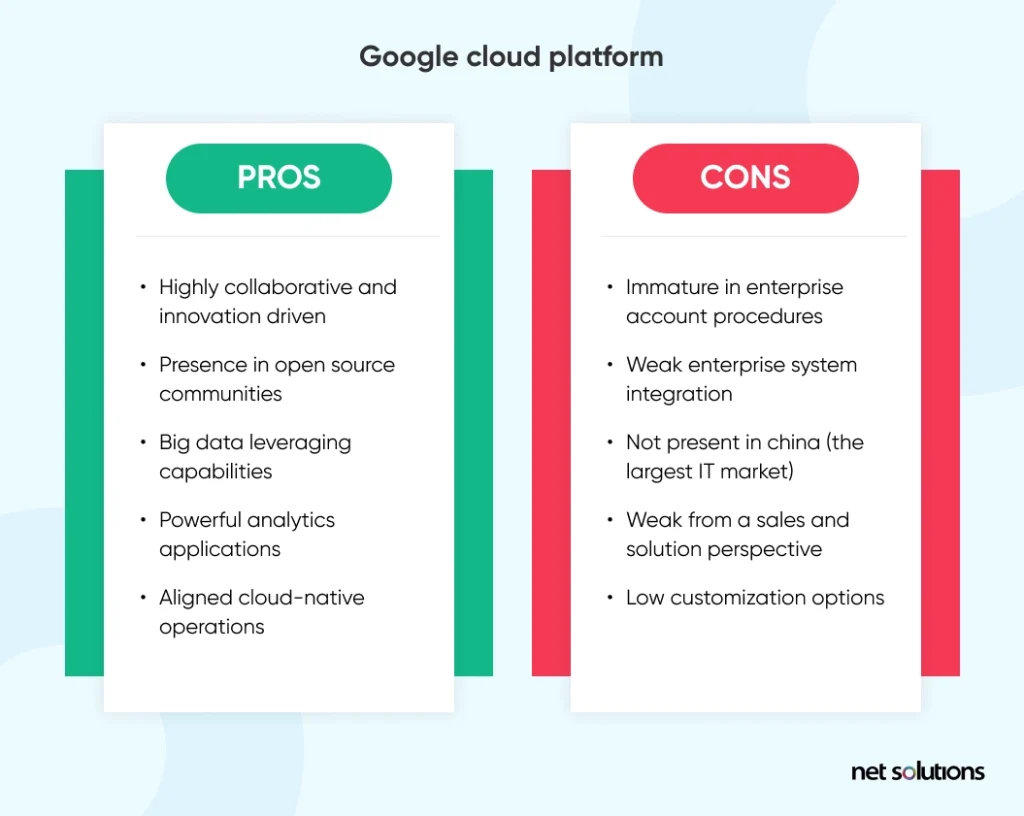
- The essential advantage of Google Cloud Platform narrows down to Google Kubernetes Engine, a powerful container manager. With its new service, Anthos, which runs on Google Kubernetes Engine, Google plans to bring other mainstream cloud-based services, such as AWS and Azure, to Kubernetes.
- Google Cloud Platform offers live migrations of virtual machines.
- Flexible cost structure and added flexibility due to its open-source nature.
Google Cloud Disadvantages
- GCP is often used as a secondary provider instead of a strategic one.
- According to Gartner reviews, GCP shows the immaturity of processes and procedures with enterprise accounts.
- Google needs to up its game regarding the range of services it offers. AWS vs Azure offers stiff competition in that regard.
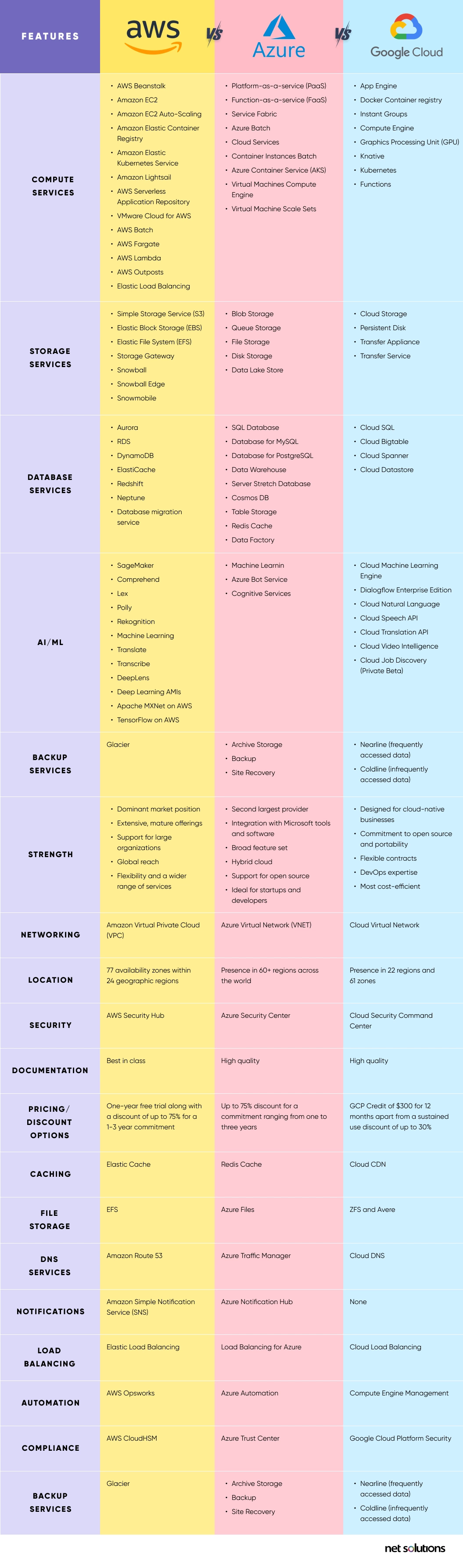
What are the Major Differences between AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud?
Public cloud service adoption for Azure is the highest, followed by AWS, and Google Cloud, according to Flexera 2022 State of the Cloud Report. It implies the immense popularity that the three cloud providers enjoy.
Here’s an AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud services comparison to help you choose your cloud partner.
1. Market Share
The AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud market share in 2022 has shown considerable growth. Here is how the market share is fairing for the three cloud services in Q3, 2022 compared to the previous year.
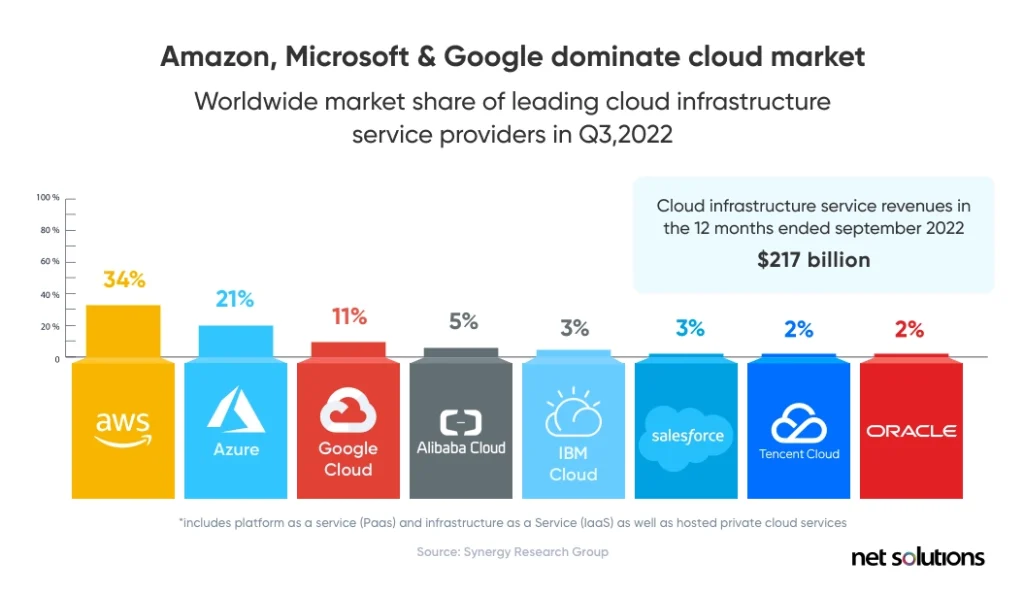
2. Services
Regarding AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud service offerings, AWS is the leader with around 200+ service offerings, followed by Azure with about 100 services and Google Cloud with about 60 services. These services come under the following domains:
Compute Services
| Services | AWS | Azure | GCP |
|---|---|---|---|
| IaaS | Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud | Virtual Machines | Google Compute Engine |
| PaaS | AWS Elastic Beanstalk | App Service and Cloud Services | Google App Engine |
| Containers | Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud Container Service | Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) | Google Kubernetes Engine |
| Serverless Functions | AWS Lambda | Azure Functions | Google Cloud Functions |
Database Services
| Services | AWS | Azure | GCP |
|---|---|---|---|
| RDBMS | Amazon Relational Database Service | SQL Database | Google Cloud SQL |
| NoSQL: Key–Value | Amazon DynamoDB | Table Storage |
Google Cloud Datastore Google Cloud Bigtable |
| NoSQL: Indexed | Amazon SimpleDB | Azure Cosmos DB | Google Cloud Datastore |
Storage Services
| Services | AWS | Azure | GCP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Object Storage | Amazon Simple Storage Service | Blob Storage | Google Cloud Storage |
| Virtual Server Disks | Amazon Elastic Block Store | Managed Disks | Google Compute Engine Persistent Disks |
| Cold Storage | Amazon Glacier | Azure Archive Blob Storage | Google Cloud Storage Nearline |
| File Storage | Amazon Elastic File System | Azure File Storage | ZFS/Avere |
Networking Services
| Services | AWS | Azure | GCP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virtual Network | Amazon Virtual Private Cloud(VPC) | Virtual Networks (VNets) | Virtual Private Cloud |
| Elastic Load Balancer | Elastic Load Balancer | Azure Load Balancer | Google Cloud Load Balancing |
| Peering | Direct Connect | ExpressRoute | Google Cloud Interconnect |
| DNS | Amazon Route 53 | Azure DNS | Google Cloud DNS |
3. Key Cloud Tools
There’s cut-throat competition among AWS, Azure, and Google cloud in terms of cloud tools. Now and then, each cloud provider keeps adding new services and will continue doing so in the future.
AWS Key Tools
- Artificial Intelligence & Machine Learning: Deeplens, an AI-powered camera for developing and deploying machine learning algorithms for optical character recognition. AWS has also announced an open-source deep learning library called Gluon, using which you can build neural networks without any knowledge of AI.
- Serverless: AWS SageMaker, a tool for training and deploying machine learning models. AWS also offers Lex conversational interface for powering Alexa, Greengrass IoT messaging, and Lambda serverless computing services.
Azure Key Tools
- Cognitive Services: Microsoft Azure offers machine learning and a bot service, a Text Analytics API, Bing Web Search API, Face API, Computer Vision API, and Custom Vision Service. Microsoft also has several analytics and management services and a serverless computing service called Functions.
- Support for Microsoft Software: Azure offers tools to support on-premises Microsoft software, such as Azure Backup and Visual Studio Team Services.
Google Cloud Key Tools
- IOT to Serverless: Google cloud platform offers APIs for natural language, speech, and translation. It also provides IoT and serverless services in beta previews.
- Bing on AI: Google cloud platform offers an open-source library called TensorFlow for building machine learning applications.
| Vendor | AL/ML | IoT | Serverless |
|---|---|---|---|
| AWS |
Comprehend Lex Polly Rekognition Machine Learning Translate Transcribe DeepLens Deep Learning AMIs SageMaker Apache MXNet on AWS TensorFlow on AWS |
IoT Core FreeRTOS Greengrass IoT 1-Click IoT Analytics IoT Button IoT Device Defender IoT Device Management |
Lambda Serverless Application Repository |
| Azure |
Machine Learning Azure Bot Service Cognitive Servicesk |
IoT Hub IoT Edge Stream Analytics Time Series Insights |
Functions |
| Google Cloud |
Cloud Machine Learning Engine Dialogflow Enterprise Edition Cloud Natural Language Cloud Speech API Cloud Translation API Cloud Video Intelligence Cloud Job Discovery (Private Beta) |
Cloud IoT Core (Beta) |
Cloud Functions (Beta) |
4. Hybrid and Multi Cloud Options
Here are the hybrid and multi cloud offerings you can get in AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud:
| AWS Hybrid and Multi Cloud | Azure Hybrid and Multi Cloud | Google Cloud Hybrid and Multi Cloud |
|---|---|---|
|
AWS Snowball AWS Snowcone AWS Outposts AWS Local Zones VMware Cloud on AWS AWS Wavelength Amazon ECS Anywhere Amazon EKS Anywhere |
Azure Arc Azure Backup Azure Active Directory Azure Security Center Azure Blob Storage Azure Stack Azure Centinel |
Anthos Traffic Director Looker Cloud Build Operations Cloud Run for Anthos |
5. Pricing
Here’s a comparison among the pricing models of AWS, Azure, and GCP based on the machine type that they provide:
| Machine Type | AWS Pricing | Azure Pricing | Google Cloud Pricing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smallest Instance | The most basic instance of AWS includes 2 virtual CPUs and 8 GB of RAM. It would cost you around US$69 per month. | A minor instance in Microsoft Azure contains 2 vCPUs and 8 GB of RAM, in Azure. It would cost you around US$70/month. | The most basic instance of GCP contains 2 virtual CPUs and 8 GB of RAM at a 25 percent cheaper rate. It would cost you around US$52/month. |
| Largest Instance | The largest instance offered by AWS includes 3.84 TB of RAM and 128 vCPUs. It would cost you around US$3.97/hour. | The largest instance offered by Azure contains 3.89 TB of RAM and 128 vCPUs. It would cost around US$6.79/hour. | The largest instance of GCP includes 3.75 TB of RAM and 160 vCPUs. It would cost you around US$5.32/hour. |
AWS has also started offering pay-per-minute billing recently. Azure already provides it, while Google Cloud offers pay-per-second billing models that let users save more than AWS or Azure.
However, GCP offers up to 50 percent discount in some cases, making it more affordable than other cloud providers. Gartner states, ‘Google offers deep discounts and exceptionally flexible contracts to try to win projects from customers.’
Which is Better: AWS or Azure or Google Cloud?
Choosing between AWS vs Azure vs Google Cloud solely depends on your business needs and corresponding workloads. It is not necessary that your competitor’s cloud service adoption might be the best fit for you too.
Here is when to choose what cloud service:
- When to choose AWS: If you are looking for a wide range of cloud services and tools with maximum reach, AWS is your best fit.
- When to choose Azure: If you have your operations running on Windows and Microsoft applications, Azure is the best choice to make
- When to choose Google Cloud: Though it may not look viable compared to the other two providers, it is a committed platform for small, web-oriented startups. If you are keen on machine learning, Google Cloud can be a good pick.
Frequently Asked Questions
Both Azure and AWS have their strengths and weaknesses. Choosing between them depends on your specific needs and requirements. Here are the factors you must consider while comparing Azure and AWS:
- Azure is known for its excellent support for Microsoft products and services, while AWS has a wider variety of services.
- AWS is seen as more cost-effective for smaller businesses, while larger enterprises often prefer Azure.
- If you already use Microsoft products or services, Azure may be a better choice for you, as it offers seamless integration with Microsoft tools.
- Finalize your project’s visual elements
- Both platforms offer good support, but AWS has a larger user community and a more comprehensive range of resources.
It would be best to choose Google Cloud over AWS because it offers billing per second, which is way more cost-efficient than AWS’s per-hour model billing. This way, you have to bear fewer expenses than using AWS. Also, GCP offers long-term discounts, which can save you more money.
Many experts claim that AWS is much easier to learn and get certified in. However, you can also get along with Azure quickly if you’re already familiar with AWS. It is because both platforms have a similar set of services and infrastructure.
You don’t need to learn coding to use AWS and Azure. Many certifications and training programs involve user interfaces, not programming.